Regents Chemistry Vocabulary- Nuclear Chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion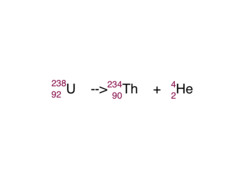
Also known as radioactive natural decay; when an unstable isotope spontaneously emits a decay particle (alpha, beta or positron) and becomes a new element
answer
Natural transmutation
question
When a large, unstable nucleus is hit with a neutron and splits into two smaller nuclei, which release neutrons that can be used to begin another reaction. Releases a large quantity of energy.
answer
Nuclear fission
question
When two small, light nuclei come together to form a heavier nucleus; releases a large quantity of energy.
answer
Nuclear fusion
question
The amount of time it takes for one half of a radioactive sample to go through a natural transmutation and turn into a more stable element.
answer
Half-life
question
The kind of radiation with the greatest penetrating power; has no mass or charge
answer
Gamma radiation
question
radioactive particle with the least penetrating power; has a mass of 4 and a charge of +2
answer
Alpha particles
question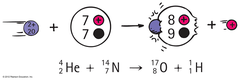
When a nucleus is bombarded with a particle to cause a non-spontaneous change to the nucleus (creating a new element)

answer
Artificial transmutation
question
radioactive particle with low penetrating power; has a mass of 0 and a charge of -1
answer
Beta particles
question
Any radioactive particle or energy released by another radioactive substance.
answer
emanation
question
the ability of radiation to remove electrons from other atoms; damages living tissue
answer
ionizing power
question
the ability of radiation to cross barriers; the higher the energy of the radiation, the greater the penetrating power.
answer
penetrating power
question
radioactive particle with low penetrating power; has a mass of 0 and a charge of +1.
answer
positron
question
atoms of the same element but different in mass; different number of neutrons.
answer
isotope
question
an atom with an unstable nucleus due to the unbalanced number of protons and neutrons; emits radioactive particles as it decays.
answer
radioisotope
question
Also known as natural transmutation; when an unstable isotope spontaneously emits a decay particle (alpha, beta or positron) and becomes a new element
answer
spontaneous decay
question
theory that explains that mass is converted to energy during fission and fusion reactions.
answer
theory of relativity
question
the process of determining the age of rocks or living tissue from the decay of their radioactive elements
answer
radioactive dating



