Project Management – Project Management Basics Continued – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Projects vs Operational Work
answer
Projects and operations differ primarily because operations are ongoing & produce repetitive products, services or results. They are temporary and end. Operations work supports the business environment where projects are executed.
question
Relationships between Program and Portfolio Management

answer
Program Management: A program is a group of related projects managed in a coordinated way to obtain benefits & control. May use the same resources, the results of a project may feed into another. Are part of a larger project broken down into smaller projects. Portfolio Management: Portfolio refers to the collection of projects or programs & other work that is grouped together to facilitate effective management of that work to meet strategic business objectives.
question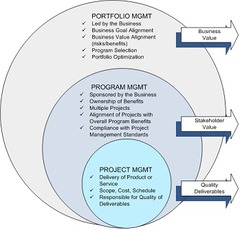
Relationships between Projects and Strategic Planning

answer
Projects are often utilized as a means of achieving an organizations strategic plan. They are typically authorized as a result of one or more of the following strategic considerations: >Market demand >Strategic opportunity/business need >Customer request >Technological advance >Legal requirements >Cost Savings
question
Project Management Office (PMO)

answer
An organizational body that centralize & coordinate management of those projects under its domain. The responsibilities of a PMO can range from providing project management support functions to actually being responsible for the direct management of a project.
question
Role of a Project Manager
answer
The PM is the person assigned by the performing organization to achieve the project objectives.
question
Functional Manager
answer
Focused on providing management oversight for an administrative area., Responsible for authority over a single unit within an organization, such as a department.
question
Operations Manager
answer
Are responsible for a facet of the core business., A manager who is responsible for managing an organization's production system and for determining where operating improvements might be made.
question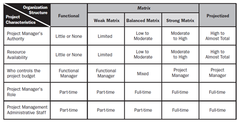
Organizational Structure

answer
Organizational Structure is an enterprise environment factor which can affect availability of resources and influence how projects are conducted. Organizational structure range from functional to projectized, with matrix structures between them.
question
Functional Organization
answer
An hierarchy where each employee has one clear supervisor., An organization where each employee has a one clear supervisor. Staff members are grouped by specialty, such as production, marketing, engineering and accounting and work is completed independent of other functional departments
question
Weak Matrix Organization
answer
Weak matrices maintain many of the characteristics of a functional organization, & the PM role is one of a coordinator or expediter than that of a true project manager. Project Expediter- * Acts primarily as a staff assistance & communication coordinator. * Cannot personally make enforcement decisions. Project Coordinator- * Similar to Project Expediter * But has some power to make decisions, some authority and reports to higher management.
question
Balanced Matrix Organization
answer
Recognizes the need for a PM, it does not provide the PM with the full authority over the project & project funding., Power is shared between the functional manager and the project manager. Although, the project manager has full time role, he has only part time project management administrative staff under him. In a balanced matrix both managers control the project budget.
question
Strong Matrix Organization
answer
Many characteristics of projectized organization. Can have full-time PMs with considerable authority & full-time project administrative staff., Maintains many of the characteristics of the projectized organization, and can have full-time project managers with considerable authority and full-time project administrative staff
question
Projectized Organizations
answer
Any organizational structure in which the project manager has full authority to assign priorities, apply resources, and direct the work of persons assigned to the project.
question
Composite Organization
answer
Any organization composed of various individuals, units, agencies, or disciplines who or which are required to work together to achieve a successful resolution for a given problem. Virtually all tactical operations are conducted by composite organizations
question
PMO Functions
answer
Primary function of PMO is to support project managers in a variety of ways which may include, but are not limited to: >Managing shared resources across all projects administered by the PMO; >Identify & develop project management methodology, best practices & standards; coaching, mentoring, training & oversight; >Monitoring compliance with project management standards, policies, procedures and templates via project audits; >Developing & managing project policies, procedures, templates & other shared documentation (organizational process assets) and coordinating communication across projects.
question
The Project Life Cycle
answer
A project life cycle is a collection of generally sequential & sometimes overlapping phases. A life cycle can be documented with a methodology. The project life cycle can be determined or shaped by the unique aspects of the organization, industry or technology employed. While every project has a definite start & a definite end, the specific deliverables & activities that take place in between will vary widely with the project. The life cycle provides the basic framework for managing the project, regardless of the specific work involved.
question
Characteristics of the Project Life Cycle
answer
All projects can be mapped to the following life cycle structure >Starting the project >Organizing & preparing >Carrying out the project work and >Closing the project -Cost and staffing levels are low at the start, peak as the work is carried out and drop rapidly as the project draws to a close. -Stakeholder influences, risk and uncertainty are greatest at the start of the project. These factors decrease over the life of the project. -Ability to influence the final characteristics of the project's product, without significantly impacting cost, is highest at the start of the project & decreases as the project progresses towards completion.
question
Product vs Project Life Cycle Relationships
answer
The product life cycle consists of generally sequential, non-overlapping product phases determined by the manufacturing & control need of the organization.
question
Common Project Management Process Interactions
answer
Discrete elements with well- defined interfaces between the previously mentioned Project Management Process Groups. In practice, these process groups overlap and interact in many different ways.
question
Project Phases
answer
A collection of logically related project activities, usually culminating in the completion of a major deliverable. Project phases are mainly completed sequentially, but can overlap in some project situations. A project phase is a componenet of a project life cycle. A project phase is not a Project Management Process Group.
question
Initiating Process
answer
The project management process group that allows a project to be chartered and authorized.
question
Planning Process Group
answer
Those processes required to establish the scope of the project, refine the objectives, and define the course of action required to attain the objectives that the project was undertaken to achieve.
question
Executing Process Group
answer
Those processes performed to complete the work defined in the project management plan to satisfy the project specifications.
question
Monitoring& Controlling Process Group
answer
Addresses the skills needed to review progress and document benchmarks. After initiating, planning, and executing a project, the project is then officially underway, though the project manager has been hard at work since the initiation process.
question
Closing Process
answer
Those processes performed to finalize all activities across all Project Management Process Groups to formally close the project or phase.
question
Project Governance
answer
Provides a comprehensive, consistent method of controlling the project and ensuring its success. This should be described in Project Management Plan.
question
Phase to Phase Relationships
answer
The phases are part of a generally sequential process designed to ensure proper control of the project and attain the desired product, service, or result
question
Sequential Relationship
answer
A phase to phase relationship where a phase can only start once a previous phase has completed
question
Overlapping Relationship
answer
A phase to phase relationship where the phases start prior to the completion of the previous one
question
Iterative Relationship
answer
A phase to phase relationship where only one phase is planned at any given time and planning for the next is carried out as work progresses on the current one
question
Enterprise Environmental Factors (EEF)
answer
Any or all external environmental factors and internal organizational environmental factors that surround or influence the project's success. These factors are from any or all of the enterprises involved in the project, and include organizational culture and structure, infrastructure, existing resources, commercial databases, market conditions, and project management software.
question
Organizational Process Assets (OPA)
answer
Any or all process related assets, from any or all of the organizations involved in the project that are or can be used to influence the project's success. These process assets include formal and informal plans, policies, procedures, and guidelines. The process assets also include the organizations' knowledge bases such as lessons learned and historical information. OPA's may be grouped into two categories: 1. Processes and Procedures 2. Corporate Knowledge Base
question
Processes and Procedures of an OPA
answer
The organization's processes and procedures for conducting project work include, but are not limited to: -Initiating and Planning: Guidelines and criteria for tailoring the organization have set of standard processes and procedures to satisfy the specific needs of the project. Specific organizational standards such as policies (e.g., human resources policies, health and safety policies, ethics policies, and project management policies), product and project life cycles, and quality policies and procedures (e.g., process audits, improvement targets, checklists, and standardized process definitions for use in the organization) Templates (e.g., risk register, work breakdown structure, project schedule network diagram, and contract templates). -Executing, Monitoring and Controlling: Change control procedures, including the steps by which performing organization standards, policies, plans, and procedures or any project documents will be modified, and how any changes will be approved and validated. Financial controls procedures (e.g., time reporting, required expenditure and disbursement reviews, accounting codes, and standard contract provisions) Issue and defect management procedures defining issue and defect controls, issue and defect identification and resolution, and action item tracking. Organizational communication requirements (e.g., specific communication technology available, authorized communication media, record retention policies, and security requirements); Procedures for prioritizing, approving, and issuing work authorizations; Risk control procedures, including risk categories, risk statement templates, probability and impact definitions, and probability and impact matrix; and Standardized guidelines, work instructions, proposal evaluation criteria, and performance measurement criteria. -Closing: Project closure guidelines or requirements (e.g., lessons learned, final project audits, project evaluations, product validations, and acceptance criteria)
question
Corporate Knowledge Base of an OPA
answer
Organizational Process Assets - Corporate Knowledge Base The organizational knowledge base for storing and retrieving information includes, but is not limited to: -Configuration management knowledge bases containing the versions and baselines of all performing organization standards, policies, procedures, and any project documents. -Financial databases containing information such as labor hours, incurred costs, budgets, and any project cost overruns. -Historical information and lessons learned knowledge bases -Issue and defect management databases containing issue and defect status, control information, issue and defect resolution, and action item results. -Process measurement databases used to collect and make available measurement data on processes and products; and Project files from previous projects.



