Principles of Lesion Localization in Neurology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Problem w/ Cerebrum
answer
Encephalopathy
question
Problem w/ spinal cord
answer
myelopathy
question
Problem w/ nerve root
answer
radiculopathy
question
Problem w/ nerve
answer
Neuropathy
question
problem w/ neuromuscular junction
answer
Myasthenia
question
problem w/ muscle
answer
Myopathy
question
What must ONE do before considering cause or differential diagnosis?
answer
Localize the Lesion
question
-Brain or Brainstem - MRI Brain > CT Brain -Spinal Cord - MRI Spine -Nerve Root - MRI spine, EMG -Nerve - EMG w/ NCS -Muscle - EMG -NMJ- EMG w/ repetitive stimulation EMG = electromyography NCS = nerve conduction study
answer
Lesion Location and Corresponding Diagnostic Test of Choice
question
-Hemiparesis -Hemisensory loss -Hemiataxia Long tracts run vertically Localize in the L-to-R direction
answer
Vertical Findings
question
-Aphasia or neglect -Visual field deficit -Gaze deficit / diplopia -Vertigo -Radiculopathy Cortex, cranial nerves, and nerve roots run horizontally. Localize in the rostral-caudal direciton
answer
Horizontal Findings
question
-first order neurons, (CNS) -cell bodies in cerebral cortex (frontal lobe) -Travel in pyramidal tract (corticobulbar (brainstem-CNs) & corticospinal (spinal tract-Ventral Nerve Roots)) -Synapse on LMN in brainstem or spinal cord (anterior horn)
answer
Upper Motor Neurons
question
-Second order neurons, start in CNS, end in PNS -Cell bodies in brainstem & spinal cord (anterior horn) -Travel in CNs & Spinal Nerves (ventral roots) -Innervate skeletal muscle
answer
Lower Motor Neurons
question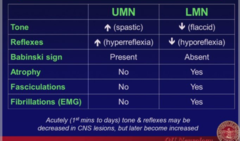

answer
Upper & Lower Motor Neuron Weakness
question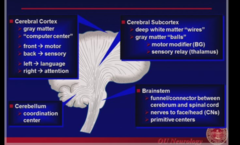

answer
Brain Anatomy Basics
question
-Gray Matter -Computer Center -Front = motor -Back = sensory -Left = language -Right = attention
answer
Cerebral Cortex
question
-Deep white matter "wires" -Gray matter "balls" -Motor modifier (BG) -Sensory Relay (Thalamus)
answer
Cerebral Subcortex
question
-coordination center -muscle communication center
answer
Cerebellum
question
-funnel/connector b/w cerebrum and spinal cord -nerves to face/head (CNs) -Primitive centers
answer
Brainstem
question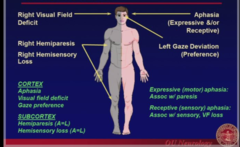
Right body probs -Right visual field deficit -Right hemiparesis -Right heminsensory loss Aphasia Left Gaze Preference Cortex = aphasia, visual field deficit and gaze preference Subcortex = hemiparesis and Hemisensory loss

answer
Left (dominant Hemisphere) Damage Signs
question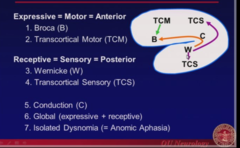
Expressive = Motor = Anterior -1.) Broca (B) -2.) Transcortical Motor (TCM) Receptive = sensory = posterior -3.) Wernicke (W) -4.) Transcortical Sensory (TCS) -5.) Conduction -6.) Global (expressive + receptive) -7.) Isolated Dysnomia (Anomic Aphasia)

answer
Aphasia 7 Types and Overview
question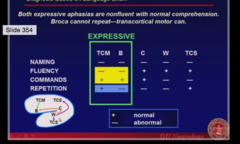
-Non fluent, normal comprehension (commands) -TCM - repetition = normal -Broca- repetition = not normal

answer
Expressive Aphasia
question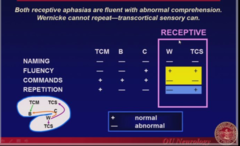
-Fluent! (they be sayin weird shit but it's fluent!) -But abnormal Comprehension (commands)! -Wernicke - abnormal repetition -TCS - normal repetition

answer
Receptive Aphasia
question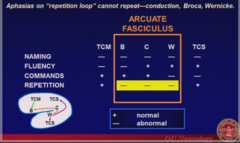
-On repetition loops so CANNOT repeat! -Conduction, broca, Wernicke

answer
Conduction Aphasia
question
Global Apahsia -(expressive + receptive) aphasias -Due to large multifocal dominant hemisphere injury -All abnormal! Isolated Dysnomia -due to lesion anywhere in dominant hemisphere -Only Naming abnormal

answer
Global Aphasia vs Isolated Dysnomia
question

answer
Aphasia Categories
question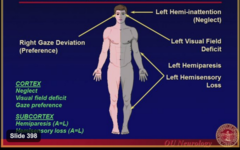
-Left hemi-inattention (neglect) -Left visual field deficit -Left hemiparesis -Left Hemisensory loss -Right Gaze Deviation Cortex = neglect, visual field deficit and gaze preference Subcortex = Hemiparesis and Hemisensory Loss

answer
Right (nondominant) hemisphere
question
-Syndrome of lack of attention to (and lack of awareness of) one side of space --> not attributable to weakness, sensory loss, or visual field loss - typically contralateral to a brain lesion -Hemispatial neglect or hemi-inattention -Due to partial lesion in NONDOMINANT hemisphere - thus typical finding = LEFT DENIAL of hemispace and hemibody (Cause usually Right = nondominant usually) Parietal Lesions = Primary Site of Causing Neglect
answer
Neglect
question
What lobe is usually the primary site of Causing Neglect?
answer
Parietal Lobe
question
Severe Neglect -Denial of illness = anosognosia -Denial of body partts = asomatognosia Less-severe neglect -Extinction to double simultaneous stimulation (DSS), visual, tactile or auditory (assuming normal visual fields, sensation, ; hearing w/ single stimuli)
answer
Neglect Degrees of Severity
question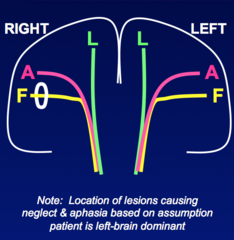
Contralateral Lower Face (UMN) weakness Associated symptoms -None -Partial Seizure -Contralateral sensory loss -Contralateral visual field deficit -Neglect If lesion on left, aphasia instead of neglect

answer
Inferolateral Cerebral Cortex Focal Leasion
question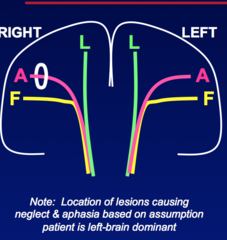
Contralateral Hand or Arm (UMN) Weakness Associated Symptoms -None -Partial Seizure -Contralateral sensory loss -Contralateral visual field deficit -Neglect If lesion on left, aphasia instead of neglect

answer
Superolateral Cerebral Cortex Focal Lesion
question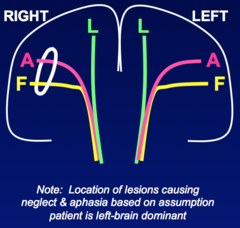
Contralateral lower face and arm (NO LEG) (UMN) weakness Associated Symptoms -None -Partial Seizure -Contralateral sensory loss -Contralateral visual field deficit -Neglect If lesion on left, aphasia instead of neglect

answer
Lateral Cerebral Cortex Focal Lesion
question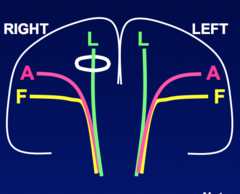
Contralateral Leg (UMN) weakness Associated Symptoms -None -Partial Seizure -Contralateral sensory loss Axons from "F" - travel via corticbulbar tract Axons for "A,L" travel via corticospinal tract

answer
Medial Cerebral Cortex Focal Lesion
question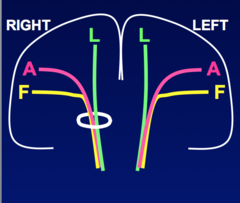
Contralateral Face = arm = leg (UMN) weakness Associated Symptoms -None -Contralateral sensory loss -Contralateral Ataxia If "bilateral lesions" may have PSEUDOBULBAR PALSY - bifacial weakness, dysarthria, dysphagia, emotional lability, diffuse spasticity, urinary incontinence Seizures - Cerebral Cortex Memory Loss (amnesia or dementia) - thalamus or medial temporal lobe

answer
Cerebral Subcortex Focal Lesion
question
-Cross Signs! (one side face ; contralateral body) (Lateral Medullary Syndrome) -Hemiparesis -Hemisensory loss -Quadriparesis -Sensory loss in all 4 limbs
answer
Brainstem Localizations
question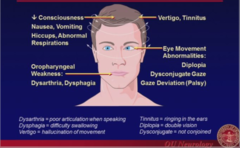
-decrease consciousness, nausea, vomiting, hiccups, abnormal respirations -Vertigo, tinnitus -Oropharyngeal weakness - dyarthria, dysphagia -Eye mvmt: diplopia, dysconjugate gaze, gaze deviation (palsy)

answer
Brainstem lesion typical signs
question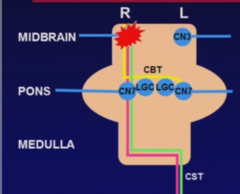
Contralateral face = arm = leg (UMN) weakness Associated Symptoms -Ipsalateral CN3 palsy -Vertical diplogia /ophthalmoplegia -ptosis -mydriasis Lesion is most often due to ischemia (Weber Syndrome) or compression (Uncal Herniation)

answer
Rostroventral Midbrain Focal Lesion
question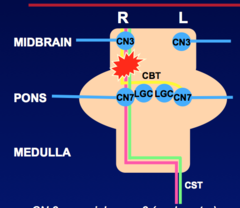
Contralateral face = arm = leg (UMN) weakness NO Associated symptoms Lesions above CN 7 nucleus in midpons result in LOWER FACIAL WEAKNESS on the same side as arm and leg weakness

answer
Rostroventral Pons Focal Lesion
question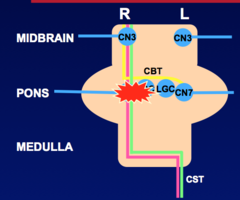
Contralateral arm = leg (UMN) weakness Ipsilateral Upper and Lower face (LMN) weakness Associated Symptoms -None -Ipsilateral gaze palsy Lesions involving the LGC/CN6 nucleus result in gaze palsy, not diplopia (NO DOUBLE VISION)

answer
Ventrolateral Midpons Focal Lesions
question
Ipsilateral upper and lower face weakness Associated symptoms -decrease taste ant 2/3 of tongue -retroauricular pain -hyperacusis "Bell's Palsy" -inflammatory peripheral CN 7 lesion that is either idiopathic or due to herpes simplex infection
answer
Cranial Nerve 7 focal lesions
question
inflammatory peripheral CN 7 lesion that is either idiopathic or due to HERPES simplex infection
answer
Bell's Palsy
question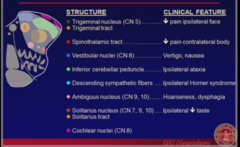
ipsilateral pain loss to face, contralateral pain loss to body**** (pathognomonic) -usually due to PICA territory damage -Usually due to embolism in vertebral artery , after that cardioembolism

answer
Lateral Medulla Wallenburg Syndrome
question
-Decreased consciousness due to ARAS inhibition -ARAS = Ascending Reticular Activating System - upper brainstem (midbrain and pons) -ARAS axons innervate & stimulate thalami and cortex of both cerebral hemispheres -Decreased consciousness due to ARAS inhibition via: 1.) Brainstem - abnormal eye movements (CNs 3,4,6) (tumor, stroke, abscess) 2.) Bicerebral - normal eye movements (hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, OH intox, fever)
answer
Depressed Consciousness Brainstem Vs Bicerebrum
question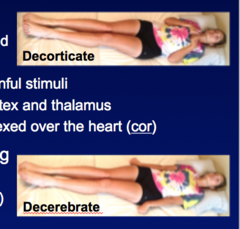
Decorticate (flexor) posturing -Arm flexed over chest, leg extended -w/o cortex -may occur spontaneously or to painful stimuli -Lesion @ thalamus or b/w cortex and thalamus -If deCORticate - arms felxed over heart (COR) -main things that cause - drowning, accel-deccel injury (shearing) Decerebrate (extensor) posturing -arm extended, leg extended (arm internally rotated, wrist FLEXED) -W/O CEREBRUM -may occur spontaneously or to painful stimuli -Lesion @ MIDBRAIN (upper brainstem) -If decErebrate, arms Extended -common: Uncal herniation

answer
Coma and Posturing
question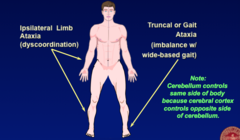
-signs involving coordination -IPSILATERAL limb ataxia -truncal or gait ataxia (imbalance w/ wide based gait)

answer
Cerebellum Lesions
question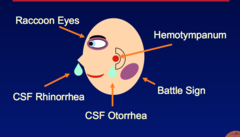
-Raccoon Eyes (periorbital hematoma) -Battle Sign (hematoma behind the ear) -CSF Rhinorrhea (CSF out of nose) -CSF Otorrhea (CSF out of ear) -Hemotympanum (blood in ear)

answer
Skull Fracture Signs
question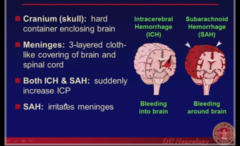

answer
Hemorrhage & the Brain Coverings
question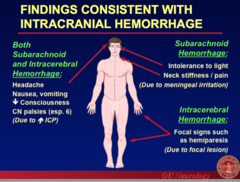

answer
Intracranial Hemorrhage Findings
question
-Weakness (para-or-quadriparesis/plegia) -Numbness (sensory lvl) -Autonomic dysfxn (urinary incontinence, sexual dysfxn, constipation)
answer
Spinal Cord Lesion (Myelopathy)
question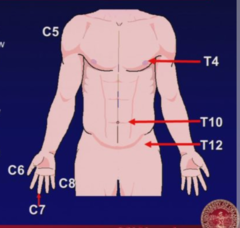
Sensory level -decrease sensation below (if few dermatomes below - "hung level" -"tight belt" sensation @ lesion level Reflex level -reflex changes below lesion (decrease acute, increase chronic) Myeloradiculopathy -radiculopathy at level of lesion, myelopathy below lesion

answer
Key Cervical and Thoracic Dermatomes
question
-inflammation of spinal cord -entire cord syndrome -Sensory: hanging lvl at or below level of lesion; abnormal pain, temp, touch, vibration and joint position sense -Motor level (C1-C8: arm + leg weakness); (T1-L2: leg weakness only) -Autonomic dysfunction: Bladder, bowel, sexual dysfunction; (c1-t6: autonomic dysreflexia risk = NEUROLOGIC EMERGENCY!) -Acute (hours) --> sub acute (days) -Tx: IV steroids and/or antibiotics -Etiologies (idiopathic URI, Monophastic), infectious (HIV, Herpes, TB), Autoimmune (MS, SLE, Sarcoidosis) -wide open central canal, but has patchy lesions (can be MS!)
answer
Trasverse Myelitis or compression
question
BLT w/ Ketchup and Pickles -Breast, lung, thyroid, kidney and prostate
answer
Cancers that go to bone
question
-Hemicord syndrome!*** -Ipsilateral Symptoms vibration and joint position ( weakness, sensory level: touch, vibration and joint position sense) -Contralateral symptoms pain and temp (normal strength, sensory level pain + temp) -Etiology: stabbing, lateral compression / trauma, vertebral fracture
answer
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
question
-Usually lower T or L ( spinal artery of adamkiewicz)**** -Motor lvl (weakness)-para or quadriparesis -Sensory (ABNORMAL pain + temp) (NORMAL touch vibration, joint - SPARES POST COLUMNS) -Etiology: anterior spinal artery : (ACCIDENTAL LIGATION DURING SURGERY**; abdominal aortic aneurysm, systemic hypotension, ) -Infarctions MOSTLY IN GRAY MATTER!
answer
Anterior Spinal Artery Infarction
question
-Posteriolateral cord syndrome -Motor level (weakness below the level of lesion) -Sensory: abnormal touch, vibration and joint; NORMAL PAIN AND TEMP) -Motor: weakness below level of lesion -SO IT'S LIKE TABES DORSALIS BUT YOU ALSO HAVE MOTOR PROBS! -Etiology: dorsal column and corticospinal tract degen -B12 DEF**; Cu def** (zinc toxicity), HIV
answer
Subacute Combined Degenration
question
-Posterior cord syndrome -Sensory : (abnormal touch, vibration, joint position; NORMAL PAIN TEMP, STRENGTH) -Don't know where their feet are SO THEY STOMP THROUGH THE HOSPITAL*** -Degen of posterior column -NEURO - SYPHILLIS!!!
answer
Tabes Dorsalis
question
-Central Cord Syndrome (cervical >>> thoracic) -WIDENING OF CENTRAL CANAL -Sensory symptoms early (pain + temp, CAPE LIKE DISTRIBUTION Sensory Loss - shoulders and arms, normal below) -Motor symptoms ONLY LATE! (hand weakness + atrophy, arms before legs) -Etiology: increased central canal pressure - TRAUMA (horse riding), chiari malformation, tumor)
answer
Syrinx / syringomyelia
question
Lower motor neuron weakness -Decreased reflexes, fasciculations (clinical) / fibrillations (EMG) -atrophy Sensory symptoms in specific patterns -Peripheral neuropathy: distal > proximal -Mononeuropathy: one nerve distribution -Radiculopathy: dermatomal pattern CNs = nerve roots in head Further localization to axon vs myelin w/ EMG & NCS
answer
Nerve Root (radiculopathy) & nerve (neuropathy)
question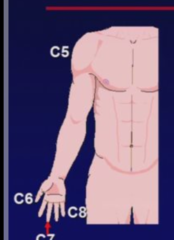
Sensory Symptoms -Dermatomal Sensory loss to pain & temp and/or dermatomal radiating pain -Localize specific dermatome by : Hx - Where the pain ENDS; exam - pinprick loss in the MIDDLE of dermatome Weakness -Radiculopathy (LMN @ lesion) C5--> Biceps, deltoid C6--> Biceps, brachioradialis, wrist extensors C7--> Triceps C8--> Triceps, finger flexors Reflex Changes -decreased or absent reflexes @ the biceps (C5-6), brachioradialis (C5-6), or triceps (C7-8)

answer
Cervical Radiculopathy
question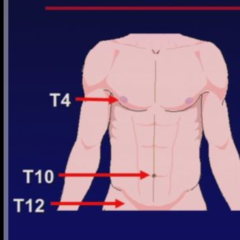
Sensory Symptoms -Dermatomal sensory loss to pain & temp and/or dermatomal radiating pain -Localize specific dermatome by : Hx - where the pain ENDS, Exam-pinprick loss in the MIDDLE of dermatome

answer
Thoracic Radiculopathy
question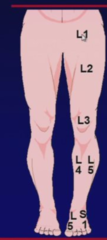
Sensory Symptoms -Dermatomal sensory loss to pain & temp and/or dermatomal radiating pain -localize specific dermatomes by: Hx - where the pain ENDS Exam- pinprick loss in the MIDDLE of dermatome Patterns of weakness - radiculopathy (LMN @ lesion) Reflex changes -decreased or absent reflexes at the knee (L3-4) or ankle (S1-2) Normal reflexes?? - L5!!!

answer
Lumbosacral Radiculopathies
question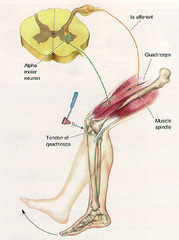

answer
Deep tendon reflexes
question
-Urinary incontinence /dysfunction -due to dyssynergia - lack of coordination b/w bladder & sphincters UMN -Lesion from pons to sacral spinal cord -bladder is small, spastic (hypertonic) -Symptoms = urgency, hesitancy, frequency, small volumes LMN -lesions from sacral nerve roots to peripheral nerves -Bladder is Large!, flaccid, (hypotonic) -Symptoms = overflow, incontinence, drippling
answer
Neurogenic Bladder
question
-Median at wrist compressive mononeuropathy -numbness, tingling, pain (thumb, index, middle or ring fingers) -Thenar muscle atrophy (chronic) -Common cause = prolonged or repetitive grip/finger flexion, wrist felxion
answer
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Median Nerve)
question
Compressive Mononeuropathy (saturday night palsy, honeymoon palsy) - wrist drop + numbness, over dorsum of hand -Normal Biceps Strenght -Common cause = pressure at humerus, C6 radiculopathy, radial nerve compression
answer
Radial Nerve Neuropathy
question
Axonal = toxic-metabolic / vascular -Diabetes Mellitus -Lyme disease -HIV infection -Acute intermittent porphyria -Lead toxicity -Barium salt toxicity -Mononeuritis multiplex -ABNORMAL EMG Myelin - demyelination - autoimmune -Guillain Barre Syndrome - AIDP (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy) -CIDP (chronic) -ABNORMAL NCS
answer
Axon vs Myelin Peripheral Neuropathy
question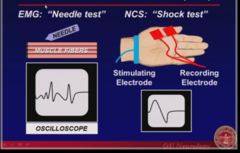

answer
EMG vs NCS
question
-muscle weakness -proximal > distal -NOT fatigable weakness -No sensory complaints -Causes - Thryoid, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, muscular dystrophies, Drugs (steroid, AZT, statin) -"Hair, Chair, and Stair" weakness
answer
Myopathy
question
-Neuromuscular Junction -proximal > distal -episodic, fatigable (worse late i day, after exercise) -extraocular/bulbar weakness -no sensory complaints -further dinstinguish if presynaptic or postsynaptic by hx & EMG repetitive stimulation
answer
Myasthenia
question
-PRESYNAPTIC -Neurotoxin from Clostridium Botulinum -impaired ACh vesicle docking, fusion, and release from presynaptic side -constipation -generalized & extraocular muscle weakness -difficulty swallowing and breathing, @ times requiring mechanical ventilation
answer
Botulism
question
-PRESYNAPTIC antibodies against VGCC (voltage gated calcium channels - cause synaptic vesicles to release ACh) -Autoimmune, frequently paraneoplastic - small lung carcinoma = most common**; lymphomas (LOOK FOR CANCER) -Reduced ACh released from Presynaptic terminals --> up-regulation of "starving" postsynaptic receptors in the muscle membrane folds -Limb weakness: apparent fatigability, but transient improvement of strength and reflexes w/ brief muscle exercise -Dysautonomia: Dry mouth and dry eyes, impotence, constipation -**Incremental response** on FAST Repetitive Nerve Stimulation
answer
Lambert-Eaton Syndrome
question
-Acquired -Autoimmune -Postsynaptic -Fatigability (improved w/ rest) -Weakness 1.) ocular - binocular, diplopia, ptosis; fluctuating symptoms-variable weakness of extraocular muscles; normal pupillary responses 2.) Bulbar (chewing, swallowing, speaking) 3.) Limbs (proximal > distal)
answer
Myasthenia Gravis
question
-can give you NMJ weakness -CNS (seizures) -Muscarinic (SLUDGEM)
answer
Organophosphates / Nerve Agents
question
Aminoglycosides D-penicillamine
answer
Drug-induced Myasthenia
question

answer
Mysthenia and EMG
question

answer
Visual Loss Differential Diagnosis
question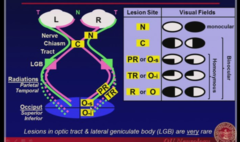
-Ant chiasm lesion = monocular -At or behind chiasm = binocular -temporal or inferior occipital lobe = superior quadrantinopsia -parietal or superior = inferior quadrantinopsia

answer
Visual Pathways and Fields
question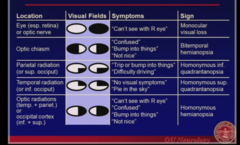

answer
Visual Field symptoms and signs



