Physics Test – Nuclear Physics – S2T3 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is meant by a radioactive substance?
answer
If an atom is radioactive it means it emits ionizing radiation or particles. When the binding force of the nucleus is not strong enough, it is unstable (therefore radioactive).
question
What is meant by the term, "isotope" and what happens to unstable isotopes when they decay?
answer
An isotope is the same element (so the same # of protons) with different numbers of neutrons. When an atom is unstable to become more stable, it will give off particles and/or energy such as alpha, beta, or gamma radiation.
question
What is meant by the "half-life" of a radioactive sample?
answer
The half life of a radioactive isotope is the average time it takes for the number of nuclei of the isotope in the sample to halve.
question
A radioactive sample of iodine-131 give a count rate of 1200 counts per second. The half-life of iodine-131 is 8 days. How many days will it take for the sample count rate to fall to 75 counts per second?
answer
??
question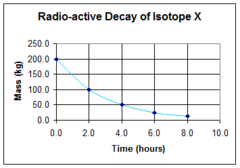
What is the half-life of the radioactive sample shown in the graph (see answer for picture)

answer
2 hours is the half-life
question
Which type of nuclear radiation is most ionizing and has the lowest range in air?
answer
Alpha
question
Which type of nuclear radiation is the least ionizing and has the greatest range in air?
answer
Gamma
question
What is required to stop beta radiation?
answer
aluminum 5mm thick or a few meters in air
question
Inside a radiation badge there are sections with small sheets of copper, aluminium, and lead, why is this?
answer
It is so they can test which types of radiation are present, and how much of the radiation there is.
question
Explain what is meant by ionizing radiation
answer
Ionizing power is the ability of different types of radiation to cause atoms to lose electrons and therefore form ions.
question
Explain why ionizing radiation is dangerous
answer
It changes the atom's composition, knocking electrons out of atoms and making them charged. When atoms in living cells become ionized, they usually either die, repair themselves, or mutate incorrectly and can become cancerous.
question
Explain what happens to gamma radiation in magnetic or electric field - draw if it helps.
answer
Nothing because gamma radiation doesn't have a charge.
question
How does the path change for a charged particle in a magnetic field? Give an example.
answer
The positive charges would be directed toward the negative part of the magnetic field and visa verse. If beta radiation was in a magnetic field it would flow to the positive side.
question
Explain how you could use a geiger-muller counter to test the range of different types of nuclear radiation.
answer
The nuclear radiation ionizes that gas inside the tube, therefore, with the ions formed a flow of charge can momentarily flow through this path completing the circuit and therefore counting the presence of nuclear radiation.
question
Would a geiger-muller counter work if the tube had no gas in it (a vacuum)?
answer
No, because there would be nothing to ionize, and therefore nothing to form a charge. You need it to close the circuit.
question
Would a gamma source be suitable for automatic thickness monitoring of aluminium foil? Explain your answer?
answer
No, because it passes straight through aluminum.
question
Beta radiation can be stopped by Aluminium. Why can it be used for monitoring thickness of aluminium foil?
answer
Because it can only be stopped by 5mm of aluminum. Variations in thickness of aluminum would show how much radiation is exposed.
question
Why is an alpha source most appropriate for use in a smoke detector?
answer
It is the easiest to block. The smoke easily blocks the radiation, so the alarm goes off.
question
Explain how the age of an igneous rock can be determined by Uranium dating?
answer
Many rocks contain Uranium in them. By measuring the amount of Uranium-238 and lead-206, you can determine how old the rock is. uranium decays into lead. Because we know the half life of uranium, we can calculate how old it is.
question
Why would the age of rock not be possible to determine using a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 15 hours?
answer
If the half-life was that short, you wouldn't be able to measure anything that was very old at all because the amount of the radioactive substance would be so (SO) small.
question
Explain why nuclear radiation can be dangerous?
answer
When atoms in living cells become ionized , one of 3 things happen: the cell dies, the cell repairs itself, or the cell mutates incorrectly and can become cancerous.
question
Explain why a radioactive gamma source with a half life of 6 hours is suitable for medical imaging as a tracer.
answer
You don't want someone to intake a radioactive substance with a long half life because then you would walk around radiating dangerous radiation. You want to trace it through the body, and then not need to worry about it again. The radiation also passes easily through many substances. Gamma penetrates through the body.
question
What are nucleons?
answer
Neutrons and protons are called nucleons since they form the atomic nucleus.
question
Describe the strong nuclear force and its connection to the stability of an atom's nucleus.
answer
The binding energy is found form the Einstein equation E = mc^2. Many details about the nuclear strong force are not yet known, but we do know that it is a very short-range attractive force. It does not exist outside the nucleus. Within a nucleus, protons attract other protons, neutrons attract other neutrons, and they attract one another.
question
Which of the following spontaneous reactions exemplifies alpha decay? Explain why.
answer
Alpha decay occurs when an alpha part ice (a helium nucleus 4 2 HE) is ejected from the nucleus of a parent atom. This also results in a relative mass reduced by 4 and an atomic number reduced by 2.
question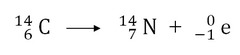
Which of the following spontaneous reactions exemplifies beta decay? Explain why.
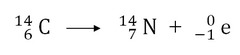
answer
The atomic # is increased by one. Free neutrons decay into a proton, an electron, and a subatomic particle called an antineutrino (Ve).
question
Which of the following spontaneous reactions exemplifies gamma decay? Explain why.
answer
There is no mass or other charge, only the wave release.
question
A sample of 300 grams of a radioactive isotope with half-life of 10 years decays for 50 years. The time period for the decay is equivalent to ___________.
answer
5 half lives
question
A sample of 300 grams of a radioactive isotope with half-life of 10 years decays for 50 years. Calculate how much of the original isotope will remain at the end of the 50 year period.
answer
1/32*300= 9.375grams ?
question
Nuclear fission is a process in which
answer
??
question
Nuclear fusion is a process in which
answer
All of the above: Extremely high temperatures are required, light nuclei collide at high speed, and light nuclei loose mass and release energy.
question
Who is known as the "father of the atomic bomb"?
answer
J. R. Oppenheimer
question
What is nuclear fusion?
answer
When nuclei collide at high speeds and fuse together
question
The sun is powered by fission or fusion?
answer
fusion
question
Does fusion or fission power hydrogen bombs?
answer
fusion
question
Is fission or fusion used in atomic bombs?
answer
fission
question
Who invented the neutron bomb?
answer
Sam Cohen
question
Who discovered x rays?
answer
Wilhem Conrad Rontgen
question
What was one way x rays were "misused?"
answer
shoe fitting
question
who was the first casualty of x ray radiation?
answer
Clarence Madison Dally in 1900.
question
X-ray
answer
an electromagnetic wave of high energy and very short wavelength, which is able to pass through many materials opaque to light.
question
Electromagnetic spectrum
answer
a continuum of all electromagnetic waves arranged according to frequency and wavelength
question
List the types of mutations
answer
Deletion, Insertion, Substitution, Inversion, Reciprocal translocation
question
Deletion
answer
remove segment of DNA
question
Insertion
answer
add segment of DNA
question
Substitution
answer
a particular base is replaced with 1 other 3 nucleotide base
question
Reciprocal traslocation
answer
excision of segments from 2 non-homologous chromosomes. These portions are inserted into other chromosomes. i.e. Chromosome 1 will gain the section from Chromosome 2 and Chromosome 2 will gain the section from Chromosome 1.
question
Mutation (natural)
answer
change in genome of organisms caused by normal recombination and segregation
question
Mutagenesis
answer
inducing mutations within organisms' genome
question
What 2 scientists did early work on mutagenesis (separately).
answer
Muller & LJ Stadler
question
Name 4 things to know before you experiment with mutagenesis
answer
1. Safety is a major concern 2. Know the mutation type and mechanisms of your experimental tissue 3. Have tissue specific reactions 4. Know how your species and ploidy levels affect mutation response to the mutagen.
question
What equation gives the amount of energy contained within matter?
answer
E=mc^2
question
What is the most commonly used fuel for nuclear reactors?
answer
Uranium-235
question
What is a common absorber of neutrons used in control rods?
answer
Boron-10
question
Fission
answer
the splitting of larger unstable atoms into smaller atoms into smaller mores stable atoms through releasing neutrons and radiations in the process.
question
Fusion
answer
the merging of small atoms into larger atoms creating heat
question
If an object has a mass of 10 kg, how much energy does it have?
answer
E = 10*(3*10^8)^2 E = 9*10^17 Joules
question
What year were the clean air acts passed?
answer
1970
question
What are two negative things about getting energy form fossil fuels?
answer
Air pollution and Greenhouses gases
question
List one negative effect of air pollution:
answer
Disease
question
True or False: Greenhouse gas has the same effects as pollution.
answer
False (greenhouse gasses are worse)
question
How did the citizens of America bring awareness to the bad air in big cities?
answer
Protest (media coverage)
question
What is a commonly used fossil fuel that causes pollution?
answer
Coal & oil
question
What is the atomic number and mass of Americium?
answer
Atomic #: 95. Atomic Mass: 243 a
question
How is Americium formed of what does it decays into?
answer
Americium forms from the compilation of Plutonium and neutrons with a nuclear reactor; deteriorates into Neptunium.
question
What types of radioactive emissions create the electrical current necessary to detect smoke?
answer
Alpha particles & gamma radiation
question
What specifically does the Americium alarm detect, and why is it a liability?
answer
Americium detects smoke; however, when smoke is detected, the fires will spread within a matter of minutes.
question
How is the Photoelectric alarm better than the Americium alarm?
answer
The reflection of light immediately warns of a possible fire
question
How much Americium does a detector require with the half life of 432 years?
answer
0.29 micrograms
question
nuclear medicine
answer
A branch of medicine that uses radioactive substances in either research, treatments, or diagnosing.
question
What are the three types of radiation therapy?
answer
External, internal, and systematic
question
List 2 of the 5 characteristics scientists look at for choosing a radionuclide
answer
1. a half-life greater than the time to prepare for injection and longer than the examination 2. low toxicity 3. suitable chemical form and reactivity 4. photon energy between 50 and 500 keV (kiloelectron volts) 5. stability or near-stability of the product
question
External radiation therapy
answer
uses high-energy x-ray beams targeted at a patient's tumor. These beams are generated by a linear accelerator, targeted to destroy the cancer cell while sparing the surrounding tissue.
question
In systematic radiation therapy, the radio-pharmaceuticals are bound to what?
answer
anti-bodies
question
internal radiation therapy
answer
uses a radiation sources that is placed within a small implant which is placed very close to or even inside the tumor so it harms as few healthy cells as possible.
question
Alpha radiation
answer
symbol: α range in air: 5 cm stopped by: thin paper ionizing ability: strong
question
Beta radiation
answer
symbol: β range in air: 1 m stopped by: aluminum (few mm) ionizing ability: moderate
question
Gamma radiation
answer
symbol: γ range in air: unlimited stopped by: cms of lead OR 1 m of concrete ionizing ability: weak



