Ovaries – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Primordial gern cells originate in yolk sac and migrate to induce?
answer
Gonadal Formation
question
Primitive sex cords differentiate into either ovaries or testes at what week?
answer
7th
question
What is the adult length of the ovary?
answer
3 cm L
question
How do we calculate the volume of the ovary?
answer
L X W X H X 0.523
question
Prepubertal volume of the Ovary is?
answer
3 cm^3
question
Menstrual volume of the ovary is?
answer
9.8 cm^3
question
Post menopausal volume of the ovary is?
answer
5.8 cm^3
question
Attaches the inferior margin of the ovary to uterine cornu?
answer
Ovarian ligament
question
Suspends superior ovary from the posterior/lateral wall?
answer
Infundibulopelvic ligament
question
Double layer of the peritoneum extending from posterior surface of broad ligament?
answer
Mesovarium
question
What are the four ovarian layers?
answer
Germinal epithelium Fibrous capsule (tunica albuginea) Ovarian parenchyma Central Medulla
question
Which layer is the thin layer that surrounds the tunica albuginea?
answer
Germinal epithelium
question
What layer of ovary is the dense connective tissue that covers the cortex?
answer
Fibrous capsule (tunica albuginea)
question
Which layer is the cortex of the ovary?
answer
Ovarian parenchyma- cortex
question
Which layer of ovary holds all the follicles?
answer
Ovarian parenchyma (cortex)
question
What follicles grow each month?
answer
Graafin
question
How many follicles becomes the dominant follicle?
answer
One
question
The dominant follicle can get to what measurement before before it ruptures?
answer
1.8-2.4 cm
question
What is pain associated with ovulation called?
answer
Mittelschmerz
question
With pregnancy what happens to the corpus luteum and what is it then called?
answer
Enlarges and becomes corpus luteum cyst of pregnancy
question
Without pregnancy what happens to the corpus luteum and what is it then called?
answer
Shrinks(involutes) and becomes corpus albicans
question
What pelvis are ovaries located? True pelvis or false pelvis?
answer
True
question
What fossa do ovaries sit in?
answer
Waldeyer's Fossa
question
What two arteries supply ovaries?
answer
Adnexal branch of UT artery Ovarian artery
question
Left ovary vein blood supply drains into?
answer
Left renal vein then IVC
question
Right ovary vein blood supply drains into?
answer
directly to IVC
question
Normal doppler waveform will include what resistance?
answer
High resistance- multiphasic
question
What happens to the flow of the dominant follicle for ovarian doppler?
answer
Increased diastolic flow
question
The abnormal resistive index (RI) for ovaries should be?
answer
less than or equal to 0.4
question
The abnormal Pulsatility index (PI) for the ovaries should be?
answer
less than or equal to 1
question
Is ovarian doppler a sensitive indicator of malignancy?
answer
No
question
Cancer of the ovary would show what waveform?
answer
Low resistant- constantly wants blood
question
Neovascularity of ovarian cancer lacks what?
answer
Muscle make-up of normal vessels
question
What are the types of ovarian functional cysts? (4)
answer
Follicular Corpus luteum Hemorrhagic Theca lutein
question
The ovarian cyst usually regresses if its what measurement?
answer
;5cm
question
Mature follicle that fails to ovulate or fails to shrink postovulation is what kind of cysts?
answer
Follicular cysts
question
What size are the follicular cysts?
answer
2-20 cm (variable)
question
If the follicular cyst regresses or spontaneously pop what should you expect to see?
answer
Cul de sac fluid
question
No involution of corpus luteum would result in what kind of cyst?
answer
Corpus luteum cyst
question
Corpus luteum cysts are usually what measurement?
answer
;4 cm
question
Corpus luteum cysts are unilateral or bilateral?
answer
Unilateral (only comes from side that just ovulated)
question
What are corpus luteum cysts prone to?
answer
Hemorrhage/Rupture
question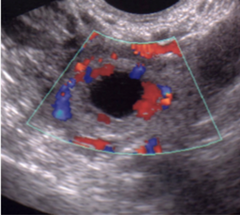
The corpus luteum cyst will create what kind of doppler image?

answer
Ring of fire (complex echo pattern)
question
Corpus luteum cysts that happen in pregnancy produce what?
answer
Progesterone
question
The corpus luteum cyst will resolve when?
answer
Week 16 of pregnancy
question
What type of cyst occurs with: Variable echogenicity Debris Septa (weblike) (PROBABLY MOST IMPORTANT) Enhancement (from fluid) Cul de sac fluid (as result of ovulation or cyst popped)
answer
Hemorrhagic Cyst
question
What cysts is associated with high levels of hCG?
answer
Theca lutein cysts
question
Molar pregnancy can become?
answer
Cancerous
question
What is the largest of the functional cysts?
answer
Theca lutein
question
Are theca lutein cysts unilateral or bilateral?
answer
Bilateral
question
GTD is aka?
answer
Molar pregnancy (Gonadal trophoblastic disease)
question
Abnormal pregnancy tissue takes over uterus?
answer
Molar pregnancy (GTD)
question
Theca lutein cyst had what kind of walls?
answer
Thin walls
question
What syndrome is a complication of ovulation induction?
answer
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS/ OHS)
question
What are the size of the ovaries and cysts associated with OHSS?
answer
large ovaries/ large cysts
question
Which syndrome is an endocrine disorder and does not ovulate?
answer
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
question
What are the size of ovaries and cysts associated with PCOS?
answer
large ovaries/ small cysts (string of pearl)
question
What would there be a deffisciency of in PCOS? (2)
answer
FSH LH (because you do not ovulate with this syndrome)
question
Those with Stein leventhal syndrome typically experience what symptoms? (Name the two most important)
answer
Infertility (cyst fail to become dominant follicle) Hiruitism (abnormal facial growth)
question
PCOS will happen unilaterally or bilaterally?
answer
Bilaterally
question
Ovarian remnant syndrome usually occurs with what surgery?
answer
Salpingoophrectomy
question
What syndrome has residual tissue that produces functional cysts?
answer
Ovarian remnant syndrome
question
Most common gonadal dysgenesis?
answer
Turners syndrome (A chromosomal disorder in which a female is born with only one X chromosome)
question
Turners syndrome will effect what chromosome?
answer
45, XO
question
People who have turners syndrome may have complete or partial absence of?
answer
Ovary
question
If you find ovaries on a patient with turners syndrome, what may you not find?
answer
Follicles
question
Women who have turners syndrome will have menorrhea or amenorrhea?
answer
Amenorrhea (no periods)
question
What syndrome will you see streak gonads, no follicles or ovaries, and women who have amenorrhea?
answer
Turners syndrome
question
Cysts that are caused by surgery and adhesions trap peritoneal fluid around the ovaries?
answer
Peritoneal inclusions cysts
question
Are peritoneal inclusion cysts ovarian in nature?
answer
No
question
A cyst with: Multioculated (multiple pockets) Cystic adnexal mass Presence of intact ovary within margin of cyst (PROBABLY MOST IMPORTANT)
answer
Peritoneal Inclusion Cysts
question
Cysts that happen from embryonic remnant?
answer
Paraovarian cyst
question
Why do paraovarian cysts not undergo cyclic changes?
answer
Not ovarian in nature - separate from ovary
question
Paraovarian cysts typically occur in what aged women?
answer
30-40 yrs old
question
What is a chocolate cyst?
answer
Endometrioma
question
Localized endometriosis is called?
answer
Endometrioma
question
Who usually gets endometriomas?
answer
Those who suffer from endometriosis
question
Ovaries typically have what kind of resistance?
answer
High
question
PID stands for?
answer
Pelvic inflammatory disease
question
Ovary rotates on its pedicle?
answer
Ovarian torsion
question
What time of life does torsion normally occur? (2)
answer
Childhood Adolescent
question
Ovarian torsion is associated with what kind of masses?
answer
Adnexal
question
What side does ovarian torsion normally occur?
answer
Right side
question
Cystic teratoma is AKA?
answer
Dermoid cysts
question
What is the most common germ cell tumor?
answer
Cystic teratoma (Dermoid cysts)
question
What is the most common ovarian tumor?
answer
Cystic teratoma (Dermoid cysts)
question
Do cystic teratomas usually turn malignant?
answer
No
question
A cyst that: Fat fluid level Anechoic mass w/ echogenic foci (teeth?) Calcification May mimic bowel gas Tip of iceberg sign (PROB most important)
answer
Cystic Teratoma
question
What is the more common epithelial tumor? (serous cystadenoma or mucosal cystadenoma)
answer
Serous cystadenoma
question
What is the second most common benign tumor?
answer
Serous cystadenoma
question
The key for serous cystadenomas is?
answer
Thin septations
question
What is the less common cystadenoma?
answer
Mucinous cystadenoma
question
Whats larger, serous cystadenoma or mucinous cyst adenomas?
answer
Mucinous cystadenoma
question
If we saw a thin walled septated cyst and it was multilocular, what would we guess it is?
answer
Serous cystadenoma (because it is more common)
question
Benign epithelial tumor that is uncommon that occur in 1.5-2.5% of ovarian neoplasms that are usually unilateral is?
answer
Brenner tumor
question
The key about Brenners tumor is that its associated with?
answer
Ipsilateral neoplasm (something else thats happening on that same ovary ex: Dermoid and Brenners on same ovary)
question
Benign stromal tumors? (2)
answer
Fibroma Thecomas
question
Meigs syndrome will usually occur when the patient has either? (3)
answer
Fibroma, Brenners tumor Massive Ascites Pleural effusion
question
How often do meigs syndrome occur?
answer
Rare
question
Is meigs syndrome malignant?
answer
No
question
What kind of tumor is a thecoma?
answer
Stromal
question
Thecomas produce what hormone?
answer
Estrogen- more feminizing features
question
What symptoms do women get in thecomas?
answer
Abnormal uterine bleeding
question
What are Sertoli leydig cells called?
answer
Androblastomas
question
A rare type of ovarian tumor in which the tumor cells secrete a male sex hormone. This may cause virilization (the appearance of male physical characteristics in females)?
answer
Androblastoma aka Sertoli leydig cell
question
Whats important to know about androblastomas?
answer
Malignant potential!
question
Cell tumor that sends out estrogen into body and more common in postmenopausal women?
answer
Granulosa cell tumor
question
Granulosa cell tumor cause what symptoms? (3)
answer
Early onset of puberty Bleeding Full breasts
question
If granulosa cell tumors get to large they can torse and cause what syndrome?
answer
Meigs
question
What does arrhenoblastoma send out into body?
answer
Testosterone
question
About out of how many women develop ovarian cancer?
answer
1 in 70
question
Leading cause for GYN malignancy?
answer
Ovarian cancer
question
Ovarian cancer is usually called?
answer
Silent cancer
question
Ovarian cancer is most common in?
answer
Postmenopausal
question
Any ovarian cancer are what in nature?
answer
90% Epithelial tumors
question
What is a key to differnitiate ovarian cancer?
answer
Thick walls
question
What stage of cancer is confined to just ovary?
answer
Stage 1
question
What stage of cancer has a lesion to one or both ovaries with extending into pelvis?
answer
Stage 2
question
What stage of cancer effects both ovaries with intraperitoneal mets, nodes, mental/small bowel involvment?
answer
Stage 3
question
What stage of cancer effects one or both ovaries with distant mets, include liver, pleural effusion?
answer
Stage 4
question
What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer? (6)
answer
55-59 Hx of breast cancer Family hx of ov cancer hx of colon Ca Nulliparous Increased years of ovarian activity (OHSS)
question
What can protect you from ovarian cancer? (5)
answer
Pregnancy Lactation Birth control (OCP's) Short reproductive span (period later than life) Early menopause
question
What is one lab they can do on women on ovarian cancer?
answer
CA125
question
Is CA125 a good indicator to determine ovarian cancer?
answer
No, but still good to do it
question
What is the treatment options for ovarian cancer? (3)
answer
Surgery Radiation therapy Chemotherapy
question
What is the 5 year survival rate of ovarian cancer?
answer
20-30%
question
What is the survival rate for stage 4 ovarian cancer?
answer
5%
question
Most common epithelial cancer?
answer
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
question
What is a key for muctinous cystadenocarinoma?
answer
Septations that are thick
question
How do they determine if its serous cystadenocarcinoma or mucinous?
answer
Surgery
question
Least common epithelial tumor is?
answer
Endometroid tumor
question
Endometroids are associate with? (2)
answer
Endometriosis Endometrial cancer
question
Endometriod tumor have what kind of walls?
answer
Thick
question
Can teratomas become malignant?
answer
Yes but rare
question
Teratomas are comprised of all?
answer
Germ cell layers
question
Teratoma labs are? (3)
answer
HCG AFP (alphafetalprotein) LDH (lactate dehydrognase)
question
Most common pediatric ovarian mass?
answer
Dysgerminoma
question
Young women mass known as?
answer
Dysgerinoma
question
Dysgerminoma grow slow or rapid?
answer
Rapid
question
Mets is unilateral or bilat?
answer
Bilat
question
Mets mimics what?
answer
Stage I and II Ovarian cancer
question
Specific type of ovarian met that contains signet ring cells and is usually from a gastric primary cancer?
answer
Krunkenberg tumor
question
Krunkenberg tumors may be what shaped?
answer
Kidney shaped ovary
question
Krunkenberg tumors are small or big?
answer
Big (huge)
question
For ovarian doppler, what is recommended/used? (2)
answer
PI RI
question
How do we want to get doppler, TA or TV?
answer
TV preferred because better resolution
question
Normal ovarian impedance is low or high?
answer
High
question
Ovarian malignancy would show on doppler what kind of impedance?
answer
Decreased (low resistance)
question
What are other reasons the PI may be low other than ovarian malignancy? (4)
answer
Inflame process Germ cell tumors Corpus luteum cysts Endometriomas



