Organic Chemistry (Reactions) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What free radical is most is likely to be formed from bromination?
answer
A tertiary radical (Most stable)
question
What are nucleophiles?
answer
Electron-rich species that are attracted to a positively polarized atom (i.e. a carbonyl carbon)
question
What is a better nucleophile I or F?
answer
Flourine
question
What is a better leaving group I or F?
answer
Iodine
question
What doesn't a nucleophile play a role in the rate of an Sn1 reaction?
answer
It is not involved in the rate-determining step...the formation of the carbocation.
question
What factors will help carbocation formation and therefore increase the rate of an Sn1 reaction?
answer
1. Highly substituted carbons. 2. Polar solvents (Surround and isolate the carbocation) 3. Good leaving groups (Weak bases)
question
Why is a Sn2 reaction bimolecular?
answer
Its rate-determining step is dependent on TWO species; both the substrate and the nucleophile.
question
What are the best conditions for an Sn2 reaction?
answer
You must have a strong nucleophile for the backside attack (thats what she said) with no steric hindrance.
question
With respect to optical activity, what do your end products of Sn1 and Sn2 reactions become?
answer
Sn1 = racemic mixture (nucleophile can attack from either the top or the bottom of the planar carbocation), therefore loss of optical activity. Sn2 = inversion of configuration and remains optically active.
question
What role does tosylate usually play in reactions?
answer
It usually acts as a good leaving group and a good protecting group.
question
Whats another word for ethyne?
answer
acetylene
question
How do you make OH- a good leaving group for Sn1 and Sn2 reactions?
answer
For Sn1 you can protonate it and make water the leaving group. For Sn2 you can convert it to tosylate which is also a good leaving group.
question
What is jones reagent and what does it do?
answer
it is CrO?, H?SO? in acetone and it oxidizes primary alcohols to carboxylic acids (STRONG!)
question
Do ethers boil at high or low temperatures?
answer
Low...no H-bonding.
question
How can you get ketones or aldehydes?
answer
Oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols. Or ozonolysis of alkenes.
question
How do you get an acetal or ketal?
answer
When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with two equivalents of alcohol. A hemiketal or hemiacetal you get from one equivalent of alcohol.
question
What is a cyanohydrin?
answer
When al and ke react with HCN.
question
What is a wittig reaction and what is its goal?
answer
The goal is to make CARBON-CARBON double bonds by converting aldehydes and ketones into alkenes.
question
What oxidizes an aldehyde and what do you get?
answer
KMnO?, CrO?, Ag?O, H?O? and you get a carboxylic acid.
question
What reduces aldehydes and ketones?
answer
LAH or NaBH?
question
What are the reagents for Wolff-Kishner Reduction of al and ke?
answer
H?NNH?, then a base and heat.
question
What are the reagents for Clemmensen Reduction?
answer
Hg(Zn) and HCl
question
Why are carboxylic acids that much more acidic?
answer
Resonance stabilization of between the alcoholic oxygen and the carbonyl oxygen.
question
Electron withdrawing vs donating...what do each do to a negative charge and acidity?
answer
Withdrawing delocalize/stabillize the negative charge (spread it over the molecule) which increase acidity. Donating do the opposite.
question
What is significant about the ? hydrogens on a ?-dicarboxylic acid?
answer
They are very acidic due to stabalization!
question
Only primary alcohols can be oxidized to carboxylic acids. T/F?
answer
True!
question
Is there a way to convert primary and secondary alkyl halides into carboxylic acids? Sure!!
answer
nitrile formation followed by acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis.
question
How do you form an ester with a carboxylic acid?
answer
Addition of a primary alcohol under ACIDIC conditions.
question
When might decarboxylation occur?
answer
When carboxylic acids are heated, they may spontaneously loose a CO?
question
What is the order of reactivity for carboxylic acid derivatives?
answer
Acyl halide ; anhydrides ; esters ; amides
question
How do you get an acyl halide from a carboxylic acid?
answer
SOCl?
question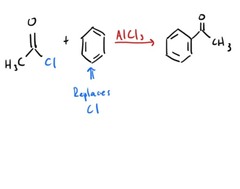
Friedel Crafts Acylation

answer
Aromatic ring acylated through electrophillic aromatic substitution.
question
Reduction of acyl halide?
answer
H? Pd/BaSO? Quinoline
question
How can one make an anhydride?
answer
React a carboxylic acid with a carboxylate salt or heat! to stabilize the carboxylic acid.
question
The conversion of a carboxylic acid into ANYTHING depends on what?
answer
The nucleophile!!
question
When carbonyl's are attacked by hydrolysis, what does the nucleophile look like in acidic vs basic conditions?
answer
Acidic: H?O is attacking Basic: OH- is attacking In acidic conditions the carbonyl oxygen is protonated.
question
How can you think of Lithium Aluminum Hydride?
answer
It is like an H- nucleophile.
question
Can nitrogen containing compounds form hydrogen bonds?
answer
Yes, but the are not as strong as the hydrogen bond between H and oxygen! (Therefore lower boiling point).
question
Can nitrogen-containing compounds be optically active?
answer
Usually not because of nitrogen inversion but sometimes they can be isolated if the structure hinders inversion.
question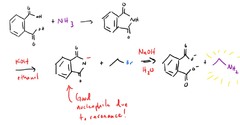
How what is Gabriel Synthesis for?

answer
Gabriel drank ammonia! OH NO!
question
What is hofmann rearrangement?
answer
An amide to a primary amine (Pg 389)
question
What is a wash?
answer
When you are using the extraction to remove impurities rather than separate out the desired product.
question
Gravity filtration vs vacuum filtration
answer
Gravity filtration is used for when the desired product is in solution (usually hot) where as vacuum filtration has the desired product being a solid.
question
Why is temperature important in recrystallization?
answer
The product needs to be soluble in high temps and insoluble in lower temperatures. IMPURITIES need to be soluble at all temperatures so that they stay in solution.
question
When would distillation be favored over a separatory funnel?
answer
When two liquids are miscible, the separatory funnel cannot be used therefore distillation is more ideal.
question
When is vacuum filtration used?
answer
ABOVE 150 C BOILING POINTS! Vacuum will lower the pressure of the apparatus to ensure that the liquids do not decompensate under the extreme temperatures.
question
Fractional distillation
answer
Repeated distillations on inert objects like glass beads that help separate two liquids with boiling points less than 25 C apart.
question
Thin-Layer Chromatography

answer
Silica gel is polar!!
question
Column Chromatography
answer
Ion Exchange Chromatography Size-Exclusion Chromatography Affinity Chromatography
question
In gas chromatography what is the eluant and what is the stationary phase?
answer
The eluant or mobile phase is a gas (He or N) and the stationary phase is the temperature-regulated column. Retention time: How long it took for each compound to travel through the column.
question
How does isoelectric focusing work?
answer
All proteins have an isoelectric point (no charge). When the molecule reaches the field that is equal to its isoelectric point, it will stop moving!
question
How do Agrose gel and SDS-PAGE electrophoresis separate molecules?
answer
Based on SIZE
question
What is the purpose of Infrared (IR) spectroscopy?
answer
Certain bonds absorb infrared light at different frequencies and this can then be measured through what is absorbed vs what is transmitted. Used for FUNCTIONAL GROUP identification.
question
The difference between oligo and polysaccharide?
answer
Oligo is short poly is long.
question
Where do you start numbering a carbohydrate?
answer
On the carbonyl end.
question
What are epimers?
answer
Diastereomers that differ in the configuration of ONE carbon.
question
What are anomers?
answer
They differ only in the newly formed chiral carbon (after ring formation). Can be ? vs ?. Glucose the ? anomer is trans and the ? anomer is cis (both pointing up!)
question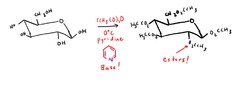
Monosaccharide ester formation

answer
All hydroxyl groups will be esterified!
question
What happens in a Tollens' Test?
answer
Testing for the presence of a reducing sugar. Aldoses and ketose can be oxidized to carboxylic acids and therefore reduce Ag+ in the Tollens' test to metallic silver (Ag+ to Ag)
question
What happens in a Benedict's test?
answer
Testing for the presence of a reducing sugar. Aldoses and ketose can be oxidized to carboxylic acids and therefore producing Cu?O (red) from benedict's reagent (started with Cu(OH)?
question
How do you get glycosides from your hemiacetal monosaccharide?
answer
Alcohol in the presence of ACID!!
question
How do you get a disaccharide?
answer
From the same reaction that gave us the glycoside! Its just that now the alcohol is.....ANOTHER MONOSACCHARIDE! YAY!
question
What kind of bond does Cellulose have vs Starch and glycogen?
answer
BETA 1, 4 vs the ALPHA of starch and glycogen (some ? 1,6 in there too!)
question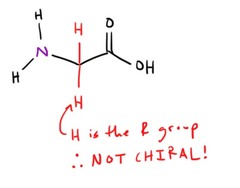
What is the only amino acid that is NOT CHIRAL?

answer
Glycine
question
Naturally-occuring amino acids are L-enantiomers. T/F? Fischer projection?
answer
True!! Fischer projections of amino acids have amino group to the left!
question
What is a zwitterion and how does an amino acid look as such?
answer
They are dipolar ions where each half neutralizes the other.
question
Amino acids are amphoteric. Why?
answer
They can act as an acid or a base. They have at least two dissociation constants (from H's on the n and c terminus)
question
When does an amino acid take on the zwitterion form?
answer
At the isoelectric point or isoelectric pH between pKa? and pKa?
question
What looses an H first in basic titration, the amino or carboxyl group?
answer
The carboxyl group duh!
question
Things to know about titration of amino acids...
answer
1.Buffering capacity is greatest at the Ka's 2. Two moles of base need to be added in order to deprotonate one mole of most a.a. 3. When adding base, the carboxyl group looses the H first. 4. Titrations can be done in reverse starting with a basic solution and adding acid.
question
How many moles of acid are needed to neutralize 1 mole of a basic amino acid?
answer
3 moles because of the extra R amino group.
question
What is an amino acid called after it becomes a part of a peptide?
answer
A residue.
question
Why is rotation of the peptide bond limited?
answer
There is resonance about the C-N bond giving it some double bond character.
question
What level of structure is guided by hydrogen bonds for proteins?
answer
Secondary structure resulting in ?-helix and ?-pleated sheets.
question
What level of structure determines whether you have collagen or myoglobin?
answer
Tertiary structure in that at this level you have the determination of fibrous vs globular proteins.
question
What is a conjugated protein?
answer
One that gets part of their function from a prosthetic group.
question
What is zaitsev's rule?
answer
When producing alkenes (usually from elimination reactions) there will be a major and minor product, the major one being the more subsituted and stable form.
question
What is a Diels-Alder Reaction?
answer
...



