Organic Chemistry Lab Midterm – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Molecular structure of cyclohexane
answer
just a simple cyclo-6 carbon. C6H12
question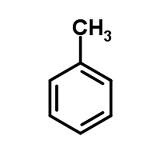
Molecular structure of Toluene

answer
a benzene with a CH3 attached on the top Carbon. C7H8
question
What is the purpose of distilling something?
answer
separating compounds based on differences in their boiling points.
question
What kind of mixture is used for simple & fractional procedure?
answer
volatile compounds in this case cyclohexane and toluene.
question
purpose of boiling stones
answer
to avoid "bumping" which is the sudden eruptive release of vapor
question
Define boiling point
answer
the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the external pressure applied to the surface of the liquid. This external pressure is commonly atmospheric pressure.
question
What is a distillate?
answer
A liquid condensed from vapor in distillation. A purified form.
question
What is volatile?
answer
Having relatively high vapor pressures and low boiling points.
question
What is a theoretical plate and what apparatus has more of them?
answer
Each condensation and revaporization that occurs on a fractionating column is called a theoretical plate. A fractionating column with a large number of theoretical plates accomplishes many condensation-revaporization steps and very efficiently separates the compounds in a mixture. Fractional.
question
What is a condensation line?
answer
a condensation line of vapor can be observed as it moves up the distilling head.
question
When do you use simple distillation?
answer
when boiling points are far apart and nonvolatile
question
When do you use fractional distillation?
answer
volatile fluids with close boiling points
question
Movement water through condenser
answer
The fluid is evaporated and then liquifies as it moves though the condensor. As the condensed liquid falls toward the pot, the pot gradually contains a higher and higher percent of the less volatile compound. Thus, a separation of the two compounds is achieved.
question
What is codistillation?
answer
Distillation performed on mixtures in which the two compounds are not miscible.
question
What is steam distillation?
answer
When one of the compounds being distilled is water
question
What does steam distillation avoid?
answer
This process avoids decomposition, that might occur at the normal boiling point of the compound of interest.
question
What kind of mixture is used for the clove oil procedure?
answer
an excess of water is added to the compound of interest in a distilling flask.
question
Iron III chloride Test
answer
Is a test for phenols. The formation of a red, blue, green, or purple coloration indicates the presence of phenols.
question
Testing with potassium permanganate
answer
Test for alkene and alkyne. The disappearance of the purple color and the appearance of a brown suspension is a positive test.
question
Testing with Bromine in Dichloromethane
answer
triple bonds and phenols.he formation of a white precipitate (a brominated phenol) indicates that the unknown was a phenol.
question
What is an emulsions?
answer
a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible
question
What class of organic compounds does caffeine belong to?
answer
alkaloids
question
What is a drying agent?
answer
a substance that promotes drying
question
Recrystallization of caffeine
answer
Evaporate the remaining dichloromethane from the crude caffeine • Dissolve the crude caffeine crystals in a minimal amount of hot 2-propanol, cool, and add hexane • Filter the purified caffeine and wash with 1:1 diethyl ether/hexane solution • Weigh the crystals
question
Melting point of caffeine
answer
234-236
question
molar mass of caffeine
answer
194.19 g/mol
question
Purpose of activated charcoal
answer
purification
question
How did you purify acetanilide?
answer
Recrystallization
question
What is the difference between the treated and untreated product?
answer
treated product will be free of impurities (white) and lighter
question
What does recrystallization do?
answer
used to remove impurities from organic compounds that are solid at room temperature.
question
For recrystallization of acetanilide: Do you want your compound to be soluble or insoluble at room temperature?
answer
insoluble
question
For recrystallization of acetanilide:Do you want your compound to be soluble or insoluble at hot temperatures?
answer
soluble
question
What is "oiling out"?
answer
if a solvent's boiling point is higher than the compound's melting point
question
What is a solvent pair?
answer
Two solvents are selected that are miscible with each other, but have opposite abilities to dissolve the compound.
question
What is a solvent?
answer
A substance that dissolves a Solute
question
Criteria for selecting recrystallizing solvent?
answer
(1) Compound being purified must be insoluble in solvent at room temperature (2) Compound must be soluble in boiling solvent (3) Solvent's boiling point must be lower than the compound's melting point (4) An abundant quantity of crystals must be recoverable from the cool solvent
question
Vacuuming filter is (faster or slower) and gives you (more or less) product
answer
faster; less product
question
Gravity filter is (faster or slower) and gives you (more or less) product
answer
slower; more product
question
What is a melting point range?
answer
the span of temperature from the point at which the crystals first begin to liquefy to the point at which the entire sample is liquid.
question
eutectic temperature
answer
The lowest temperature at which a mixture of two elements will completely melt.
question
eutectic composition
answer
both solid X and solid Y are in equilib. with the liquid
question
How can you tell if something is pure using melting point range?
answer
1-2 C melting point range reveals a pure compound
question
Orientation melting point
answer
The melting point at which the sample is heated 10-15 C until it melts and then cooled to 15 below the "orientation melting point"
question
What is sweating?
answer
Sometimes slight changes, such as shrinking and sagging, occur in the crystalline structure of the sample before melting occurs. Also, traces of solvent may be present due to insufficient drying and may appear as droplets on the outside surface of the sample.



