Organic Chemistry (CHEM 227) Alcohol Reactions – Chap. 17 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Alcohol + Alkali Metals/Strong base(NaH, NaNH2, Grignard Reagent)
answer
Preparation of Alkoxides from alcohols by reaction with alkali metals or strong bases Acid/Base proton transfer
question
Aldehyde + LiAlH4(in ether)/NaBH4(in ethanol)
answer
Reduction of Aldehydes Reduction of aldehydes yields primary alcohols, Nucleophilic attack of a hydride forms an alkoxide ion intermediate which, in a second step, is protonated to yield the corresponding alcohol product
question
Ketone + LiAlH4(in ether)/NaBH4(in ethanol)
answer
Reduction of Ketones Reduction of ketones yields secondary alcohols Nucleophilic attack of a hydride forms an alkoxide ion intermediate which, in a second step, is protonated to yield the corresponding alcohol product
question
Ester + LiAlH4(in ether)
answer
Reduction of esters Reduction of esters yield primary alcohols. Nucleophilic attack of a hydride followed by elimination of an alkoxide ion yields an aldehyde that on further reduction yields an primary alcohol
question
Carboxylic Acids + LiAlH4(in ether)
answer
Reduction of Carboxylic acids Reduction of Carboxylic acids yield primary alcohols Nucleophilic attack of a hydride on the carboxylate anion gives a high energy dianion intermediate which yields an aldehyde which on further reduction yields a primary alcohols
question
Aldehydes + Grignard Reagent(in ether)
answer
Reaction of Aldehydes with Grignard reagents Aldehydes yields a secondary alcohols Nucleophilic attack of a Grignard reagent forms an alkoxide ion intermediate which, in a second step, is protonated to yield the corresponding alcohol product The presence of any other functional group with acidic protons must be avoided
question
Ketone + Grignard Reagent (in ether)
answer
Reaction of Ketones with Grignard reagents Ketones yield tertiary alcohols The presence of any other functional group with acidic protons must be avoided Nucleophilic attack of a Grignard reagent forms an alkoxide ion intermediate which, in a second step, is protonated to yield the corresponding alcohol product The presence of any other functional group with acidic protons must be avoided
question
Esters + Grignard Reagent (in ether)

answer
Reaction of Esters with Grignard Reagents Esters react with two equivalents of Grignard reagents to yield tertiary alcohols. Nucleophilic attack of a Grignard reagent forms a ketone which on further reaction with a second equivalent of the Grignard reagent forms an alkoxide. This, in a second step, is protonated to yield the corresponding tertiary alcohol product
question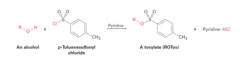
Alcohol + Tosyl Chloride (in pyridine)

answer
Conversion of Alcohols into Tosylates The formation of the tosylate does not affect the configuration of any existing chirality centers The displacement of a tosylate in an Sn2 reaction proceeds with inversion of configuration
question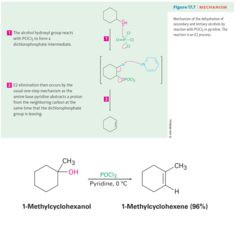
Alcohol + POCl3 (in Pyridine)

answer
Dehydration of secondary alcohols with phosphorus oxychloride Phosphorus reacts with a secondary alcohol to form a dichlorophosphate which is a good leaving group The elimination step is an E2 reaction
question
Alcohol + Carboxylic acids (in a strong acid)
answer
Conversion of Alcohols into Esters Alcohols react with carboxylic acids in the presence of a strong acid to give esters Sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid are often used as catalysts
question
Primary/Secondary Alcohol + CrO3/KMnO4/Na2Cr2O7
answer
Oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols with chromium or manganese bases reagents E2 elimination to generate a carbon-oxygen double bond Primary or secondary alcohols react with several chromium or manganese reagents to yield carboxylic acids or ketones respectively. Oxidation of primary alcohols with Na2Cr2O7 or CrO3 makes it very difficult to isolate the initial aldehyde; milder oxidizing reagents are preferred for this purpose
question
Primary/Secondary Alcohol + DMP/PCC
answer
Oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols with mild oxidizing reagents E2 elimination to generate a Carbon-Oxygen double bond Primary or secondary alcohols react with mild oxidizing reagents like Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP) or Pyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC) to give aldehydes and ketones respectively
question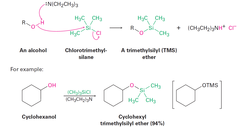
Alcohols + Chlorotrialkylsilane(TMS), Cl-SiR3 (in base)

answer
Protection of Alcohols with Chlorotrimethylsilane and Regeneration of the Alcohol Alcohols react with a chlorotrialkylsilane, CL-CiR3, in the presence of a base to yield a trialkylsilane ether, ROSiR3. Reaction of the TMS ether with aqueous acid regenerates the alcohol.
question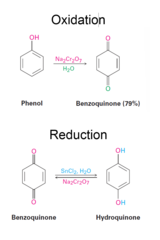
Phenol + Na2Cr2O7 (in water) then followed by Sn2Cl2

answer
Oxidation of Phenols to Quinones and Reduction of Quinones to Hydroquinones Na2Cr2O7 other milder oxidizing reagents like Ferric Iron (FeCl3) or Silver oxide Effective reducing reagents are SnCL2, Na2S2O4 (sodium dithionite) The quinone/hydroquinone equilibrium is electrochemically reversible
question
Glycol(vicinal diol) + Strong Acid(H2SO4)
answer
Pinacol Rearrangement Acid catalyzed dehydration of a glycol (a vicinal diol) yields a rearranged carbonyl product. Proceeds through a carbocation intermediate



