Organic Chemistry Chapter 6 and 7 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
alkyl halide
answer
halogen atom bonded to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom that is tetrahedral
question
primary alkyl halide
answer
One carbon attached
question
secondary alkyl halide
answer
2 carbons
question
tertiary alkyl halide
answer
3 carbons
question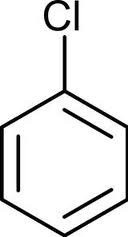
aryl halides

answer
halogen bonded to an aromatic ring
question
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
answer
a nucleophile displaces a leaving group in the molecule that undergoes the substitution
question
electrophile
answer
electron loving (needs more electrons) Gets rid of the positive charge
question
leaving group
answer
always a species that takes a pair of electrons with it when it departs
question
nucleophile
answer
always a lewis base, may be negatively charged or neutral (wants to get rid of electrons)
question
always a lewis base
answer
nucleophile
question
any negative ion or uncharged molecule with an unshared electron pair is a
answer
potential nucleophile
question
a good leaving group is a substituent that can leave as
answer
a relatively stable, weakly basic molecule or ion
question
bimolecular
answer
two species are involved in the step whose rate is being measured
question
Sn2 reaction means
answer
substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular
question
Sn2 reaction undergoes
answer
inversion (its tetrahedral bonding configuration is turned inside out)
question
transition state
answer
a state on a potential energy diagram corresponding to an energy maximum
question
reaction coordinate
answer
indicates the process of the reaction, in terms of the conversion of reactants to products
question
free-energy diagram
answer
plot free energy of the reacting particulate (y-axis) against the reaction coordinate (x-axis)
question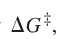
free energy of activation
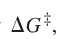
answer
difference in energy between the reactants and the transition state
question
free energy change for the reaction
answer
the difference in energy between the reactants and the products
question
the top of the energy hill corresponds to
answer
the transition state
question
uphill on potential energy diagram is
answer
endergonic
question
downhill on potential energy diagram
answer
exergonic
question
as you go down the periodic table the atoms get larger making longer bonds that
answer
lower the energy
question
as you go down the periodic table the atoms get
answer
larger
question
physical properties of organic halidees
answer
low solubility in water soluble in nonpolar sovlents
question
Mechanism of Sn2
answer
1 step transition state inversion attack from the back
question
nucleophiles approaches from what side in sn2 reactions
answer
back side, away from the LG
question
carbocations are
answer
trigonal planar
question
carbocations have
answer
2 empty p orbitals
question
Sn1and optical active compounds
answer
optically active substrate transformed into racemic products
question
Solvolysis
answer
the solvent act as the nucleophile in a substitution reaction
question
hyper conjugation
answer
electron delocalization from a filled orbital to an adjacent unfilled orbital
question
hyper conjugation does what to carbocations
answer
stabilized
question
Sn1 mechanism
answer
1. nucleophilic attack 2. solvent used 3. charges balances (possible use solvent again)
question
stability of carbocations
answer
increase the number of C attached to the center c, makes the carbocation more stable
question
carbon compounds are never
answer
the leaving group
question
steric hinderance
answer
an affect on the relative reaction rates caused by the space-filling properties of those parts of a molecule attached at or near the reacting site hinders a reaction
question
steric hinderance is due to
answer
space filling properties
question
negatively charged nucleophiles are more reactive than their
answer
conjugate acids
question
the lower the pKa
answer
the stronger the acid, the weaker the base
question
The higher the pKa
answer
the weaker the acid, the stronger the base
question
nucleophilicity parallels basicity when comparing nucleophiles with the same nucleophilic atom
answer
RO- > HO >> RCO2- > ROH > H2O
question
nucleophilicity is measured by
answer
relative rates of reaction
question
steric hinderance blocks
answer
where the nucleophile can come and attack the carbocation
question
molecules that great the slowest will not likely react via an Sn2 pathway, though what other pathway might such molecules proceed?
answer
they are too bulky to travel via Sn2 pathway (steric hinderance) so they are able to go down an Sn1 pathway
question
the more - charged nucleophile the
answer
faster the reaction
question
nucleophilicity parallels basicity when comparing nucleophiles with the same electrophilic atom (example)
answer
RO- > HO >> RCO2- > ROH > H2O
question
nucleophilicity
answer
how well the nucleophile performs
question
lewis acid
answer
accepts
question
4 factors that affect the rates of Sn1 and Sn2 reactions
answer
1. the structure of the substrate 2. the concentration and reactivity of the nucleophile (for bimolecular reactions only) 3. The effect of the solvent 4. The nature of the leaving group
question
solvolysis
answer
nucleophile is a molecule of the solvent (sn1)
question
Sn2 order of reactivity
answer
methyl > primary > secondary >> tertiary
question
steric hinderance
answer
spatial arrangements of the atoms or groups at or near the reacting site of a molecule hinders or retards a reaction
question
hammond-leffler postulate
answer
the structure of a transition state resembles the stable species that is nearest it in free energy
question
Since the nucleophile does not participate in the rate-determining step of an Sn1 reaction
answer
the rates of Sn1 reactions are unaffected by concentration or identity of nucleophile
question
Relative nucleophile strength
answer
1. a negatively charged nucleophile is always a more reactive nucleophile than its conjugate acid 2. In a group of nucleophiles in which the nucleophilic atom is the same, nuclophilictges parallels basicities
question
Which one is a better nucleophile HO- or ROH
answer
HO- (negatively charged)
question
protic solvent
answer
has a hydrogen atom attached to an atom of strong electronegative element
question
aprotic solvent
answer
solvents whose molecules do not have a hydrogen atom that is attached to an atom of strongly electronegative element
question
rates of Sn2 reactions generally are vastly increased when they are carried out
answer
in polar aprotic solvents
question
what are good leaving groups
answer
weak bases
question
what is a protic solvent
answer
a solvent with an O-H or a N-H bond which can serve as a source of protons (H+)
question
3 types of solvents common come upon
answer
non-polar, polar aprotic, and polar protic.
question
rates of Sn2 reactions are significantly increased in
answer
polar aprotic solvents
question
rates of Sn1 reactions are significantly increased in
answer
polar protic solvents



