Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion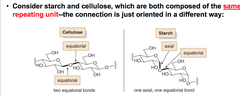
study of spatial arrangements of atoms in molecules and the effects of those arrangements on the chemical and physical properties of substances minor differences in 3D structure can result in vastly different properties. Starch vs Cellulose in image.

answer
stereochemistry
question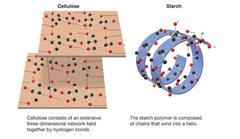
chemical and physical properties are very different, the differences stem from a seemingly minor difference in bond orientation -- a stereochemical difference!

answer
Starch and Cellulose
question
there are ___ major classes of isomers: constitutional and stereoisomers.
answer
2
question
________/______ isomers have different IUPAC names, the same or different functional groups, and different physical and chemical properties.
answer
Constitutional/Structural
question
differ only in the way the atoms are oriented in space. Have identical IUPAC names except for an extra prefix (such as cis vs trans or R vs S) differ from one another in "configuration"
answer
stereoisomers
question
not superimposable (not identical) on its mirror image. (Think hands, right hand is mirror of left hand, not identical!)
answer
chiral
question
a molecule or object that is superimposable on its mirror image is _____. think of socks, left and right are identical!
answer
achiral
question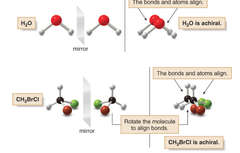
achiral or chiral?

answer
achiral
question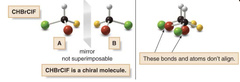
achiral or chiral? Molecule A and B are not superimposable! NO MATTER HOW YOU ROTATE a and b, can never get all atoms to align. A and B are different compounds. this molecule CHBrClF has a Ca tom with four different groups attached. this C is a stereogenic center, stereocenter or a chiral center.

answer
chiral
question
A and B are stereoisomers, so they are _______
answer
enantiomers
question
stereogenic center, or chiral center. has all different groups attached to it.
answer
Stereocenter
question
a molecule with no stereogenic centers will ____ be chiral. (few exceptions)
answer
NOT
question
with one stereogenic center, a molecule will _____ be chiral. two or more sterogenic centers, a molecule may or may not be chiral.
answer
always
question
____ molecules contain a plane of symmetry; chiral molecules do not. plane of symmetry means a mirror plane that cuts the molecule in half, so that one half of the molecule is a reflection of the other half.
answer
Achiral
question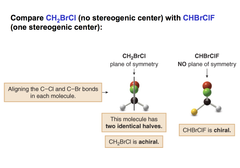
plane of symmetry

answer
plane of symmetry
question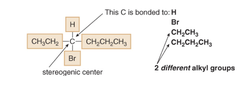
to locate a stereogenic center, examine each tetrahedral C and look at the four _____ not just the four atoms- bonded to it. if you can find any different, even far from the carbon in question, that means you have "different groups" attached. look at whole substituent.

answer
groups
question
____ and _____ hybridized C cannot be stereogenic centers.
answer
SP or SP²
question
_____ molecules can have two, three, or even hundreds of stereogenic centers.
answer
larger
question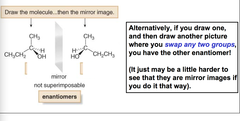
drawing ______ of a chiral compound, arbitrarily place the four groups on any bond to the stereogenic center, then draw the mirror! or swap any two groups, may be harder!!!

answer
Enantiomers
question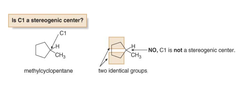
stereogenic centers may also occur in _____. to find the stereo centers on -___ carbons, draw the _____ as flat polygons, and look for carbons that are bonded to four "different groups".

answer
rings
question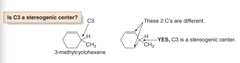
is c3 stereogenic?

answer
Yes
question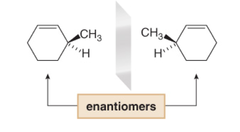
substituents above and below the face of the ring are drawn with _____ and ______ as usual.

answer
wedges and dashes
question
Enantiomers are different, they need to be distinguished by name. Done by adding the prefix ___ or ____ to the IUPAC name of the enantiomer. must assign priorities to assign each group bonded to the stereogenic center.
answer
R or S
question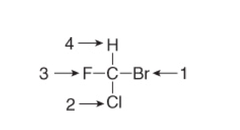
rules for assigning priorities: 1. atom of highest atomic number test the highest priority.

answer
priority R or S rule 1
question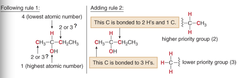
If two atoms on a stereocenter are the same, assign the priority based on the atomic number of the atoms bonded to these atoms. no immediate difference, move further down each "chain" until you find the first point of difference.

answer
priority rule 2
question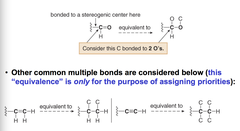
treat a multiply bonded atom like an equivalent number of singly-bonded atoms. For example the C of a C=O is evaluated as if it were "bonded to two O atoms" equivalence only for the purpose of assigning priorities.

answer
priority rule 3
question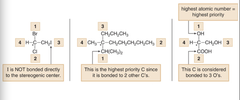
Do you understand why these _____ were given?

answer
Priorities
question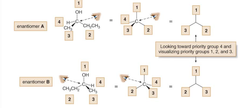
1. Orient molecule, so lowest priority substituent is pointing away(draw it so that a "dashed line bond goes to that one)

answer
Assigning S or R step 1
question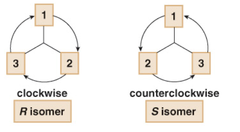
Draw a circle from priority group 1 to 2 to 3. If this process goes clockwise, you have the R isomer. If the process goes counterclockwise you have the S-isomer.

answer
Assigning S or R step 2
question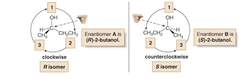
the R or S designation goes in front of the rest of the IUPAC name as shown in image.

answer
Assigning S or R step 3
question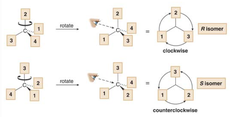
what if the lowest priority substituent is not already conveniently pointing away from you? ________ the thing around until it is. In doing this only chaining the conformation not the configuration!

answer
rotate/ twirl
question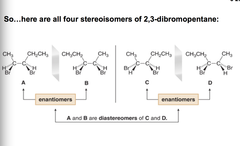
for a molecule with n stereo centers, the maximum number of sterioisomers is 2ⁿ molecules with two adjacent stereocenters are often drawn to place the centers side by side in a "sawhorse" style view. draw one stereoisomer, then draw mirror image. place B directly on top of A, then rotate B 180° and place it on top of A to see if the atoms align. you can twirl the tends around to try to line them up if you want, but you must keep the perspective correct, don't break bonds. switching the position of any two groups on one stereocenter of either A or B, forms a new stereoisomer (labeled C) that is different from A and B, the mirror image of C is labeled D . So the relationship b/t a nd c is they aren't enantiomers, they are ________.

answer
diastereomers
question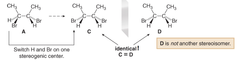
an achiral compound that contains stereogenic centers. steps: start with stereoisomer A and its mirror image B, switch the position of two groups on one stereocenter of one enantiomer, which gives a diastereomeric C, now mirror it. if the mirror of C is identical to C, C is achiral! for the image, because one stereoisomer is a _____ ______m there are only 3 stereoisomers, vs the maximum of four (2ⁿ rule)

answer
meso compounds
question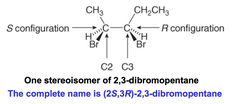
____ and____ assignemnts in compounds with two or more stereogenic centers. -identical compounds have the same ____ and _____ designations at every tetrahedral stereogenic center. -enantiomers have exactly opposite R,S designations. -Diastereomers have the same R,S designation for at least one stereogenic center and the opposite for at least one of the other seterogeinc centers.

answer
R and S
question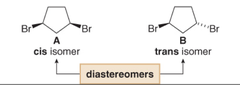
substituents can be on the same face of the ring(Cis-isomer) or on opposite faces of the ring(a trans-isomer) they are stereoisomers, but not mirror images, so they are diastereomers.

answer
disubstituted cycloalkanes
question
-to consider other possible stereoisomers draw mirror images of each compound and determine whether the compound and its mirror image are superimposable, -the cis isomer is superimposable on(identical to) its mirror image. Thus, the cis isomer is an achiral mess compound. -cis isomers with other structures are not always mess. Note that this one has a plane of symmetry.

answer
disubstituted cycloalkanes
question
-the trans isomer is not superimposable on its mirror image,(c) making B and C enantiomers of each other. -because one stereoiosmer is superimposable on its mirror image (the cis one), there are only three stereoisomers of 1,3-dibomocyclopentane, not four.

answer
disubstituted cycloalkanes
question
pair of enantiomers will have identical physical properties, except for how they interact with polarized light. plane-ploarized (polarized) light has an electromagnetic vector that oscillates in a single plane. It is generated by passing ordinary light through a polarizer. polarimeter- instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a tube containing a solution of a compound. It measures the degree to which the solution rotates plane-polarized light.
answer
Optical activity
question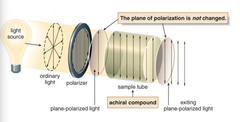
a compound that does not change the plane of polarized light . achiral compounds, the light that exits the sample tube remains unchanged.

answer
optically inactive
question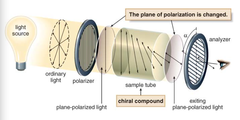
(pure) chiral compounds, the plane of the polarized light is rotated through an angle alpha, the angle alpha is measured in degrees, and is called the observed rotation. sample that rotates polarized light is said to be ____ _____.

answer
optically active
question
plane that is rotated clockwise, rotation is labeled D or (+)
answer
dextrorotatory
question
rotation is counterclockwise, labeled l or (-)
answer
levorotatory
question
two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light to an _____ extent, but in ______ directions.
answer
equal, opposite
question
___ _________ between R and S prefixes and (+) and (-) designations that indicate optical rotation.
answer
no relationship
question
___ ___ or a racemate, an equal amount of two enantiomers, is optically inactive. often arise from chemical reactions wherein new stereocenters are created.
answer
racemic mixture
question
would have no rotation like any other achiral compound.
answer
meso compound
question
[alpha] = alpha/(lxc)

answer
specific rotation
question
optical purity measure of how much of one enantiomer is present in excess of the other. denoted by symbol ee. ee=% of one enantiomer - %of the other enantiomer can also be calculated if the [alpha] of a mixture is measured and compared to the [alpha] of a pure enantiomer. ee=([aplha] mixture/[alpha] pure enantiomer) x 100
answer
enantiomeric excess
question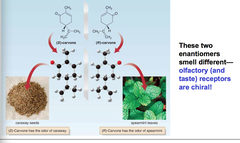
a pair of enantiomers will have identical ____ ____ except for their reaction/interaction with other chiral species. for example: olfactory (and taste) receptors are chiral.

answer
chemical properties
question
many drugs are _____ and may function by interacting with a chiral receptor or enzyme. one enantiomer of a drug may be effectively treat a disease whereas its mirror image may be ineffective or even toxic.

answer
chiral



