Test Questions on Organic Chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Organic Chemistry
answer
The branch of chemistry which deals with carbon compounds, including those with no relationship to life.
question
Covalent Bond
answer
Inter-atomic relationship created by the sharing of at least one pair of electrons.
question
Saturated Hydrocarbon
answer
Contain only only carbon-to-carbon single bonds. The most chemically inert of all organic compounds.
question
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
answer
Contain carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds.
question
Atomic Structure of Carbon
answer
Atomic Number = 6, Protons = 6, Electrons = 6, Atomic Weight = 12.0. Electrons in first energy level = 2; second energy level = 4.
question
Carbon
answer
An element that has the capacity to share four electrons in order to achieve a more stable configuration.
question
Bonding: Carbon to Hydrogen or Halogens
answer
Shares one electron.
question
Bonding: Carbon to Oxygen or Sulfur
answer
Shares up to two electrons.
question
Bonding: Carbon to Nitrogen
answer
Shares up to three electrons
question
Halogens
answer
Flourine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), and Iodine (I).
question
Hydrocarbon Molecule
answer
Contains only carbon and hydrogen. Can be divided into aliphatic and aromatic classes.
question
Substituted Hydrocarbon
answer
One or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by another atom or group of atoms called a Functional Group.
question
Aliphatic Hydrocarbon
answer
A saturated hydrocarbon that contains only hydrogen (the maximum number) and carbon. Does not contain benzene ring.
question
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
answer
Contain at least one benzene ring or similar structural features.
question
Benzene
answer
Consists of a ring of six carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds.
question
Alkanes
answer
(CnH2n+2)
question
Cycloalkanes
answer
(CnH2n)
question
Classification: Primary
answer
(1°) Carbons that are covalently bonded to one other carbon. They are at the end of a carbon chain and referred to as terminal carbons.
question
Classification: Secondary
answer
(2°) Carbons that are covalently bonded to two other carbons.
question
Classification: Tertiary
answer
(3°) Carbons that are covalently bonded to three other carbons.
question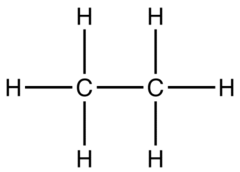
Structural Formula

answer
Shows the actual bonding of atoms to each other.
question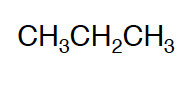
Condensed Formula
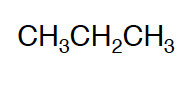
answer
Shows all the atoms in a molecule and places them in a sequential order.
question
Molecular Formula
answer
States the actual number of each kind of atom found in a molecule.
question
Structural Isomerism
answer
Compounds that have identical molecular formulas but different structures.
question
Cis-trans Isomerism
answer
The formation of cis-trans isomers is a consequence of the absence of free rotation. Geometric isomers that only differ from each other in the 3-dimensional arrangement of the substituents in space. They have identical bonding and substituents.
question
Alkane
answer
Saturated hydrocarbons (containing only carbon-to-carbon single bonds); derivatives of methane. Noted by the suffix "-ane" and sometimes by the prefix "cyclo-"
question
Alkene
answer
Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond. Noted by the suffix "-ene"
question
Alkyne
answer
Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. Noted by the suffix "-yne"
question
Functional Group
answer
An atom or group of atoms arranged in a particular way that is primarily responsible for the chemical and physical properties of the molecule in which it is found. There are a total of 10 of these.
question
Alcohols
answer
Organic compounds that contain the hydroxyl group (R-OH). Noted by the the suffix "-ol"
question
mono-
answer
Contains one group
question
di-
answer
Contains two groups.
question
tri-
answer
Contains three groups.
question
tetra-
answer
Contains four groups.
question
Thiols
answer
Any organic compound having the -SH functional group (R-SH). Also called the sulfhydryl. Noted by the suffix "-thiol"
question
Carboxylic Acids
answer
Organic compounds that contain the carboxyl functional group, also referred to as organic acids. Noted by the suffix "-oic acid"
question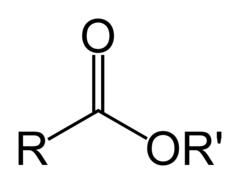
Esters

answer
Organic compounds formed by the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Noted by the suffix "-oate"
question
"-yl"
answer
Nomenclature for the alchohol group in an ester.
question
"-oate"
answer
Nomenclature for the acid group in an ester.
question
Aldehydes
answer
Hydrocarbon derivatves in which two of the hydrogen atoms, attached to a terminal carbon, have been replaced by a double-bonded oxygen atom (carbonyl group). Noted by the suffix "-al"
question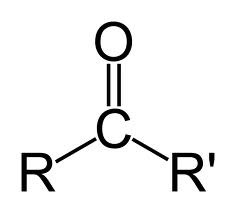
Ketones

answer
Organic compounds containing the carbonyl group attached to two organic radicals. Noted by the suffix "-one"
question
Ethers
answer
An organic compound whose molecules have two alkyl groups joined to the same oxygen atom (R-O-R). Noted by the suffix "-oxy" and "-ane"
question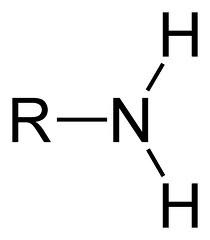
Amines

answer
Organic compounds derived from ammonia by replacement of one or more of its hydrogen atoms by one or more hydrocarbon radicals (R-NH-R). Noted by the prefix "amino-"
question
Amides
answer
Organic compounds whose molecules have a carbonyl nitrogen bond. They are the product formed in a reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine.
question
The organization that formulated nomenclature rules to name hydrocarbons.
answer
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
question
Meth-
answer
Prefix - 1 carbon.
question
Eth-
answer
Prefix - 2 carbons.
question
Prop-
answer
Prefix - 3 carbons.
question
But-
answer
Prefix - 4 carbons.
question
Pent-
answer
Prefix - 5 carbons.
question
Hex-
answer
Prefix - 6 carbons.
question
Hept-
answer
Prefix - 7 carbons.
question
Oct-
answer
Prefix - 8 carbons
question
Non-
answer
Prefix - 9 carbons
question
Dec-
answer
Prefix - 10 carbons.
question
Hydrocarbon Combustion
answer
The reaction of alkanes, alkenes, or alcohols with excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide, water, and heat.
question
Hydration
answer
A reaction involving th addition of water (H2O).
question
Dehydration
answer
Removal of water (H2O).
question
Oxidation (OIL)
answer
[o] Loss of hydrogen or electron, the gain of oxygen.
question
Reduction (RIG)
answer
[R] Loss of oxygen, the gain of hydrogen or an electron.
question
Halogenation

answer
The substitution of Hydrogen with one or more Halogens (Group VIIA elements).
question
Hydrogenation
answer
A reaction involving the addition of Hydrogen.
question
Disulfide
answer
When two thiols undergo oxidation, they yield this structural unit which is composed of a linked pair of sulfur atoms (R-S-S-R).



