Organic Chemistry 2 Final, Reagents and Reactions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Overall Reactivity of Carbonyl Groups
answer
Acyl Chloride > acid anhydride > aldehyde > ketone > ester = carboxylic acid > amide
question
aldehyde plus Grignard forms a
answer
secondary alcohol
question
When a carbon is bonded to 2 hydrogen and 2 non-identical groups
answer
enantiotopic (1 signal)
question
When a carbon is bonded to 2 hydrogens in a compound with an asymmetric center
answer
diastereotopic (2 signals)
question
(2C + 2 - #H - #X + #N)/2
answer
Formula for degree of unsaturations
question
rings and double bonds count for how may degrees of unsaturation?
answer
1 - One
question
Triple bonds count for how many degrees of unsaturation
answer
2 - Two
question
What are the steps to determining NMR spectrum
answer
1) Determine degree of unsaturation 2) Look of rings at 6.5 - 8.0 - Number of sub. = 6 - #aromatic protons 3) Look for aldehydes (sharp singlet past 9) Look for alcohols (broad anywhere) 4) Add up integration and match to formula 5) Start putting the pieces together
question
Nucleophiles act by donating a pair of ________________________ or its electron _________________________.
answer
electrons, density
question
Formaldehyde + Grignard
answer
primary alcohol
question
Ketone + Grignard
answer
tertiary alcohol
question
When an organometallic performs ring opening, it attacks the __________________ substituted side.
answer
less
question
What are the three main oxidizing agents
answer
1) Chromic Acid (H2CrO4) - Na2Cr2O7 / H2SO4 2) PCC / Ch2Cl2 3) NaOCl / Ch3COOH
question
Chromic Acid will oxidize a secondary alcohol to a __________________.
answer
Ketone
question
Chromic Acid will oxidize a primary alcohol to an __________________ and then to a ______________________.
answer
aldehyde, carboxylic acid
question
PCC will oxidize a primary alcohol to an _____________________.
answer
aldehyde
question
To oxidize a primary alcohol to an aldehyde, use ___________.
answer
PCC
question
To oxidize a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid, use _________________.
answer
Chromic Acid
question
Terminal alkyne + strong base (NaNH2) = _____________________
answer
acetylide ion
question
Acetylide + aldehyde/ketone + weak acid (pyridine) = __________________
answer
alcohol with triple bond
question
Reaction of cyanide with an aldehyde/ketone = ___________________
answer
cyanohydrin (alcohol with C triple bond N)
question
Acid catalyzed hydrolysis of cyanohydrin produces an _____________________________.
answer
alpha carboxylic acid
question
What are the two main hydrides used in reduction reactions
answer
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride
question
Which hydride is used to reduce aldehydes and ketones
answer
sodium borohydride
question
sodium borohydride reduces aldehydes to _________________ and ketones to __________________.
answer
primary alcohols, secondary alcohols
question
What is required following the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a hydride?
answer
acid work-up to protonate and create the alcohol
question
Catalytic addition of hydrogen with H2 to a cyanohydrin forms a ________________________.
answer
primary amine
question
What is the best way to make a terminal alkene
answer
Wittig Reaction
question
The Wittig reaction involved the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a _______________ _______________.

answer
phosphonium ylide
question
The Wittig reaction replaces the carbon oxygen double bond with a _______________, ________________ double bond.
answer
carbon carbon
question
Addition of water to an aldehyde or ketone, produces a ______________.
answer
Hydrate
question
What is a hydrate and what reagents are need to form it.
answer
Molecule with two -OH groups bonded to the same carbon. H2O and Acid - acid catalyzed
question
Acid Catalyzed reaction of aldehydes and ketones with alcohols forms a ____________________ after one addition and a ________________ after the second addition.
answer
hemiacetal, acetal
question
Using a 1,2-diol as a protecting group forms a ___________ membered ring and the use of 1,3-diol forms a ___________ membered ring.
answer
five, six
question
Reaction of aldehydes and ketones with a primary amine and trace acid produces an ___________________.
answer
Imine
question
In the formation of an imine, the carbon, oxygen double bond is replaced by a __________________, ____________________double bond.
answer
carbon, nitrogen
question
What reagents required for the synthesis of imine?
answer
1) aldehyde / ketone 2) primary amine (RNH2) 3) trace acid
question
An enamine is a ________________ amine with a ______________ bond in the alpha, beta position relative to the nitrogen.
answer
tertiary, double
question
In the formation of an enamine...After reacting an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine, ________________ is eliminated forming the tertiary amine.
answer
water
question
Integrated values on an NMR are reported in the _______________ form.
answer
reduced
question
The peak intensity changes/remains constant in a double of doublets.
answer
remains constant
question
What determines the reactivity of organometallics?
answer
The electronegativity of the metal. The more electronegative, the more reactive
question
Why are organolithiums more reactive than organocuprates?
answer
The Organolithium bond is more polar than the organocuprate bond.
question
When determining the number of signals in a compound with cyclohexane, keep in mind that the ring can _____________.
answer
ring flip
question
Which reducing agent is used to reduce carboxylic acids and esters
answer
Lithium aluminum hydride
question
What determines the ease in preparation of ylides?
answer
sterics and degree of substitution.
question
When an ylide reacts with an aldehyde or ketone, the P-C bond is ________________ and a ______________ double bond forms between the ______________ carbon and the carbon from the ylide.
answer
broken, new, carbonyl
question
How do you determine if hydrogens are homotopic. enantiotopic. or diastereotopic?
answer
Deuterium substitution
question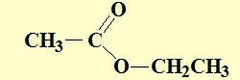
Steps for naming esters

answer
1) R group attached to carboxylic oxygen named first 2) followed by name of acid with "ic acid" replaced by "ate" ethyl ethanoate
question
___________________ agents convert alcohols to carbonyls
answer
oxidizing
question
PCC oxidizes primary alcohols to ___________________ and secondary alcohols to ________________?
answer
aldehydes, ketones
question
Chromic acid oxidizes secondary alcohols to _______________ and primary alcohols to ____________________?
answer
ketones, carboxylic acids
question
Wittig reactions form terminal __________________.
answer
alkenes
question
Retrosynthetic analysis of Wittig reagents favor the ________________ substituted alkyl halide.
answer
less
question
When a Grignard reacts with CO2, __________________ is produced.
answer
a carboxylic acid
question
Strong base add _____________________ without the aid of an ___________________ catalyst.
answer
irreversibly, acid
question
What are the strong bases
answer
1) Grignards 2) Organolithium 3) Hydrides 4) Wittig
question
When strong bases add to carbonyl carbons, they add 1,___ and acid is added in a ________________ step.
answer
2, separate
question
Weaker bases require the assistance of an acid _______________.
answer
catalyst
question
Reactivity within aldehydes and ketones is reliant on....
answer
Substituents. (Both hydrogen is most reactive, 2 large bulky substituents are least reactive)
question
If a carbonyl is in the presence of acid, the oxygen acts as a ________________ base and is more _______________.
answer
Lewis, electrophilic
question
The addition of an acid catalyst increases the ________________ of the reaction only.
answer
rate
question
Why is hydrate formation reversible?
answer
Water and alcohols are weaker nucleophiles
question
What conditions are required for hydrate formation and why?
answer
acidic to increase the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon
question
Protecting groups, protect ___________________ carbons from reactions that they otherwise would not survive.
answer
carbonyl
question
Grignards in the presence of an _______________ proton, will quench!
answer
acidic
question
When a nucleophile attacks an sp2 carbon, ______________ products can form.
answer
multiple/2
question
Conjugate addition is known as the _____________ product.
answer
thermodynamic
question
Direct addition is known as the _____________ product.
answer
kinetic
question
Enamines are similar to ___________, except that the carbonyl oxygen is replaced with NR2.
answer
enolates
question
The formation of enamines is _________________ catalyzed.
answer
acid
question
Why is water/acid added stepwise with grignards?
answer
Quench
question
What conditions are necessary when using PCC and why
answer
anhydrous to prevent further oxidation
question
Bleach oxidation turns secondary alcohols to ___________________ and primary alcohols to ___________________.
answer
ketones, aldehydes
question
In the reduction reaction with hydrides, the nucleophile is the _________________.
answer
hydride ion (H)
question
In a phosphonium ylide, the majority of electron density resides on which atom?
answer
carbon
question
Wittig reactions are preferred for making ___________________ alkenes.
answer
terminal
question
Alpha hydrogens are more acidic because the conjugate ________________ is more stable through _____________.
answer
base, resonance
question
Aldehydes an ketones are more acidic because in an ester, two pairs of protons __________________ for delocalization.
answer
compete
question
LDA will convert ________________ of a carbonyl compound to enolate ions.
answer
ALL
question
Halogenation of the alpha carbon uses what reagents?
answer
X2 and acid
question
Halogenation can be _________________ catalyzed or _________________ promoted.
answer
acid, base
question
In a base promoted halogenation, the base removes an alpha proton and _______________ alpha protons are replaced by the halogen.
answer
ALL
question
In an acid catalyzed halogenation, ______________ alpha proton is replaced.
answer
One
question
In a base promoted halogenation, the _______________ attacks the electrophilic halogen.
answer
enolate
question
Alpha carbon alkylation requires the removal of an alpha carbon with _______________.
answer
LDA
question
____________________is the required solvent for LDA.
answer
THF
question
The kinetic alkylation product is formed _________________ and uses LDA at -78.
answer
faster
question
The thermodynamic alkylation product can be formed using 0.95% _________________ and 0.05% __________________.
answer
LDA, NaOH
question
In an aldol addition, the alpha carbon of one aldehyde/ketone acts as the ________________, and attacks the ________________ carbon of another.
answer
nucleophile, carbonyl
question
The first step of an aldol addition is the removal of an alpha proton with a ________________.
answer
base
question
An alcohol in the 3 position indicates a _________________ addition.
answer
aldol
question
Dehydration of aldol addition forms _____________________________- aldehydes and ketones
answer
alpha, beta unsaturated
question
Aldol condensation requires
answer
heat and acid, or base and heat
question
In a crossed aldol, one of the reactants must have no _________________ protons.
answer
alpha
question
Aside from using one reactant without alpha protons, you can use _____________ and add the other slowly.
answer
LDA
question
To determine the starting material of an aldol addition, locate the new ___________-____________ bond (formed with the alpha carbon, and draw the two reactants.
answer
carbon carbon
question
To determine the starting material of an aldol condensation, convert the _____________-______________ unsaturated carbonyl to a _________________-hydroycarbonyl.
answer
alpha, beta, beta
question
When two ester molecules undergo condensation, the process is called a ____________ condensation.
answer
Claisen
question
The base used in a Claisen condensation is the same as the _________________________.
answer
leaving group
question
Carboxylic acids with a carbonyl group at the 3 position will undergo _________________________ in the presence of acid and heat.
answer
decarboxylation
question
Decarboxylation is easier under ______________ conditions
answer
acidic
question
The malonic ester synthesis combines the _______________ of an alpha carbon and the __________________ of a 3-oxocarboxylic acid.
answer
alkylation, decarboxylation
question
The product of the acetoacetic ester synthesis is a ______________ __________________.
answer
methyl ketone
question
Acyl chlorides can react with what to form what?
answer
1) alcohols to form esters 2) water to form carboxylic acids 3) amines to form amides
question
Acyl chloride reaction with amines to form amides require ___________ equivalents of the _______________.
answer
two, amine The first to attack and the second to deprotonate the intermediate
question
Esters can react with what to form what?
answer
1) water to form carboxylic acids 2) alcohol to form new ester 3) amine to form amide (1 equivalent)
question
Reaction of an ester with an amine must be in what environment and why.
answer
basic to avoid the protonation of the amine.
question
Ester hydrolysis is an _______________ catalyzed process which also has protonation of the leaving group.
answer
acid
question
How does an acid catalyst increase the rate of ester hydrolysis?
answer
Increases formation of intermediate by protonating the carbonyl oxygen and increases the leaving ability of the LG by protonating it.
question
In the reaction of an ester with an alcohol, excess ______________ is required.
answer
alcohol
question
Carboxylic acids react with what to form what?
answer
1) alcohols to form esters
question
Amides DO NOT react with...
answer
halides, alcohols, or water
question
Amides will react with water and alcohol under ______________ conditions
answer
acidic / heat
question
An amide will react with acid and heat will form a
answer
carboxylic acid
question
An alkyl halide can react with _______________ to form a nitrile which is then converted to a ______________ ________________.
answer
cyanide, carboxylic acid
question
An acid anhydride reacts with water to form two equivalents of a ____________________ __________________.
answer
carboxylic acid
question
Esters and Acyl chlorides undergo _______________ successive reactions to form _________________ ________________.
answer
two, tertiary alcohols
question
Acyl chlorides undergo __________________ successive reactions with hydrides to form a ___________________ alcohol.
answer
two, primary
question
An ester can be reduced to an aldehyde only by using ___________________ at _________________ Celsius.
answer
DIBALH, -78
question
A Michael reaction involves the attack of an ___________________ on a ________________ carbon of an a,b-unsaturated ketone.
answer
enolate, beta
question
Michael reactions form ________________ diketones.
answer
1,5
question
Enolates are ____________ bases and therefore add _________,_________.
answer
weak, 1,4
question
The Robinson Annulation combines the _______________ addition and the _____________ reaction.
answer
Aldol, Michael
question
The product of a Robinson Annulation is a _________,___________-_____________________ ketone.
answer
a,b-unsaturated
question
Reaction of an aldehyde/ketone with a secondary amine forms a ________________.
answer
enamine
question
Enamines resemble and react the same as _______________.
answer
enolates
question
Aldehydes and ketones can be alkylated/acylated at the alpha carbon through an _______________ intermediate.
answer
enamine
question
Using an enamine allows formation of a ___________________ alkylated product without using LDA.
answer
monoalkylated
question
Enamine can also act as an enolate and attack the ________________ position of an a,b-unsaturated.
answer
beta
question
The Diels-Alder reaction is a _________,__________ addition reaction.
answer
1,4
question
A Diels-Alder reaction involves a conjugated _______________ and a ______________.
answer
diene, dienophile
question
The reactivity of a dienophile is increased if an electron ___________________ group is attached to one of its sp2 carbons.
answer
withdrawing
question
If the dienophile has two carbon carbon double bonds, _________________ successive reactions occur
answer
two
question
What are the five common electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions
answer
1) halogenations 2)nitration 3) sulfonation 4) Friedel-Crafts acylation 5) FC alkylation
question
The _____________ acidic the proton, the _____________ enolate is formed.
answer
more, more
question
Acid catalyzed ester hydrolysis produces a
answer
carboxylic acid
question
What is an enamine
answer
tertiary a,b-unsaturated amine
question
What reagents are used to remove the enamine protecting group?
answer
acid and water
question
In a Diels-Alder reaction, when the conjugated diene is in the locked s-cis cyclic position, the product is a _____________________ bicyclic compound.
answer
bridged
question
Which is formed faster, the endo or exo product in a diels alder?
answer
Endo is formed faster when the dienophile has a substituent with pi electrons.
question
What reagents are required to activate the electrophile for bromination
answer
Br2 + FeBr3
question
What reagents are required to activate the electrophile in nitration
answer
HNO3 + H2SO4
question
What is the electrophile in nitration reactions
answer
NO2+ (nitronium ion)
question
What reagents are required to activate the electrophile for sulfonation
answer
H2SO4+ and heat
question
What is the electrophile in sulfonation reations
answer
SO3H+ (sulfonium ion)
question
FC acylation does what to a benzene ring
answer
places an acyl group on it
question
What is the electrophile in a FC acylation
answer
acylium ion (R-C+=O)
question
How is the electrophile for FC acylation activated?
answer
an acyl chloride (Cl) attacks the Al of AlCl3 and the Cl is then eliminated.
question
What happens to primary carbocations?
answer
they rearrange
question
How can a benzene substituted with a straight-chain alkyl group be formed?
answer
Through acylation reduction
question
What are the three different sets of reagents used to reduce a carbonyl to a methylene group?
answer
1) H2 / Pd C 2) Zn(Hg), HCl, heat - acidic 3) H2NNH2, OH-, heat - basic
question
Which reducing reagents can reduce all carbonyl compounds
answer
Clemmensen and Wolff-Kishner
question
What are the reagents in the Clemmensen reduction
answer
Zn(Hg), HCl, heat - acidic
question
What are the reagents in the Wolff-Kishner reduction?
answer
H2NNH2, OH-, heat - basic
question
What is the stipulation to use H2 / Pd,C
answer
Only a ketone carbonyl adjacent to a benzene ring can be reduced
question
What is the slow step of EAS?
answer
addition of the electrophile to the nucleophilic aromatic ring
question
What will increase the rate of the slow step (addition of electrophile) of EAS?
answer
A substituent that makes benzene a better nucleophile (electron donating)
question
The transition state of EAS resembles what?
answer
the carbocation intermediate
question
What are moderately activating substituents?
answer
Can donate electrons in two directions. To the ring and away.
question
What are moderately deactivating substituents?
answer
Carbonyl group attached to ring.
question
What are strongly deactivating substituents?
answer
positive charge attached to ring
question
What are strongly activating substituents?
answer
Donate electrons to ring only - OR attached
question
What are halogen substituents?
answer
weakly deactivating
question
All activating and weakly deactivating direct...
answer
ortho and para
question
All substituents with a positive or partial positive attached to the ring direct _________________.
answer
meta
question
The mirror image of a D-sugar is a ________ sugar
answer
L
question
What are epimers?
answer
Diastereomers that differ in configuration at only one asymmetric center
question
Groups on the Left in a Fisher are ____________ in a Haworth.
answer
up
question
Groups that are Right on the Fisher are ___________ in a Haworth.
answer
down
question
Two sugars that differ in configuration only at the carbon that was the carbonyl carbon in the open chain form are called ______________.
answer
anomers
question
In the alpha anomer, the -OH group is ____________.
answer
down (trans to the primary alcohol)
question
In the beta anomer, the -OH group is ____________.
answer
up (cis to the primary alcohol)
question
In the Fisher projection, R equals ___________ and S equals __________.
answer
D, L
question
To draw the Haworth, lay the Fisher down on its _________________ side.
answer
right
question
The -OH on the number ____________ carbon attacks the carbonyl carbon.
answer
five
question
The acetal of a sugar is called a ______________.
answer
glycoside
question
The bond between the anomeric carbon and the alkoxy oxygen is a ________________ bond.
answer
glycosidic
question
Acetals are _____________________ sugars.
answer
non reducing
question
Grignards do not react with ______________ or _______________.
answer
carboxylic acids, amides
question
When you see an alcohol with 2 identical groups, think __________________.
answer
Grignard
question
What reagents synthesize an alcohol to an alkyl chloride?
answer
Thionyl chloride.
question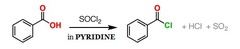
What reagents synthesize an acid chloride from a carboxylic acid?

answer
Thionyl chloride in pyridine.
question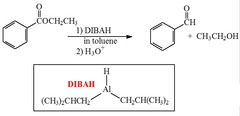
What reagent(s) will reduce an ester to an aldehyde?

answer
Di-Isobutyl Aluminum Hydride (DIBAH)
question
What reagents converts a ketone to an enolate? What is it used for?
answer
With an enolate, an alkyl substituent group can be added. LDA will alkylate on the less-hindered side of C=O.
question
What is decarboxylation?
answer
Decarboxylation is the loss of CO2.
question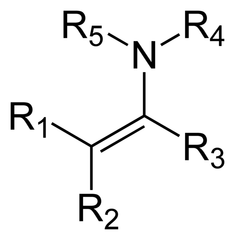
What is an enamine?

answer
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine.
question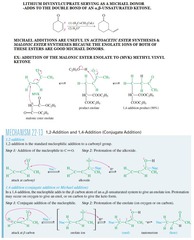
What is the "Michael Reaction" and draw the mechanism.

answer
The "Michael Reaction" or "Michael addition," is the nucleophilic addition of a carbanion or another nucleophile to an ?,? unsaturated carbonyl compound. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions.
question
What is the claisen condensation? Draw a mechanism.
answer
A claisen condensation is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a ?-keto ester or a ?-diketone.
question
*ALKENE REACTIONS*
answer
*ALKENE REACTIONS*
question
Hydration: Reagants
answer
Strong Acid, H20
question
Hydration: Products
answer
Alcohol (Regioselective: Markovnikof)
question
Oxymercuration/Demercuration: Reagents
answer
1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O 2. NaBh4, NaOH
question
Oxymercuration/Demercuration: Products
answer
Alcohol (Regioselective: Markovnikof)
question
Addition of a Hydrogen Halide: Reagents
answer
H-X
question
Addition of a Hydrogen Halide: Products
answer
Alkyl Halide (Regioselective: Markovnikof)
question
Hydrogenation: Reagents
answer
H2, Pt
question
Hydrogenation: Products
answer
Alkane (Stereospecific: Syn)
question
Cyclopropanation: Reagents
answer
Carbene
question
Cyclopropanation: Products
answer
Cyclopropane (Stereospecific: Syn)
question
Epoxidation: Reagents
answer
mCPBA
question
Epoxidation: Products
answer
Epoxide (Stereospecific: Syn)
question
Acid-Catalzyed Epoxide Ring Opening: Reagents
answer
H30
question
Acid-Catalzyed Epoxide Ring Opening: Products
answer
Diol (Stereospecific: Anti) (A diol contains two hydroxyl groups)
question
Syn-Dihydroxylation: Reagents
answer
OsO4, H2O2
question
Syn-Dihydroxylation: Products
answer
Diol (Stereospecific: syn)
question
Formation of a Halohydrin: Reagents
answer
X2, H2O
question
Formation of a Halohydrin: Products
answer
Halohydrin ( functional group in which a halogen and a hydroxyl are bonded to adjacent carbon atoms) (Stereospecific: Anti) (Regioselective: Mark addition of -OH)
question
Addition of X2: Reagents
answer
X2
question
Addition of X2: Products
answer
Vicinal Dihalde (Stereospecific: Anti)
question
Addition of HBr and Peroxides: Reagents
answer
HBr, H2O2
question
Addition of HBr and Peroxides: Products
answer
Alkyl Bromide (Regioselective: Anti-Mark)
question
Hydroboration/Oxidation: Reagents
answer
BH3,THF
question
Hydroboration/Oxidation: Products
answer
Alcohol Stereospecific: Syn) (Regioselective: Anti-Mark)
question
Oxidative Cleavage: Reagents
answer
KMnO4, Base
question
Oxidative Cleavage: Products
answer
Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
question
Ozonolysis, Reductive: Reagents
answer
O3, Me2S
question
Ozonolysis, Reductive: Products
answer
Ketones and Aldehydes
question
Ozonolysis, Oxidative: Reagents
answer
H2O2, AcOH
question
Ozonolysis, Oxidative: Products
answer
Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
question
Grignard: Reagents
answer
a. Mg, Ether b. Carbonyl c. strong acid *OR* a. LI Alkane, Ether b. Carbonyl c. strong acid
question
Grignard: Products
answer
Alcohol (Regioselective: Reagent adds to the Carbonyl)
question
*ALKYNE REACTIONS*
answer
*ALKYNE REACTIONS*
question
Synthesis of Dihalides: Reagents
answer
NaOH, 200C *OR* NaNH3, H20
question
Synthesis of Dihalides: Products
answer
Alkyne
question
Acetylide Anion: Reagents
answer
Strong Nucleophile, H20
question
Acetylide Anion: Products
answer
Alcohol
question
Oxidation of an Internal Alkyne: Reagents
answer
KMnO4, H2O
question
Oxidation of an Internal Alkyne: Products
answer
Dicarbonyl
question
Oxidation of an Terminal Alkyne: Reagents
answer
KMnO4, H2O
question
Oxidation of an Terminal Alkyne: Products
answer
Carboxylic Acid with adjacent Ketone
question
Hydrogenation (Alkyne): Reagents
answer
H2, Pd
question
Hydrogenation (Alkyne): Products
answer
Cis Alkene (Stereospecific: Syn)
question
Dissolving Metal Reduction: Reagents
answer
Na(s), NH3, low temp
question
Dissolving Metal Reduction: Products
answer
Trans Alkene (Stereospecific: Anti)
question
Ozonolysis: Reagents
answer
O3, H2O
question
Ozonolysis: Products
answer
Carboxylic Acids
question
Addition of HBr with Peroxides: Reagents
answer
HBr, H2O2
question
Addition of HBr with Peroxides: Products
answer
Vinyl Bromide (Regioselective: Mark)
question
Addition of X2 (Alkyne): Reagents
answer
X2, CH2Cl2
question
Addition of X2 (Alkyne): Products
answer
Dohalide/Tetrahalide (Stereospecific: Anti)
question
Addition of HX: Reagents
answer
HX, Ch2Cl2
question
Addition of HX: Products
answer
Dihalide/Tetrahalide (Regioselective: Mark)
question
Hydration (Alkyne): Reagents
answer
HgSO4, H2SO4
question
Hydration (Alkyne): Products
answer
Ketone (Regioselective: Mark)
question
Hydroboration/Oxidaton: Reagents
answer
SiaBH, H20, Strong Base
question
Hydroboration/Oxidaton: Products
answer
Aldehyde (Regioselective: Anti-Mark)



