NURS 141 Unit 4-Nursing Process – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is nursing process?
answer
A framework that provides an organized systematic approach to nursing care, thereby improving the probability of positive outcomes for individuals and groups.
question
In your own words, define nursing process.
answer
Critical thinking process that nurses use to apply the best available evidence to caregiving and promoting human functions and responses to health and illness. It is the fundamental blueprint for how to care for patients.
question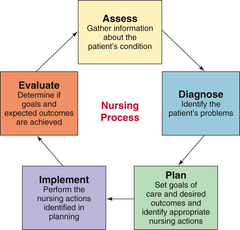
What are the 5 steps of nursing process?

answer
The five steps of the nursing process are assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation and evaluation.
question
Nursing Assessment
answer
1. Collection of information from a primary source (the patient) and secondary sources (e.g., family members, health professionals, and medical record.) 2. The interpretations and validation of data to ensure a complete database.
question
Nursing Diagnosis
answer
A clinical judgement about individual, family or community responses to actual and potential health problems or life processes that the nurse is licensed and competent to treat.
question
Planning
answer
Involves setting priorities, identifying patient-centered goals and expected outcomes and prescribing individualized nursing interventions. Ultimately during implementation your interventions resolve the patient's problems and achieve the expected goals and outcomes.
question
Nursing Implementation
answer
Formally begins after a plan of care is developed. The nurse initiates interventions that are designed to achieve the goals and expected outcomes needed to support or improve the patient's health status.
question
Nursing Evaluation
answer
Determines whether, after application of the nursing process, the patient's condition or well-being improves.
question
Nursing Intervention
answer
Any treatment based on clinical judgement and knowledge that a nurse performs to enhance patient outcomes.
question
Why do nurses need to understand nursing process?
answer
Clearly defining your patient's problems provides the basis for planning and implementing nursing interventions and evaluating the outcomes of care.
question
Why should you learn to "do" nursing process?
answer
-Complexity -Organization -Delegation -Coordination -State law mandate
question
What does the acronym NANDA mean?
answer
North American Nursing Diagnosis Association
question
What does NANDA do?
answer
Works on a classification system for computerization. Members DO NOT develop nursing diagnoses. But do research/review and work to approve them. Clinical nurses submit diagnoses to NANDA for approval.
question
Sources of data for Assessment
answer
-Patient ALWAYS primary source -Family/Significant Other -Charts and Records -Other Health Care Providers -Other records and Scientific Literature -Nurses Experience
question
How are assessments done?
answer
-Through use of all senses -Interviewing/Interactions -Observations -Physical Examination: Inspection, auscultation, palpation, percussion.
question
Who is responsible for assessments?
answer
The nurse and the patient
question
Subjective data
answer
It is your pt verbal descriptions of their health problems; only pt can provide; data usually include feelings,perceptions, and self-report of symptoms. Not measurable. e.g. nausea, pain, hungry, worry about pain affecting life.
question
Objective data
answer
are observational or measurements of a pt health status; what you observe by inspecting, percussing, palpating, and auscultating during physical examination; measurement based on accepted standard of Fahrenheit/Celsius, inches/cm, or known characteristics of behaviors (fear,anxiety). e.g.inspecting condition of surgical incision or wound, describing an observed behavior, measuring BP, vomiting
question
Examples of subjective data
answer
I feel sick to my stomach I have a stabbing pain in my side He said "I ate all my breakfast"
question
Examples of objective data
answer
Red rash on right arm You saw him eat all of his breakfast Urinated 150 ml clear yellow urine
question
What types of data do you want to validate? And why?
answer
Measurable and Observable All healthcare diagnoses,decisions, and treatments are based on data you gather during assessment so you need to be factual and complete with what you gather. The more accurate and thorough you are with your gathering, the better you will be able to help the pt.
question
How do you validate data?
answer
1. recheck data/information 2. look for factors (has this happened before physiological, emotional etc.) that may be present 3. ask someone else if they see or hear what we are seeing 4. compare subjective/objective data 5. clarify
question
Cue
answer
Info obtained through more than one sense; information gathered by using the senses eg odors, crying, coughing, etc.
question
Inference
answer
interpretation or judgement of the cues (ex:smell of urine = incontinence, crying = fear/sadness, coughing = cold/smoker)
question
Example of cue & inference
answer
cue: i'm worried about my bowels. inference: Tony may be constipated.
question
Gordon's Functional Health Patterns
answer
1. Health Perception-Health Management Pattern 2. Nutritional-Metabolic Pattern 3. Elimination Pattern 4. Activity-Exercise Pattern 5. Sleep-Rest Pattern 6. Cognitive-Perceptual Pattern 7. Self-Perception-Self Concept Pattern 8. Role-Relationship Patterns 9. Sexuality-Reproductive Pattern 10. Coping-Stress Tolerance Patterns 11. Value-Belief Pattern
question
Critical thinking skills
answer
1. Interpretation 2. Analysis 3. Inference 4. Evaluation 5. Explanation 6. Self-regulation
question
Interpretation
answer
Be orderly in data collection. Look for patterns to categorize data. Clarify any data you are uncertain about.
question
Analysis
answer
Be open-minded as you look at information about a patient. do not make careless assumptions. Does the data reveal what you belief is true, or are there other options?
question
Inference
answer
Look at the meaning and significance of findings. Are there relationship between findings? Does the data abut the patient help you see that a problem exists?
question
Evaluation
answer
Look at all situations objectively. Use criteria (e.g., expected outcomes, pain characteristics, learning objectives.) to determine results of nursing actions. Reflect on your own behavior.
question
Explanation
answer
Support your findings and conclusions. Us knowledge and experience to choose strategies to use in the care of patients.
question
Self regulation
answer
Reflect on your own experiences. Identify the ways you can improve your own performance. What will make you belief that you have been successful?
question
Concepts for a critical thinker
answer
1. Truth seeking 2. Open-mindedness 3. Analyticity 4. Systematicity 5. Self-confidence 6. Inquisitiveness 7. Maturity
question
Truth seeking
answer
Seek the true meaning f a situation. Be courageous, honest and objective about asking questions.
question
Open-mindedness
answer
Be tolerant of different views, be sensitive to the possibility of your own prejudices, respect the right of others to have different opinions.
question
Analyticity
answer
Analyze potentially problematic situations; anticipate possible results or consequences; value reason; use evidence-based knowledge.
question
Systematicity
answer
Be organized, focused; work hard in any inquiry.
question
Self-confidence
answer
Trust in your own reasoning processes.
question
Inquisitiveness
answer
Be eager to acquire knowledge and learn explanations even when applications of the knowledge are not immediately clear. Value learning for learning's sake.
question
Maturity
answer
Multiple solutions are acceptable. Reflect on your own judgements; have cognitive maturity.
question
Open-Ended Questions
answer
Prompts patients to describe a situation in more than one or two words.
question
Back channeling
answer
Encourages the patient to give more details by using active listening prompts such as "all right," "go on," or "uh-huh."
question
Probing
answer
Encourage a full description without trying to control the direction the story takes. Use further open-ended statements.
question
Closed-ended questions
answer
Limit answers to one or two words such as yes or no.
question
Examples of open ended questions
answer
1. Tell me how you are feeling 2. Tell me how your health has been. 3. Describe how your wife has been helping you. 4. Give me an example of how you get relief from your pain at home.
question
Examples of closed ended questions
answer
1. Do you think the medication is helping you? 2. Who helps you at home? 3. Do you understand why you are having the x-ray examination? 4. Are you having pain now? 5. On a scale of 0 to 10, how would you rate your pain?
question
Evidence-based knowledge
answer
Knowledge based on research or clinical expertise.
question
Levels of critical thinking
answer
Level 1: Basic Level 2: Complex Level 3: Commitment
question
Components of critical thinking
answer
Specific Knowledge base Experience Competencies Attitudes Standards
question
Scientific Method
answer
1. Identifying the problem 2. Collecting data 3. Formulating a question or hypothesis 4. Testing the question or hypothesis 5. Evaluating results of the test or study
question
Effective problem solving
answer
Involves evaluating the solution over time to make sure that it is effective. It becomes necessary to try different options if a problem recurs.
question
Decision making
answer
Is a product of critical thinking that focuses on problem resolution.
question
Diagnostic reasoning
answer
It is the analytical process for determining a patient's health problems.
question
Clinical decision making
answer
Is a problem-solving activity that focuses on defining a problem and selecting an appropriate action. Requires careful reasoning (i.e., choosing the options for the best patient outcomes on the basis of the patient's condition and the priority of the problem).
question
Critical thinking attitudes and applications in nursing practice
answer
1. Confidence 2. Thinking Independently 3. Fairness 4. Responsibility and authority 5. Risk taking 6. Discipline 7. Perseverance 8. Creativity 9. Curiosity 10. Integrity 11. Humility
question
Concept map
answer
A visual representation of patient problems and interventions that shows their relationships to one another. The primary purpose of concept mapping is to better synthesize relevant data about a patient, including assessment data, nursing diagnosis, health needs, nursing interventions, and evaluation measures.
question
How does Concept Mapping 'fit in' with nursing diagnoses?
answer
-It is a technique that can help organize data analysis. -It uses diagrams to demonstrate the relationship of one concept or piece of information to other concepts pieces of information -Its a visual representation of patient problems and interventions that shows their relationship to one another (P&P p.202)
question
Nursing health history
answer
The history is a major component of assessment. Most health history forms are structured. However, based on information you gained from your patient's story (during the patient-centered interview) , you learn which components of the history to explore fully and which require less detail.
question
Components of a patient's health history
answer
1. Physical & Developmental 2. Intellectual 3. Spiritual 4. Social 5. Emotional
question
Physical & Developmental
answer
-Perception of health status -Past health problems and therapies -Present health therapies -Risk factors -Activity and coordination -Review of systems -Developmental stage -Effect of health status on developmental stage -Members of household marital problems -Growth and maturation -Occupation -Ability to complete activities of daily living (ADL's)
question
Intellectual
answer
-Intellectual performance -Problem Solving -Educational level -Communication patterns -Attention span -Long-term and recent memory
question
Spiritual
answer
-Beliefs and meaning -Religious experiences -Rituals and practices -Fellowship -Courage
question
Social
answer
-Financial status -Recreational activities -Primary language -Cultural heritage -Community resources -Environmental risk factors -Social relationships -Family structure and support
question
Emotional
answer
-Behavioral and emotional status -Support systems -Self-concept -Body image -Mood -Sexuality -Coping mechanisms
question
Concomitant symptoms
answer
Does the patient experience other symptoms along with the primary symptom? For example, does nausea accompany pain?
question
Review of systems (ROS)
answer
A systematic approach for collecting the patient's self-reported data on all body systems.
question
What does clustering data mean?
answer
A set of signs or symptoms gathered during assessment that you group together in a logical way.
question
How is clustering used when identifying a nursing diagnosis?
answer
Data clusters are patterns of data that contain defining characteristics, the clinical criteria that are observable and verifiable. Each clinical criterion is an objective or subjective sign, symptom or risk factor that when analyzed with other criteria, leads to a diagnostic conclusion.
question
What does nursing diagnosis mean?
answer
A clinical judgement about individual, family or community responses to actual or potential health processes/life processes, It is the basis for selection of nursing interventions
question
Differentiate a medical diagnosis from a nursing diagnosis
answer
Medical Dx is the identification of a disease condition based on a specific evaluation of physical signs, symptoms, the patient's medical history and results of diagnostic tests and procedures. Medical Dx is of disease. Nursing Dx is of the human response. Nursing diagnosis involves the patient in dx process, medical does not.
question
Components of a nursing diagnosis
answer
1. Diagnostic label 2. Related factors (etiology)
question
PES
answer
1. P-Problem--NANDA label 2. E-Etiology or related factor 3. S-Symptoms or defining characteristics
question
What are the parts of an actual nursing diagnostic statement? (PES)
answer
NANDA-I label, the related factor, the defining characteristics Example: Impaired physical mobility r/t incisional pain, AEB restricted turning and positioning.
question
Discuss the rationale for having consistent terminology (NANDA) for nursing diagnoses
answer
Before using a classification system of diagnoses, nurses/HC providers would use a variety of terms to describe/document the same condition or symptoms. A classification system prevents conditions from going undiagnosed. Before 1972 (when the first conference of nursing diagnoses was held) nurses lacked the terms to described problems (outside of medical diagnoses) and also lacked the assessment questions to uncover such problems.
question
Collaborative problem
answer
An actual or potential physiological complication that nurses monitor to detect the onset of changes in a patient's status. When collaborative problems develop, nurses intervene in collaboration with personnel from other health care disciplines.
question
Defining characteristics
answer
The clinical criteria that are observable and verifiable. Supports the diagnostic judgement.
question
Related factor
answer
A condition, historical factor, or etiology that gives a context for the defining characteristics and shows a type of relationship the the nursing diagnostics and shows a type of relationship with the nursing diagnosis.
question
Actual nursing diagnosis
answer
Describes human responses to health conditions or life processes that exist in an individual, family, or community
question
Risk nursing diagnosis
answer
Describes human responses to health conditions or life processes that may develop in a vulnerable individual, family or community. These diagnoses do not have related factors or defining characteristics because they have not occurred yet.
question
Etiology
answer
or related factor of a nursing diagnosis is always within the domain of nursing practice and a condition that responds to nursing interventions.
question
How does judgement impact the diagnostic statement?
answer
We need to make professional rather than prejudicial judgements. By adding in personal beliefs/values and not focusing on the objective/subjective data you could make errors in Dx.
question
How can 'nursing judgment' potentially 'interfere' with an accurate nursing diagnosis?
answer
When there is an error in nsg Dx the interventions you plan according to the incorrect Dx will not help solve/relieve what ever the true issues are and the pt will not get better etc.
question
What are defining characteristics in Carpenito.
answer
signs and symptoms, when seen together represent a diagnosis. The major characteristic are evident in this diagnosis with a frequency score of 80-100%. Minor characteristics provide evidence but may not be present. signs (ob) & symptoms (sub) - defining characteristics must be present.
question
What is a primary nursing diagnosis?
answer
Are those nursing diagnoses or collaborative problems when not managed right away will deter progress to achieve outcomes or will negatively affect functional status.
question
What is a secondary nursing diagnosis?
answer
Are those diagnoses or collaborative problems for which treatment can be delayed without compromising present functional status.
question
When patients have multiple nursing diagnoses, how do we decide which is the most essential or primary?
answer
With multiple diagnoses, the nurse needs to establish a priority set of diagnoses to be able to direct resources toward goal achievement. Priority diagnoses are those which affect functional status if not managed immediately.
question
Priority setting
answer
The ordering of nursing diagnoses or patient problems using determinations of urgency and/or importance to establish a preferential order for nursing actions.
question
How is an outcome different/similar to a goal?
answer
A goal is a broad statement that describes a desired change in a patient's condition or behavior. An expected outcome is a measurable criterion to evaluate goal achievement.
question
What is an outcome?
answer
Condition of a patient at the end of treatment, including the degree of wellness and the need for continuing care, medication, support, counseling or education.
question
What needs to be considered when writing an outcome?
answer
1. Patient Centered--Write a goal or outcome to reflect a patient's specific behavior, not to reflect your goals or interventions. 2. Singular Goal or Outcome--Each goal and outcome should address only one behavior or response. 3. Observable--Observable changes occur in physiological findings and in the patient's knowledge, perceptions and behavior. 4. Measurable--You learn to write goals and expected outcomes that set standards against which to measure the patients response to nursing care. Terms describing quality, quantity, frequency, length or weight allow you to evaluate outcomes precisely. 5. Time-Limited--when you expect the response to occur. It is very important to collaborate with patients to set realistic and reasonable time frames. 6. Mutual Factors--Mutually set goals and expected outcomes ensure that the patient and nurse agree on the direction and time limits of care. Mutual goal setting increases the patient's motivation and cooperation. 7. Realistic--Set goals and expected outcomes that a patient is able to reach based on your assessment.
question
Patient-centered goal
answer
Reflects a patient's highest possible level of wellness and independence in function. It is realistic and based on patient needs and resources.
question
Short-term goal
answer
An objective behavior or response that you expect a patient to achieve in a short time, usually less than a week. In an acute care setting you often set goals for over a course of just a few hours.
question
Long-term goal
answer
Is an objective behavior or response that you expect a patient to achieve over a longer period, usually over several days, weeks, or months.
question
Expected outcome
answer
A specific measurable change in a patient's status that you expect to occur in response to nursing care.
question
Nursing-sensitive patient outcome
answer
A measurable patient, family or community state, behavior, or perception largely influenced by and sensitive to nursing interventions.
question
Think about how you would incorporate the client's ethnicity, culture, and diversity into the plan of care.
answer
Take the following into consideration and plan accordingly: 1. Identified cultural affiliation 2. Health beliefs and values 3. Customary health practices 4. Spiritual beliefs and practices 5. Culturally specific social structures related to health care.
question
Identify examples how/when the patient is included in determining outcomes.
answer
For example a patient may have a goal of losing 20 pounds. You think the patient can do this in 6 months, but you ask the patient what they think they can do and then you can adjust the timed goal.
question
What are the three domains of planning care?
answer
1. Cognitive 2. Affective 3. Psychomotor
question
What is the focus for the affective domain?
answer
-attitudes -feelings -values
question
What is the focus for the cognitive domain?
answer
-acquires knowledge -intellectual skills
question
What is the focus for the psychomotor domain?
answer
-motor skills
question
Write an example of the affective domain
answer
patient will "express"
question
Write an example of the cognitive domain
answer
patient will "demonstrate"
question
Write an example of the psychomotor domain
answer
patient will "ambulate"
question
How would the "domain" impact our approach to selecting interventions?
answer
The intervention must match the domain. If the outcome states "patient will have a soft formed stool within 3 days", a psychomotor domain then the intervention must address the same domain. "cathartic will be administered daily for 3 days".
question
What does this statement mean? "Outcomes are driven by the nursing diagnosis and trigger planned interventions"
answer
The nursing diagnosis and the planned interventions will directly affect the success of a pt. outcome. After the nsg Dx is made you will decide which is the best way to approach/address and resolve by choosing the best intervention to achieve the outcome.
question
How do the outcomes suggest planned interventions?
answer
Once you have an outcome set you need to use critical thinking to chose the intervention that will have the greatest likelihood of success. Planned interventions are based off outcomes.
question
What are some of the factors present when deciding which interventions are needed/appropriate?
answer
1. Characteristics of the nursing diagnoses 2. Goals and expected outcomes 3. Evidence base (e.g. research or proven practice guidelines) for the interventions 4. Feasibility of the intervention 5. Acceptability to the patient 6. Your own competency As you select interventions, review your patient's needs, priorities, and previous experiences to select the interventions that have the best potential for achieving the expected outcomes.
question
What is a nursing order?
answer
Nursing orders or interventions comes directly from the nurse, are independent and do not require input from another health care professional. They are based on scientific evidence and usually relate to ADL's, health education and promotion, and counseling and are outlined in the legal scope of nursing in each state under the Nurse Practice Acts.
question
How does this relate to a medical order?
answer
Medical orders must be provided by a physician or other health care professional. The interventions are to treat or manage medical diagnosis. Nurses can carry out these orders, but cannot write them (unless the nurse is an advance practice nurse)
question
How do nursing orders relate to scope of practice?
answer
-Under the Nurses Practice Acts, a nurse cannot practice outside of their scope of practice, meaning the nurse must follow the statutes enacted by the legislature of the state and only perform tasks for which they are trained in. -Nursing orders must follow under the same guidelines in that a nurse cannot follow an order that is not in their field or prescribe/mandate an order to be done for which they are not trained in. -The nurse can coordinate the care but cannot prescribe care outside of their scope of practice (Carp, p.43) -Nursing orders contain Date, direct verb, what, when, how often, how long, where, and a signature (Carp, p.40)
question
Independent nursing interventions
answer
Actions that a nurse initiates. These do not require an order from another health care provider.
question
Dependent nursing interventions
answer
Actions that require an order from a physician or another health care professional. The interventions are based on the physician's or health care provider's response to treat or manage a medical diagnosis.
question
Collaborative interventions
answer
or interdependent interventions, are therapies that require the combined knowledge, skill and expertise of multiple health care professionals.
question
NIC
answer
Nursing Intervention Classification
question
NOC
answer
Nursing Outcome Classification
question
Nursing Outcome Classifications (NOC)
answer
A comprehensive, standardized classification of patient/client outcomes developed to evaluate the effects of interventions provided by nurses or other health care professionals.
question
Nursing Intervention Classifications (NIC)
answer
A set of nursing interventions that provides a level of standardization to enhance communication of nursing care across all health care settings and to compare outcomes.
question
How do NIC and NOC relate to outcomes?
answer
Comprehensive, research-based, standardized classifications of nursing diagnoses, nursing interventions and nursing-sensitive patient outcomes. These classifications provide a set of terms to describe nursing judgments, treatments and nursing-sensitive patient outcomes.
question
Characteristics of the nursing diagnosis
answer
1. Interventions should alter the etiological (related to) factor or signs and symptoms associated with the diagnostic label. Ex. Acute pain related to incisional trauma: choose interventions that relieve swelling and strain on incision site (position and turning measures) and lower pain reception (analgesic). 2. When an etiological factor cannot change, direct the interventions toward treating the signs and symptoms (e.g., defining characteristics for a diagnosis) Ex. Deficient knowledge regarding surgical recovery related to inexperience--choose interventions directed toward providing information that answer patient's questions about recovery procedures and relieve anxiety. 3. For potential or high-risk diagnoses, direct interventions at altering or eliminating risk factors for diagnosis.
question
Choosing expected outcomes
answer
1. State outcomes in terms used to evaluate the effect of an intervention. This language assists in selecting the intervention. Ex. For the outcome "patient will preform urinary catheter care by discharge." the nurse will evaluate skills instruction by observing the patient perform catheter care. 2. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) is designed to show the link to Nursing Outcomes Classification (NOC). Use these reference in developing care plans.
question
Nursing care plan
answer
Includes nursing diagnoses, goals and/or expected outcomes, specific nursing interventions and a section for evaluation findings so any nurse is able to quickly identify a patient's clinical needs and situation.
question
Interdisciplinary care plans
answer
Include contributions from all disciplines involved in patient care.
question
Direct care interventions
answer
Treatments performed through interaction with patients. For example a patient receives counseling during a time of grief.
question
Indirect care interventions
answer
Treatments performed away from the patient but on behalf of the patient or group of patients. Ex. Actions for managing the patients environment, documentation, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
question
IADL
answer
Instrumental activities of daily living
question
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL's)
answer
Include skills such as shopping, preparing meals, house cleaning, writing checks, and taking medications.
question
How are the following terms related: Intervention, implementation, nursing care, and nursing order.
answer
Intervention: is an treatment based on clinical judgment and knowledge that a nurse performs to enhance patient outcomes. Implementation: is the fourth step of the nursing process, beginning after the nurse develops a plan of care. Interventions are part of the implementation process. Nursing Care: how nursing interventions are delivered. Nursing Orders: are the specific interventions that the nurse has written.
question
Who determines who will implement the plan of care?
answer
The nurse and the patient. Plan of care is a collaborative process.
question
Nursing-sensitive outcome
answer
A measurable patient or family state, behavior, or perception largely influenced by and sensitive to nursing interventions. The interventions must be within the scope of nursing practice and integral to the processes of nursing care.
question
Evaluative measures
answer
Assessment skills and techniques (e.g., observations, physiological measurements, patient interview) In fact, evaluation measures are the same as assessment measures, but you perform them at the point of care when you make decisions about the patients status and progress.
question
To objectively evaluate the degree of success in achieving outcomes of care, perform the following steps:
answer
1. Examine the outcome criteria to identify the exact desired patient behavior or response. 2. Evaluate the patient's actual behavior or response. 3. Compare the established outcome criteria with the actual behavior or response. 4. Judge the degree of agreement between outcome criteria and the actual behavior or response. 5. If there is no agreement (or only partial agreement) between the outcome criteria and the actual behavior or response, what is/are the barrier(s)? Why did they not agree?
question
standard of care
answer
The minimum level of care accepted to ensure high quality of care to patients.
question
What can be delegated?
answer
Tasks that need to be done but not the pt in entirety. e.g. asking fellow staff to obtain a sample while you attend to a pt pain medication-accomplishes two tasks for pt, more efficient.* promotes job enrichment and teamwork, improved quality of pt care, increased productivity.
question
How is this determined?
answer
Care is delegated based on assessment findings and priority setting. Must know which skills you are able to delegate (Nurse Practice Act)
question
Who is responsible for delegation?
answer
The RN is in most situations but it is not uncommon for a LPN to delegate in LTC settings.
question
How does delegation fit in with scope of practice?
answer
You can not delegate outside scope of practice. You need to know what tasks can be delegated to you and what tasks you,as a nurse, can delegate to CNAs and other nurses.
question
Discuss how implementation is impacted by "available resources"... patient and/or agency?
answer
Before implementing an intervention, it must be determined what resources are needed and if they are available. Resources can include equipment, personnel, and environment. -If equipment is required, determine if it's safe and working properly. Place supplies in convenient location and always keep extras on stock and only open if you need them (to control HC costs). -Personnel: Identify which care delivery model is being used (e.g, primary nurse or team nurse). As a nurse you are responsible for deciding whether to perform an intervention or to delegate it to another member of the nursing team. - Environment: Must be safe and conducive to implementing therapies. Pt safety is first concern. Prevent injuries by adapting environment to patient's sensory deficits, physical disabilities and altered level of consciousness. Practice using privacy to help patient relax, reduce distractions, provide adequate lighting. - Ensure patient is physically and psychologically comfortable to help patient cooperate and more fully participate in the implementation of the intervention. Consider the patient's level of endurance, plan only what can be tolerated comfortably. Be aware of the patient's psychosocial needs to help create a favorable emotional climate.
question
The five rights of delegation
answer
1. Right task-the right task is one that you delegate for a specific patient such as tasks that are repetitive, require little supervision, are relatively noninvasive, have results that are predictable, and have potential minimal risk. 2. Right Circumstances-Consider the appropriate patient setting, available resources and other relevant factors. In an cute care setting patients' conditions often change quickly. Use good clinical decision making to determine what to delegate. 3. Right Person-The right person is delegating the right tasks to the right person to be performed on the right person. 4. Right Direction/Communication-You give clear, concise description of the task, including its objective, limits and expectations. Communication needs to be ongoing between the registered nurse and the NAP during a shift of care. 5. Right Supervision/Evaluation--Provide appropriate monitoring, evaluation, intervention as needed, and feedback. NAP need to feel comfortable asking questions and seeking assistance.



