Neurology: 13 Muscle spindle, Golgi tendon organ and Reflexes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion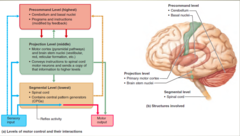
*Highest level* of the motor system?

answer
*Pre command* level
question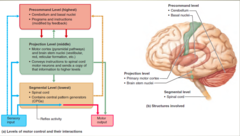
*Middle level* of the motor system?

answer
*Projection* level
question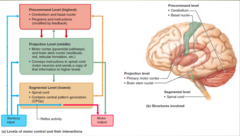
*Lowest level* of the motor system?

answer
*Segmental* level
question
What are the *functions* of the *precommand level*?
answer
Programs and instructions (modified by feedback)
question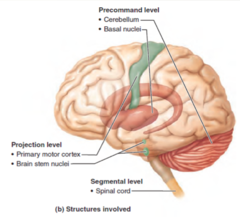
What are the *anatomical parts* of the *precommand level*?

answer
1. Cerebellum 2. Basal Nuclei
question
What are the *functions* of the *projectional level*?
answer
Conveys instructions to spinal cord motor neurons and sends a copy of that information to higher levels.
question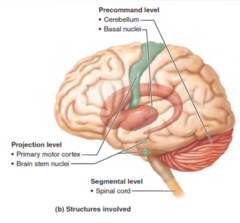
What are the *anatomical parts* of the *projectional level*?

answer
1. *Motor cortex* (pyramidal pathways) 2. *Brain stem nuclei* (vestibular, red, reticular formation
question
What are the *functions* of the *segmental level*?
answer
Contains central pattern generators (CPGs)
question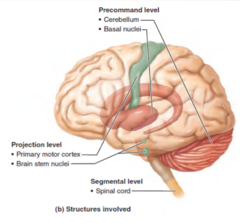
What are the *anatomical parts* of the *Segmental level*?

answer
spinal cord
question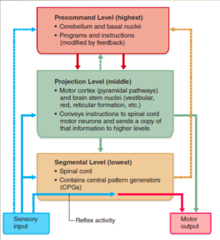
What three things *feedback* onto the precomand level?

answer
1. Sensory input 2. Projection level 3. Segmental level
question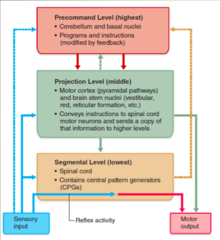
What two areas feed into *motor output*?

answer
1. Projection level 2. Segmental level
question
Function of *renshaw cells*?
answer
inhibitory interneurons found in the gray matter of the spinal cord. Inhibits itself
question
What levels have large ventral horns?
answer
C5-T1 and L2-S2
question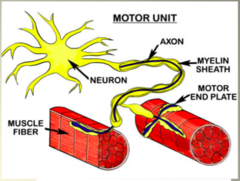
What is a *motor unit*?

answer
single motoneuron and the muscle fibers that it innervates.
question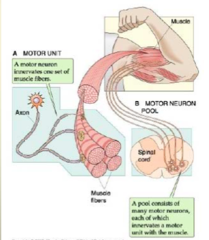
What is a *motoneuron pool*?

answer
a set of motoneurons inverting fibers within the same muscle
question
What are the two types of motoneurons?
answer
1. Alpha motoneurons 2. Gamma motoneurons
question
What do alpha motoneuron innervate?
answer
extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers
question
What do gamma motoneurons innervate?
answer
specialized intrafusal muscle fibers, (a component of the muscle spindles)
question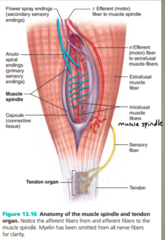
What are the proprioceptors in skeletal muscles?

answer
muscle spindles
question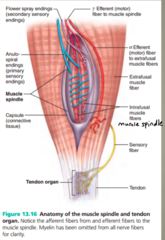
What do muscle spindles monitor?

answer
the length of skeletal muscles and participate in stretch reflexes
question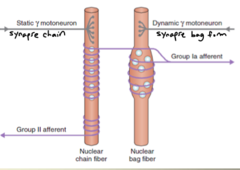
Intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles are of what two types?

answer
1. nuclear bag fibers 2. nuclear chin fibers
question
Both types of muscle spindles are present in every cell, but which one is more plentiful?
answer
*More nuclear chain fibers* then nuclear bag fibers
question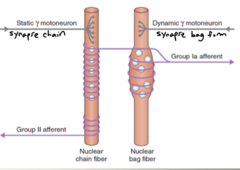
Nuclear bag fibers look like what?

answer
large, with nuclei accumulated in a central region
question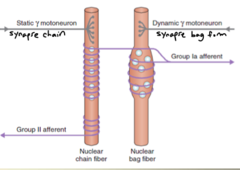
Nuclear chain fibers look like what?

answer
small, with nuclei arranged in rows
question
What innervates the central region of both the nuclear bag and chain fibers?
answer
A single group 1a afferent nerve and group II afferent nerves.
question
Group II afferent nerves are primarily on which muscle spindle?
answer
nuclear chain fibers
question
Motor innervations by gamma motoneurons have what two types?
answer
1. dynamic 2. static
question
*Dynamic* gamma motoneurons synapses where?
answer
on nuclear bag fibers in "plate endings"
question
*static* gamma motoneurons synapses where?
answer
on nuclear chain fibers in "trail ending" which spread over long distances
question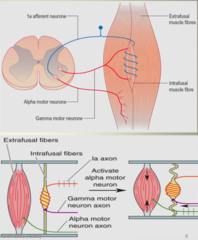
steps of muscle contraction in response to *muscle stretch*

answer
*Stretch of muscle --> stretch of muscle spindle* --> distortion of primary sensory endings at the center of intrafusal fiber --> action potential generation in 1a fibers --> stimulation of alpha-motor neurons in the spinal cord --> muscle contraction
question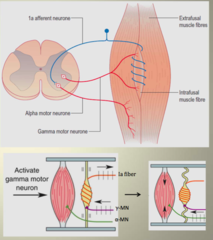
steps of muscle contraction in response *of gamma motor neurons*

answer
*activation of gamma-motor neurons --> contraction of ends of the spindle --> stretch of central part of muscle spindle* --> distortion of primary sensory endings at the center of intrafusal fiber --> action potential generation in 1a fibers --> stimulation of alpha-motor neurons in the spinal cord --> muscle contraction
question
gamma motor neurons are primarily influenced by what? and not by what?
answer
*descending fibers* NOT by primary sensory fibers
question
what is alpha-gamma motor coactivation?
answer
gamma motor discharge increases along with increased discharge of alpha motor neurons
question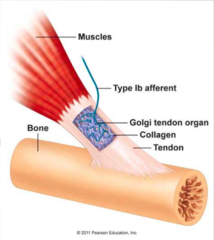
Golgi tendon organ (GTO) is what?

answer
specialized receptor that is located between the muscle and the tendon
question
Golgi tendon is made of what?
answer
capsule containing numerous collagen fibers, in series with the muscle
question
Golgi tendon is innervated by what fibers?
answer
primary afferents --> *Group Ib fibers* that are weaved between the collagen fibers
question
What is the golgi tendon organ reflex?
answer
muscle contracts shortening the extrafusal muscle fibers --> activating the golgi tendon organs --> group Ib afferent fibers synapse on inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord --> inhibiting alpha motoneuron (tension on tendon is reduced)
question
What is a reflex?
answer
a fast, involuntary, unplanned sequence of actions that occurs in response to a particular stimulus
question
when integration takes place in the spinal cord gray matter the reflex is what?
answer
a spinal reflex- stretch reflex example: patellar reflex
question
when integration takes place in the brain stem rather than the spinal cord it is what?
answer
a cranial reflex -- pupillary light reflex example: the tracking movements of the eyes as you read this
question
what autonomic (visceral) reflexes?
answer
generally not consciously perceived; involves responses of smooth muscle, cardiac, and glands example: urination, digestion
question
what are somatic reflexes?
answer
most aware of the reflex example: contraction of skeletal muscles
question
what are the two groups of reflexes?
answer
1. monosynaptic reflex 2. polysynaptic reflex (two or more synapses)



