Neurological Assessment (TEST 3) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Why is a neurological assessment important?
answer
***An Intact, appropriately functioning nervous system is critical for all human endeavors, exerts unconscious control over basic body functions, such as respirations, temp, and movement coordination, and enables very complex interactions with people and the environment
question
What are the goals of a neurological assessment?
answer
Detection of change in neuro status, particularly acute and life-threatening alterations Localize pathology Make a medical diagnosis
question
Why do nurses perform neurological assessments?
answer
Actual and potential health problems r/t neuro dysfunction and the patient's response to the problems
question
Any SIGNIFICANT CHANGES in Neurological Status include?
answer
Acute change in mental status Change in LOC not explained by known cause (sedative, etc.) Seizure activity Flexor or Extensor posturing, either spontaneous or in response to noxious stimuli Change in size and decreased reactivity to light in one or both pupils. Normal 2-6mm Onset of eye deviation
question
What are some other SIGNIFICANT CHANGES?
answer
Progressing weakness or paralysis Changes in ability to identify sensation Significant changes in vital signs
question
What is included in the Abbreviated Acute Assessment?
answer
Rapid assessment of LOC Use of Glasgow coma scale as indicated (GCS) Pupillary reaction Gross assessment of motor strength Gross assessment of sensation Vital signs
question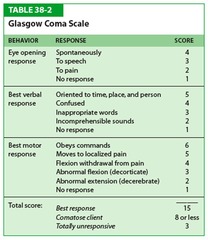
Glasgow coma scale

answer
GCS
question
What to ask in a neurologic health history?
answer
Headaches Head injury Dizziness/vertigo, seizures, tremors Weakness, coordination and gait, numbness or tingling Difficulty swallowing, speaking: expression or comprehension of speech/language Difficulty with concentration, memory, attention span Alteration in any of the senses Past history of stroke , spinal injury, meningitis, congenitial defect, alcoholism Environmental hazards: insecticides, organic solvents, lead, illegal drugs.
question
What are the history variations in infants and children?
answer
Prenatal History, Birth History, Respiratory Status at birth, Neonatal health, (Balance, seizures, developmental milestones, learning problems), Exposure to lead, Family History of Seizures and Muscular Dystrophy
question
Mother's health, medications taken, infections, exposure to rubella, CMV, toxemia, bleeding, history of trauma or stress, HTN, drug or alcohol use
answer
Prenatal Hx
question
Apgar scores, gestational age, birth weight, presentation, use of instruments, prolonged or precipitous labor, fetal distress
answer
Birth Hx
question
Supplemental oxygen, resuscitation, ventilation, cyanosis, continuous apnea
answer
Respiratory status at birth
question
infections, seizures, irritability, sucking & swallowing (poorly coordinated?)
answer
Neonatal Health
question
What are the history variations in an Aging Adult?
answer
Inability to perform ADLs Social withdrawal Pattern of increased stumbling or falling, change in gait Dizziness Memory changes, confusion Tremors Vision or hearing changes LOC Fecal or urinary incontinence Transient neurologic deficits (possibly TIAs)
question
How to Document Physical Appearance and Behavior
answer
Posture & Body movements Voluntary, deliberate, coordinated, smooth, even Dress, grooming and hygiene LOC Facial expression Symmetrical Speech Normal tone with moderate pace Mood and affect
question
How to Test Cognitive Abilities and Mentation
answer
Orientation Attention span Recent memory/Remote memory New learning ----4 unrelated words test (Fun, carrot, ankle, loyalty) ----Recall at 5, 10, 30 minute intervals Aphasia ----Word comprehension, reading, writing
question
Can copy simple drawings of objects
answer
Spatial Perception
question
Proverb interpretation/Abstract reasoning Calculation
answer
Higher intellectual functions
question
Assess long-term goals Unrealistic or impulse decisions
answer
Judgement
question
How to document Thought Processes and Perceptions
answer
Thought processes Logical, illogical, unrealistic Thought content Consistent and logical Perceptions Aware of reality, illusions, hallucinations Suicidal Ideations
question
Neuro exam should be done when the infant is in a?
answer
quiet, alert state
question
What to observe in infants?
answer
Observe spontaneous activity for symmetry and smoothness of movement
question
How to test sensory integrity in infants?
answer
All limbs to painful stimuli
question
How to test deep tendon reflexes in infants?
answer
Babinski reflex---normal until 16 to 24 months
question
What are the history variations in Children?
answer
Denver II Developmental test, measures fine & gross motor, language and personal-social skills Observe play for gait and fine motor coordination Deep tendon reflexes Behavioral checklist Mood, play, school, friends & family relations Cognitive Psychological development Coping with environment Neurological soft signs
question
***Controversial b/c do not always indicate pathology. ***They are nonfocal, functional neurological findings that often provide subtle clues to an underlying CNS deficit or a neurological maturation delay. Children with multiple soft signs often have learning disabilities ***Soft signs include but are not limited to: Short attention span Poor coordination of position Hypopactivity/Hyperactivity Impulsiveness Labile emotions Distractibility No demonstration of handedness Language and articulation problems
answer
Neurological Soft Signs
question
What are the history variations during Pregnancy?
answer
***Exam same as adult ***Deep tendon reflexes Baseline evaluation should be done at initial prenatal visit Preclampsia - exaggerated deep tendon reflexes
question
What are the history variations in the Elderly?
answer
Always assess sensory function first Allow more time for maneuvers of coordination and movement Diminished sense of smell and taste
question
Shuffle (flexion hip/knees)
answer
Gait (in Elderly)
question
What may be diminished in the Elderly?
answer
Tactile, vibratory and position sensation
question
Less brisk or absent
answer
Deep tendon reflexes (in Elderly)
question
LOC: Glascow Coma Scale
answer
Assessing Behavior (in Elderly)
question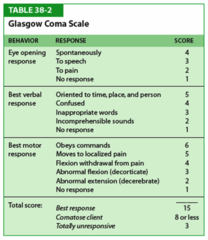

answer
Glascow Coma Scale (in Elderly)
question
Used for older adults at risk for falls

answer
Tinetti Balance and Gait Assessment Tool
question
Orientation New learning: avg 2 of 4 words after 5 minutes. Will improve with verbal cues.
answer
Cognitive Funtion (in Elderly)
question
verbal test to screen for dementia, name 10 items in four categories-fruits, animals, colors, towns Max score = 40, dementia <15
answer
Set Test (in Elderly)
question
Most widely used scoring system for quantifying LOC Simple, high degree of interobserver reliability, correlates well with outcome following severe brain injury Numeric score reflects the sum of: E - _____________ opening response V - ________________ response M - __________________ response
answer
Glascow Coma Scale (emphasized) E-EYE V-VERBAL M-MOTOR
question
Total possible score = 15. Document as 15/15 Score of 15 = FULLY ALERT STATE. Scores less than 7 reflect coma May alternately document each category as: E4 V5 M6 Particularly useful when limitations are present Patient that is intubated Spinal cord injury Severe orbital trauma
answer
Glascow Documentation
question
Limited utility in children, especially under 36 months
answer
Pediatric Glascow
question
Olfactory -Smell
answer
Cranial Nerve I
question
Optic -Visual acuity, visual fields -Examine ocular fundus for color, size, and shape of optic disk
answer
Cranial Nerve II
question
Oculomotor -Pupillary reaction -Eyelid elevation -Most EOM - 6 cardinal gazes
answer
Cranial Nerve III
question
Trochlear -Downward and inward eye movement
answer
Cranial Nerve IV
question
Trigeminal -Jaw movement -Sensation to eyes, corneal reflex -Sensation of touch, pain, and temperature to face
answer
Cranial Nerve V
question
Abducens -Lateral Eye Movement
answer
Cranial Nerve VI
question
Facial -Facial movement -Taste---anterior 2/3 of tongue
answer
Cranial Nerve VII
question
Acoustic -Hearing and Equilibrium
answer
Cranial Nerve VIII
question
Glossopharyngeal -Voluntary muscles for swallowing and phonation -Sensation of nasopharynx, gag reflex -Taste posterior 1/3 of tongue -Secretion of salivary glands -Carotid reflex
answer
Cranial Nerve IX
question
Vagus Voluntary muscles of phonation and swallowing Sensation behind ear and part of ear canal Secretion of digestive enzymes, peristalsis, and carotid reflex Involuntary action of heart, lungs and digestive tract
answer
Cranial Nerve X
question
Spinal Accessory -Sternomastoid and trapezius muscles, size and strength -Turn head, shrug shoulders
answer
Cranial Nerve XI
question
Hypoglossal -Tongue movement, lingual sounds -Have pt. say "light, tight, dynamite"
answer
Cranial Nerve XII
question
Inspect and palpate muscles (when inspecting motor system)
answer
Size, strength, tone, ROM, involuntary movements (tic, tremor)
question
Cerebellar function (when inspecting motor system)
answer
---Balance tests Observe gait Romberg test (stand with eyes closed) Shallow knee bend or hop in place ---Coordination and skilled movements Rapid alternating movements (RAM) Thumb to each finger Finger to finger Finger to nose Heel to shin
question
Testing Sensory System
answer
Compare sensations on symmetric parts of the body Decreased sensation to sensitive areas (map borders) Spinothalamic tract (eyes closed) ---Pain ---Temperature ---Light touch
question
Move Extremities
answer
Testing Position (Kinesthesia)
question
Fine Touch
answer
Testing Tactile discrimination
question
Eyes closed id objects held
answer
Testing Stereognosis
question
Id traced number in palm
answer
Testing Graphesthesia
question
Ability to distinguish two simultaneous pin pricks (will not do) **More sensitive on fingertips, less on upper arms, thighs, and back
answer
Testing Two-Point Discrimination
question
Simultaneously touch both sides of the body
answer
Testing Extinction
question
Point where touched
answer
Testing Point Location
question
How to document Deep Tendon Reflexes
answer
4+ - Very brisk 3+ - Brisker than average 2+ - Normal 1+ - Diminished 0 - Absent
question
Where to test reflexes
answer
Biceps Triceps Brachioradialis Quadriceps Archilles Plantar (Babinski's) Positive Babinski's = fanning of toes
question
Infant Motor System variations
answer
Motor system Smooth and symmetrical movements Denver II for gross and fine motor coordination Muscle tone
question
Testing for Muscle Tone in Infants (birth to 12 months)
answer
Extremities are symmetrically folded inward, hips slightly abducted, fists are tightly flexed. Breech babies, do not have flexion in lower extremities, frog position Landau reflex-raises head and arches back
question
Variations in Infants
answer
Sensory system Hypoesthesia, respond by crying or withdrawal Reflexes Rooting - 3-4 months Sucking - 10-12 mths Palmar grasp - 3-4 mths Plantar grasp - 8-10 mths Babinski's (positive Babinski's until age 2) Tonic neck (fencing position) occurs from 2-6 mths Moro reflex - startle reflex Placing reflex - hold under arms, top of foot touches underside of table, baby flexes hip and knee, then extends hip, to place foot on table - 4 days p birth Stepping reflex - disappears before voluntary walking
question
Alert Lethargic Obtunded Stupor (Semi-coma) Coma
answer
LOC Terminology
question
Drowsy state, may have decreased cough or gag reflex
answer
Obtunded
question
a state of near-unconsciousness or insensibility.
answer
Stupor



