MI Unit 2 Test – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Using what you know about genetics, SNPs, and the PTC gene, explain why it is possible for a person to be a "weak taster."
answer
A person can be a weak taster if they are heterozygous. If a person is heterozygous, then their genotype would be Tt. This means that they are able to taste PTC, but not as strongly as someone who has a genotype of TT.
question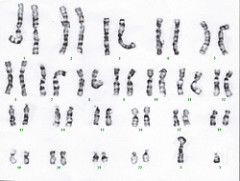
What is a karyotype

answer
Karyotype is a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. Extra or missing chromosomes, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces, can cause problems with a person's growth, development, and body functions.
question
Why a woman of older age is at a greater risk for chromosomal abnormalities?
answer
This is because her eggs are the same age, and errors in meiosis may be more likely to happen as a result of the aging process.
question
Explain the purpose and definition of gene therapy
answer
Gene therapy is the practice of inserting functional genes into a person's genome to replace faulty genes. Doctors and medical researchers are working to restore function to cells that are affected by genetic disorders. To accomplish this goal, scientists have to get the right gene to the right cells in the right tissue. This is not an easy task. Many vectors, or delivery systems, for gene therapy are actually viruses. The idea of using viruses to deliver treatment may sound frightening, but these tiny pathogens can be used as an effective way to target our cells and insert new genes.
question
How do you choose what conditions are good candidates for gene therapy?
answer
-Conditions that are caused by point mutations tend to be good candidates for gene therapy, while diseases involving many genes and environmental factors tend to be poor candidates. -You must have a copy of the gene affected available in your laboratory -You must know which tissues the disorder affects, what role the protein encoded by the gene plays within the cells of that tissue, and exactly how the mutations in the gene affect the protein's function -Must be able to deliver the gene to the cells of affected tissue
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: Retrovirus
answer
form of RNA; 8,000 base pair max; only affects dividing cells; may cause an immune response and may not integrate into the right part of cellular DNA, causing other unintended mutations
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: Adenovirus
answer
form of double stranded DNA; 7,500 base pair max; affects both dividing and nondividing cells; can cause an immune response in patient and is not permanent
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: Adeno-associated virus
answer
form of single stranded DNA; 5,000 base pair limit; affects both dividing and nondividing; needs the assistance of a "helper" virus to replicate themselves inside of cells
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: Herpes Simplex Virus
answer
form of double-stranded DNA; 20,000 base pair limit; affects cells of the nervous system; can cause an immune response in patient
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: liposome
answer
form of plasmids; no max length; not specific for any cell type; some types can be toxic. Cannot be integrated into the host cell's genome
question
explain how the vector carries genetic material, max length of DNA that can be inserted with this vector, what type of cells it affects, and disadvantages: Naked DNA
answer
in the form of plasmids; no max length; not specific for any cell type; will not integrate into the host cell's genome
question
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using viral vectors for gene therapy?
answer
Some advantages are viruses are capable of transferring the gene into the cell and that they can permanently change the cell to help the patient. A disadvantage it that they may promote an immune response from the body. Also there is a chance that the vector could go to the wrong part of the body and cause another mutation. The advantages are that you might be cured for a disease and could live a peaceful life. The disadvantages of using viral vectors for gene therapy are that the gene may be inserted wrong and it might turn on a gene that causes problems in the body
question
A young boy suffers from Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), a genetic nervous system disorder that causes tumors to grow around nerve cells. The gene for NF1, approximately 8,400 base pairs long, is located on chromosome 11. What is the best candidate for a vector for gene therapy in this case? Provide evidence from your research to support your choice.
answer
herpes simplex virus. The boy is suffering from a disorder that affects the nervous system and this vector targets and infects cells of the nervous system. Also this vector can handle a maximum length of 20,000 base pairs and this disorder is about 8,400 base pairs.
question
How does therapeutic cloning differ from reproductive cloning? Do you feel one is more acceptable than the other? Why or why not?
answer
Therapeutic cloning is where DNA is extracted from a cell to be put into a germ cell as in regular cloning. Therapeutic cloning, however, is used to treat a genetic disease in an adult individual. Reproductive cloning is simply cloning an individual in order to reproduce. I believe that therapeutic cloning is more acceptable than reproductive cloning because it does not create a full organism and it is intended to improve an individual's quality of life. Gene cloning produces copies of genes or segments of DNA. Reproductive cloning produces copies of whole animals. Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for experiments aimed at creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues. Gene cloning, also known as DNA cloning, is a very different process from reproductive and therapeutic cloning. Reproductive and therapeutic cloning share many of the same techniques, but are done for different purposes.
question
How, in general, do you create a clone from an adult cell donor?
answer
vacuum out the genes of an egg and insert new genes from a somatic cell of the donor while slightly tweaking the genes to create a clone
question
Describe the 2 methods of reproductive cloning
answer
Artificial Embryo Twinning- an early embryo is separated into individual cells inside a petri dish and placed in a surrogate mother. Somatic cell nuclear transfer- removed all of the DNA from an egg cell. They transferred the nucleus from the somatic cell to the egg cell, allowing it to behave like a fertilized embryo.
question
List pros and cons to gene therapy
answer
Cons: harmful side effects such as blood cancers, could cause cheating in professional sports ("gene doping"), not very precise, could cause blood to thicken which could be lethal. Pros: could allow a person to avoid lifelong therapies, treatment can be permanent, could provide patient with a longer life, does not rely on viruses to disperse DNA which bypasses the risk of an immune response, wide range of diseases it can treat
question
Describe a 12 week fetus
answer
sex determinable, heartbeat, arms proportional, more movement
question
Describe a 24 week fetus
answer
senses present, nails develop



