MCH Neurology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
How can you distinguish hemorrhagic CSF caused by a traumatic lumbar puncture from a true subarachnoid hemorrhage?
answer
If the LP fluid clears significantly as the sequence of tubes are collected= traumatic LP
question
When do you recommend using an LP on a peds patient?
answer
-suspected CNS infection -subarachnoid hemorrhage
question
When is LPs contraindicated?
answer
evidence of increased ICP -papilledema -depression of consciousness -focal neurologic deficits *could cause cerebral herniation
question
What is included in a CSF analysis?
answer
-cell count -protein -glucose
question
What is an electroencephalography (EEG), 3 key features

answer
records electrical activity generated by cerebral cortex 1. background patterns 2. behavioral state modulation 3. presence or absence of epileptiform patterns
question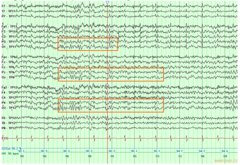
What does normal EEG look like?

answer
-general symmetry/ synchrony b/t background of the 2 hemispheres w/o localized area o high amplitude or slower frequencies
question
What do delta rhythms on an EEG suggest?
answer
underlying structural abnormality -brain tumor -abscess -stroke
question
What do spikes, polyspikes and spike and wave abnormalities indicated on an EEG?
answer
seizure
question
what are electromyography and nerve conduction studies?
answer
-assess for abnormalities of the neuromuscular apparatus -spontaneous discharge of motor fibers (fibrillations) or groups of muscle fibers (fasciculation)- indicates *denervation*
question
what do abnormal muscle responses indicate on electromyography/nerve conduction studies?
answer
neuromuscular junction disorders -myasthenia gravis -botulism
question
What are NCVs?
answer
Nerve conduction velocities -asses AP transmission along peripheral nerves *slowed in demyelinating neuropathies ie. Guillain-Barre*
question
When do you use a CT scan in peds?
answer
emergency purposes -quick, accessible *study of choice for head injury or sudden headache*
question
When do you use a MRI scan in peds?
answer
-provides fine detail, detects posterior fossa lesions, cerebral abnormalities, vascular abnormalities, tumors, ischemic changes -spinal cord views *study of choice for new onset complex partial seizures*
question
When do you use a cranial US in peds?
answer
-visualize brain, ventricles of infants -young children with open fontanelles *noninvasive bedside procedure
question
Primary vs secondary headache
answer
primary- migraines, tension secondary- viral URI, sinusitis OR symptom of serious condition (meningitis, brain tumors)
question
4 temporal patterns of childhood headache
answer
1. *Acute*- single episode of pain w/o history 2. *Acute recurrent*- pattern of attacks of pain separated by symptom free intervals 3. *Chronic progressive*- gradually increasing frequency and severity of headache; most ominous 4. *Chronic non progressive or chronic daily*- constant headache
question
S/S of tension-type headache
answer
-mild, lack associated symptoms -not disruptive of life -*global pain and sneezing or pressing* -lasts hours to days -related to stresses, depression, anxiety
question
Clinical manifestation of migraines
answer
-begin in childhood -frontal, bitemporal or unilateral -*pounding, throbbing pain aggravated by activity* -N/V, pallor, photophobia, phonophoba, want to be in dark
question
What is the most common recurrent patten of primary headaches?
answer
tension-type
question
How can you tell if a toddler is having a migraine? aka they cant tell you so what do they show you
answer
-irritability -sleepiness -pallor -vomiting
question
Signs of increased ICP in headache
answer
-associated vomiting worse when lying down or on first awakening -awakens child from sleep -remits on arising -exacerbated by cough, valsalva, bending over
question
Is head trauma a primary or secondary headache?
answer
secondary
question
When do you get imaging for headache/migraine complaint in peds?
answer
-neuro exam is abnormal -unusual neurologic features during headache -s/s of increased ICP
question
What is the diagnostic study of choice for headache/migraine in peds (if indicated)?
answer
MRI
question
Mainstay treatment of headache/migraine in peds?
answer
-intermittent symptomatic or abortive analgesics -acetaminophen or NSAIDS -hydration, antiemetics -psych support, counseling, stress management
question
What meds do you give for kido experiencing one disabling headache per week?
answer
daily preventative agents including -tricyclic antidepressants -anticonvulsants -antihistamines -BB, CCB *must work with lifestyle modification before initiation daily meds*
question
Should you consider triptans in kids with migraines?
answer
yes if symptomatic or abortive analgesics do not work
question
Describe neonatal seizures caused by hypoxic-echemic encephalopathy (postasphyxial seizures)
answer
-occur 12-24 hrs after birth asphyxia, refractory to anticonvulsants -also caused by metabolic disorders
question
seizures caused by intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in a neonate?
answer
-common in premature infants -bulging fontanelle, hemorrhage spinal fluid, anemia, lethargy, coma
question
delivery room seizures in neonates?
answer
caused by direct injection of local anesthetic agents, severe anoxia, congenital brain malformation
question
seizures after 5 days of life
answer
result of infection or drug withdrawl
question
what do subtle seizures in neonate look like
answer
-apnea -eye deviation -tongue thrusting -eye blinking -fluctuation of vital signs -starring
question
What is the immediate diagnostic test after neonate seizure?
answer
cap blood glucose level
question
treatment for neonate seizures
answer
-correction of hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia, or vitamin B6 deficiency or dependency *if there is no identifiable cause of the seizure= anticonvulsant agent*
question
symptoms of a simple focal (or partial) seizure
answer
-motor (tonic, clonic, myoclonic) -sensory -psychic or autonomic abnormalities -consciousness preserved
question
what is the difference b/t simple focal or complex partial seizures
answer
-complex partial seizures go in and out of consciousness (alternation of consciousness) aka *dyscognitive features* -starring, automatisms
question
what are automatisms?
answer
automatic semi purposeful movements of mouth (lip smacking, chewing) or extremities (rubbing of fingers, shuffling of feet)
question
what is the Jacksonian march?
answer
when focal seizures spread to whole brain, producing generalized seizures (*secondarily generalized*)
question
clinical hallmark of absence seizures
answer
brief (less than 15 seconds) loss of environmental awareness accompanied by eye fluttering or simple automatisms -4-6 year olds -eeg shows generalized 3-Gz spike and wave activity
question
how do you clinically provoke absence seizures
answer
hyperventilation or strobe light
question
atypical absence seizure
answer
episodes of impaired consciousness w/automatisms, autonomic phenomena, motor manifestations (eye opening, eye deviation, body stiffening)
question
myoclonus seizure
answer
sudden jerk of all or part of body *not all epileptic in nature*
question
atonic seizures
answer
typically brief (1-2 sec) but disabling b/c of loss of postural tone= *falls, injuries*
question
febrile seizures
answer
unrecongnized epilepsy caused by fever -6 months-6 years -generalized onset, less than 15 min, only once in 24 hours
question
do you treat febrile seizures?
answer
Nope -antipyretics don't help -can use rectal diazepam during seizure to abort prolonged event
question
psychogenic nonepileptic seizure (PNES)
answer
manifestation of *conversion disorders or malingering* -often have closed eyes, thrashing movement, tremulousness -verbalization, pelvic thrusting often initiated or terminated by suggestion get these kidos some mental health care- no meds damnit
question
most common causes of seizures
answer
perinatal conditions- ischemic encephalopathy, hemorrhage infections- encephalitis, meningitis metabolic conditions- hypoglycemia poisoning neurocutaneous syndromes systemic disorders accidental trauma, febrile illness, familial
question
benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes aka benign rolandic epilepsy
answer
-begins 5-10 -occurs during sleep, on awakening -no imaging -anticonvulsants -resolves after puberty most common epilepsy sydrome
question
childhood absence epilepsy
answer
begins early school years, resolves by adolescence -treatment= ethosuximide
question
juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
answer
myoclonic jerks exacerbated in the morning, drops objects, tonic- clonic resolve with anticonvulsant meds (*valproic acid*)
question
do you treat juvenile myoclonic epilepsy for life?
answer
yup anticonvulsants
question
infantile spasms
answer
-brief contractions of neck, trunk, arm muscles followed by phase of sustained muscle contraction *high risk for long-term neurodevelopmental difficulties*
question
how do you treat infantile spasms?
answer
adrenocorticotropic hormone, high dose coricosteroid, vigabatrin
question
west syndrome
answer
triad of infantile spasms, developmental regression, dramatically abnormal eeg pattern
question
hypsarrrhythmia
answer
chaotic high voltage slow waves, spikes, polyspikes -peak age of onset- 3-8 months
question
What is Lennox-Gastaut syndrome?
answer
frequent, multiple seizure types due to *brain injury/malformation* -respond poorly to treatment -significant intellectual disability
question
acquired epileptic aphasia (Landau-Fleffner syndrome)
answer
-abrupt loss of previous acquired language in young children -pts with autistic regression
question
causes of status epilepticus
answer
VITAMINS *V*ascular *I*nfection *T*rauma *M*etabolic *I*ngestion/W*I*thdrawal *N*eoplasm P*s*ych or epilepsy
question
management of status epilepticus
answer
ABCs O2 IV Labs- glu, BMP, anticonvulsant drug levels, toxicology studies, CBC/diff -*BENZOS*- lorazepam, diazepam, midazolam -fosphenytoin -phenobarbital -valproic acid
question
common causes of coma in peds
answer
infection- meningitis, abscess, encephalitis trauma- hemorrhages toxins (intoxication or withdrawal)- etoh, narcotics etc hypoxia-ischemia- near drowning, carbon minoxide epilepsy- postictal states, status epilepticus stroke, increased ICP migraine systemic disorders metabolic derangements
question
diagnostic approach to coma
answer
labs- glu, CMP, blood gases, ammonia, urinalysis CSF analysis neuroimaging- head CT, MRI EEG
question
DDX for transient, recurrent depression of consciousness
answer
-episodic alteration or depression of consciousness with full recovery due to seizure, migraine, syncope, metabolic abnormality -basilar artery or confusional migraines -syncope -metabolic derangements ie. hyperammonemia
question
what are the most common solid tumors in children
answer
CNS tumors -sxs caused by impingement on normal tissue or increase in ICP
question
sxs for CNS tumors
answer
increased ICP- lethargy, headache, vomiting slow growing tumors- irritability, anorexia, poor school performance, loss of developmental milestones
question
immediate treatment used to reduce tumor-associated edema
answer
-high dose dexamethasone
question
most common location of CNS tumors in children
answer
infratentorial (posterior fossa)
question
sxs of neuroblastoma
answer
abdominal pain or mass, mass palpated in flank, hard smooth, nontener -secretory diarrhea, profuse sweating, opsomyoclonus (dancing eyes/feet)
question
lab test for neuroblastoma
answer
CBC + urine (looking for catecolamines)



