Mastering Biology organic chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
functional group
answer
group of atoms that replaces hydrogen in an organic compound hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, aldehyde, ketone, sulfhydryl, methyl, phosphate
question
hydroxyl
answer
OH
question
carboxyl
answer
COOH
question
amino
answer
NH2
question
aldehyde
answer
COH
question
ketone
answer
CO
question
sulfydryl
answer
SH
question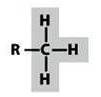
methyl

answer
CH3
question
phosphate
answer
PO4
question
organic molecule
answer
Contain carbon/hydrogen; most organic molecules important to living things are polymers
question
Momomer
answer
Small organic molecules that can either exist separately or bonded together in long chains to form polymers
question
carbon skeleton
answer
an arrangement of carbon and hydrogen atoms (basic structural component of many organic molecules)
question
hydrolysis
answer
a reaction where a large molecule to break into smaller component parts when water is added
question
hydrogen bond
answer
the bond between 2 hydrogen molecules
question
dehydration synthesis
answer
a reaction where molecules are bonded together through the removal of water
question
peptide bond
answer
a bond between amino acids where the nitogen of the amino group bonds directly to the carbon of the carboxylic acid group (polar covalent bond)
question
lipid
answer
organic molecules that are: -insoluble in water -composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen -the amount of oxygen is much less than hydrogen
question
fat
answer
often called triglycerides (1 glycerol, 3 fatty acids), important in energy storage and insulation
question
hydrocarbon
answer
molecules that are composed of only carbons and hydrogens
question
phospholipid
answer
a fat that is made of glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group
question
fatty acid
answer
a long carbon skeleton (usually 10 or more) with a carboxylic acid group attached at one end
question
amino acid
answer
what proteins are composed of; made of a carbon skeleton, amino group, and a carboxylic acid group
question
unsaturated fatty acid
answer
a fatty acid that doesn't have as many hydrogens as it can possibly hold (not completely hydrogenated) (at least 1 double bond between carbons)
question
saturated fatty acid
answer
a fatty acid that has as hydrogens as it can possibly hold (completely hydrogenated) (no double bonds)
question
purine
answer
a nitrogenous base that can be part of the nucleotide structure made of double-ring molecules (ex: adenine, guanine)
question
complex carbohydrate
answer
carbohydrates that consists of multiple monosaccharides
question
monosaccharide
answer
a simple sugar by itself
question
disaccharide
answer
2 sugars bonded together
question
trisaccharide
answer
3 sugars bonded together
question
fat
answer
lipid molecules composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
question
steroid
answer
complex lipids composed of 4 interlocking carbon rings
question
glycerol
answer
a 3-carbon skeleton with 3 alcohol groups (one on each carbon
question
protein
answer
a type of organic molecule that is made of amino acids, has a central carbon atom with a carboxyl group at one end and amino on the other and variable below
question
levels of protein organization
answer
must have at least 3 levels: Primary: order of the amino acids Secondary: coiling/folding of the primary structure to form a helix/plated sheet held together by hydrogen bonds Tertiary: 3D Quaternary: 2 or more polypeptides linked together (only the biggest proteins have a quaternary structure)
question
pyrimidine
answer
a nitrogenous base that can be part of the nucleotide structure made of single-ring molecules (ex: cytosine, thymine, uracil)
question
nucleotide
answer
makes up nucleic acids and is made of a phosphate group, a sugar (ribose/deoxyribose), and a nitogenous base
question
ribose
answer
-a 5-carbon sugar that can be part of a nucleotide -contains one more oxygen atom then deoxyribose -part of the makeup of RNA
question
deoxyribose
answer
-a 5-carbon sugar that can be part of a nucleotide -contains one less oxygen atom then ribose -part of the makeup of DNA
question
what does a straight line connecting 2 atoms (O-H) represent?
answer
a pair of atoms being shared
question
atoms found in proteins
answer
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen
question
atoms found in lipids
answer
fat: oxygen, hydrogen, carbon phospholipid: oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, phosphate
question
atoms found in nucleic acids
answer
oxygen, phosphate, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen
question
atoms found in carbohydrates
answer
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon
question
catabolic reaction
answer
reactions that result in the breakdown of larger organic compounds into smaller subunits (associated with hydrolysis)
question
anabolic reaction
answer
reactions that result in the buildup of large macromolecules from smaller building blocks (associated with dehydration synthesis)
question
Carbohydrates
answer
organic molecule, principal energy source, Structural components in cell, short-term energy storage, cell to cell recognition
question
Order in which body burns energy
answer
Carbs, lipids, proteins (PROTEIN IS A LAST RESORT)
question
Cellulose
answer
Structural carb in plants, "fiber", indigestible to humans (due to beta linkage)
question
Starches
answer
Long straight chains of glucose found in plant cells, digestible by humans (alpha linkage)
question
Glycogen
answer
"Animal starch", long branched chains of glucose in animal cells
question
Glucose
answer
C6H12O6
question
emulsifier
answer
molecules that are both polar and nonpolar (breaks down globules of fat into smaller droplets)
question
phospholipid
answer
lipid; has a hydrophilic and polar head and a hydrophobic and nonpolar tail, important components of cell membranes (made of a phosphate group and two fatty acids)
question
polypeptide
answer
a chain of molecules
question
what is the significance of protein shape
answer
shape determines function
question
DNA
answer
-double-stranded -nitrogen bases: cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine -deoxyribose sugar -has a helix
question
RNA
answer
-single-stranded -nitrogen bases: adenine, guanine. uracil, cytosine -ribose -no helix
question
ATP
answer
-adenine + ribose + 3 phosphate groups -energy carrier in cells -high energy molecule -energy released by breaking last 2 phosphate bonds (unstable and easily broken) (leaved ADP and inorganic phosphate) -reformed with input of food energy



