Macroeconomics Study Guide Exam 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The limited nature of resources (we can only have so much)
answer
Scarcity
question
How people decide what to buy, how much to work, save, and spend
answer
Economics
question
You have to give up something to get something else
answer
Principle 1: People Face Tradeoffs
question
You go to a party the night before an exam instead of studying
answer
Example of "People Face Tradeoffs"
question
Making a decision involves comparing costs and benefits
answer
Principle 2: The Cost of Something is What You Give Up to Get It
question
Whatever must be given up to maintain a cost Example: Seeing a movie costs for how much TIME you spend there
answer
Opportunity Cost:
question
Example: Is paying for an extra year of college worth the small amount of extra salary you would get?
answer
Principle 3: Rational People Think at the Margin
question
Something that makes people act
answer
Incentive:
question
Example: If gas prices rise people will respond by purchasing hybrid cars
answer
Principle 4: People Respond to Incentives
question
Example: U.S. is good with technology, and China is good with farming--everyone is good at different things, so if we trade everyone will have the best products around.
answer
Principle 5: Trade Can Make Everyone Better Off
question
A group of buyers and sellers
answer
Market:
question
The interactions between buyers and sellers determine prices
answer
Principle 6: Markets Are Usually a Good Way To Organize Economic Activity
question
When governments get involved in the economy, they are usually doing something to help costs in the longrun
answer
Principle 7: Governments Can Sometimes Improve Market Outcomes
question
When a market fails to use society's resources efficiently
answer
Market Failure:
question
Ex. A large country going into a poor one and giving 50 cent wages Technology improves the standard of living
answer
Principle 8: A Country's Standard of Living Depends on It's Ability to Produce Goods and Services
question
Increases in the general level of prices
answer
Inflation:
question
More the government produces the greater the inflation rate
answer
Principle 9: Prices Rise when the Government Prints Too Much Money
question
Inflation and Unemployment push in opposite directions
answer
Principle 10: Society Faces a Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment
question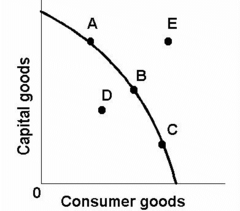
Efficient: A B C Not: D

answer
In the PPF provided, which points are efficient? Not efficient?
question
Attainable: A B C D Not: E
answer
In the PPF provided, which points are attainable? Not attainable?
question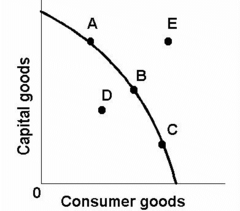
Economic growth would need to occur -New Tech etc. (That would move the curved line up so that it goes through point E)

answer
Tell how you could produce point E on the PPF Provided
question
We produce a good and sell it elsewhere
answer
Exports
question
Goods produced abroad and sold domestically
answer
Imports
question
The ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
answer
Absolute Advantage
question
Whoever has the lower opportunity cost
answer
Comparative Advantage
question
Examining additional costs and benefits of an activity
answer
Marginal Analysis
question
The most you're willing to pay
answer
Marginal Benefit
question
Relationship of all prices and quantity demanded from that price
answer
Demand
question
Price
answer
________ cannot change demand
question
Price
answer
All factors can change the demand curve except _______.
question
As price rises, quantity demanded also rises Vice Versa
answer
Demand Schedule
question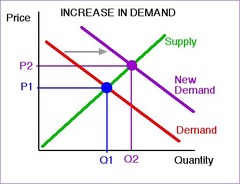
Quantity demanded increased

answer
What happened between the red and blue lines?
question
Right
answer
If demand shifts positively, the demand curve will shift to the ___________.
question
Rise, More
answer
A ___________ in consumer income can cause _________ goods to be bought
question
Coke and Pepsi. If coke gets too expensive consumers will substitute pepsi
answer
Example of a substitute
question
Fudge and Ice Cream example
answer
Example of complements
question
Price
answer
A change in _________ will not change supply
question
Relationship between all prices and quantity
answer
Supply
question
Right
answer
If demand shifts positively, the demand curve will shift to the __________.
question
Left
answer
If demand shifts negatively the demand curve will shift to the __________.
question
If the price of a product increases, you supply more. If the cost decreases, you supply less.
answer
Law of Supply
question
It shifts right (positively)
answer
What happens to the supply curve in the number of firms increases?
question
If shifts right (positively)
answer
What happens to the supply curve when technological progress occurs?
question
What consumers are willing to buy
answer
Demand
question
Excess quantity demanded over quantity supplied (so, more is wanted than can be supplied)
answer
Shortage
question
Shortage
answer
Buyers cannot purchase what they desire at the current price is an example of a
question
Increase
answer
When there is a shortage prices will _________
question
Have to charge more and higher more workers
answer
How can you fix a shortage?
question
Excess quantity supplied over quantity demanded (so, more is supplied than there is needed)
answer
Surplus
question
Surplus
answer
Sellers cannot sell what they desire at the current price is an example of a
question
Decrease
answer
When there is a surplus prices will __________.
question
Consumers and Suppliers are in agreement
answer
Equilibrium
question
Surplus, Fall
answer
If 55 cars are demanded and 70 are produced, this is a __________ and prices will ___________.
question
Maximum price charged legally
answer
Price Ceiling
question
-Shortages -People do illegal things such as scalping tickets
answer
Consequences of a Price Ceiling
question
A legal minimum that prices can be
answer
Price Floors
question
-Surplus (because sellers cannot find enough buyers) -Example: Airline fares under regulation
answer
Symptoms of Price Floors
question
Floors
answer
Price (Floors or Ceilings) get expensive
question
Micro: Individual Decision making units & how they behave Macro: Behavior of entire economies
answer
Micro vs Macro
question
1. Price Levels 2. Production 3. Unemployment
answer
3 things you study in Macro:
question
Combining many individual markets
answer
Aggregation
question
Add together the value of hot dogs and computers
answer
Example of aggregation
question
Macro
answer
Aggregation is more important for (micro/macro)
question
Together
answer
During economic fluctuations, aggregations are important because markets move ____________
question
Macro: Size of the pie Micro: What kind of pie and who eats it
answer
Pie analogy for Micro vs. Macro
question
Right
answer
Inflation occurs when demand shifts _________
question
Left
answer
Deflation occurs when demand shifts _________
question
Deflation
answer
No increase in demand =
question
Demand
answer
In a healthy economy, when both demand and supply shift, which shifts more?
question
Inflation
answer
_____________ hurts savings
question
A period of time where the total output of the economy declines
answer
Recession
question
Production falls and people lose jobs
answer
What happens to production and jobs during a recession?
question
Left
answer
During a recession, the demand curve shifts _______
question
Both aggregate demand and supply curves shift right
answer
Economic Growth occurs when
question
No, only final products are. So, the entire Ford F-150 would be
answer
Is the steering wheel for a Ford F-150 part of GDP?
question
2 quarters
answer
A recession is claimed when declines happen over how long?
question
4-5% (new tech comes out)
answer
Healthy unemployment rate
question
Recession
answer
What term can be used to describe a period where the total outputs of jobs decline?
question
Economic
answer
___________ growth occurs when aggregate supply and demand shift right
question
1. War 2. Natural disasters
answer
Two examples of things that could cause GDP to rise?
question
you can't compare wages or prices from different time periods
answer
Real GDP states that _______________.
question
Ex. That an $8.50 wage today is equal to a $1 wage in 1910
answer
What does Nominal GDP show?
question
Above: Economic Booms Below: Recessions, Wars, Panics
answer
Figure 5 in Chapter 5 shows the GDP for the U.S. since 1870. The middle line represents 0. What occurs when the GDP goes above 0? Below?
question
Demand
answer
When inflation occurs. _______ shifts right
question
Supply
answer
When deflation occurs, ______ shifts right
question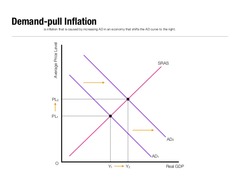
Demand shifted right

answer
The following graph is an example of inflation because ________.
question
More government spending occurred
answer
Why did general prices increase during WWI and WWII?
question
If GDP is above 0, inflation. If it's below, deflation.
answer
In the GDP Graph, how do you know when inflation or deflation is happening?
question
Inflation that occurs if the economy is growing slowly or in a recession
answer
Stagflation
question
Less
answer
If you have $1 and inflation occurs, is your dollar worth less or more?
question
Demand for single product, while aggregate demand is a collection of all products in an entire nation
answer
Demand vs Aggregate Demand
question
Demand shifts left
answer
What happens to the supply and demand graph during stagflation?
question
Loans that banks trade put pressure on interest rates
answer
Federal Reserve Impact
question
If you have bad credit, you can buy a Dodge Stratus with a 24% interest rate and it will be the same as buying a $20,000 car with a 0% interest rate
answer
Example of Federal Reserve Impact
question
Property Rights
answer
What is 1 reason some countries cannot become global?
question
1. Raise Taxes 2. Lower interest rates
answer
How to fix inflation
question
Government programs designed to prevent or shorten recessions and to stop inflation
answer
Stabilization Policy
question
TOTAL supply of goods and services that a national economy produces
answer
Aggregate Supply
question
TOTAL demand for final goods in an economy
answer
Aggregate Demand
question
Amount of output a worker produces in an hour
answer
Labor Productivity
question
productivity
answer
Raising ________ will improve that standard of living
question
Potential would be a linear line through the red--real GDP is rarely constant
answer
Potential vs Real GDP
question
Looking for work in the last 4 weeks
answer
In order to be considered in the unemployment rate, what do you have to be doing?
question
People Unemployed/Labor Force
answer
Unemployment Equation
question
Not maximizing resources
answer
What causes GDP to fall?
question
No income, hunger, psychological impacts
answer
Negatives of unemployment:
question
Everyone that holds a job, including part time workers
answer
Employed
question
People not currently working; actively looking for a job in the past 4 weeks
answer
Unemployed
question
Not looking for work at all
answer
Out of Labor Force
question
Unemployed person that gives up looking for work
answer
Discouraged Worker
question
Involuntary part-time or loss of overtime
answer
Disguised Unemployment
question
Changing jobs because you're moving, hated your boss, etc. Healthy
answer
Frictional Unemployment
question
Laid off
answer
Structural Unemployment
question
Rises during recessions, has to do with decline of economy
answer
Cyclical Unemployment
question
They rise
answer
When demand shifts right, what happens to prices?
question
Doesn't motivate people to look for jobs
answer
What is a con to having higher unemployment benefits?
question
Economic growth, rise in technology. Inflation.
answer
What causes "real wages" to rise?
question
No, firms must pay the market rate. (Giving raises to keep up with inflation).
answer
Does high inflation hurt the worker?
question
2%
answer
Suppose you get a 5% increase in your wage, but inflation rises by 3%. How much of a raise did you actually get?
question
Someone who is unemployed and is relying on savings
answer
Who does inflation hurt?
question
Pure: Less realistic; basically everything would inflate by 10% Real World: Different products increase in price differently. You may think inflation hurt you if you only buy 1 thing but it increased a lot vs. other products.
answer
Pure Inflation vs. Real-World Inflation
question
Inflation
answer
Lenders and Borrowers may get hurt by ____________.
question
Real Interest Rate + Rate of Inflation
answer
How to find Nominal (Total) Interest Rate:
question
Over time inflation will occur, and they will lose out on the interest
answer
If a bank lends you $100,000 with 0% interest, why do they lose?
question
Nominal Interest Rate - Expected Inflation
answer
How to find Real Interest Rate:
question
6%
answer
If the bank gave you a 3% interest rate and they expected inflation to increase 3% over the time it takes you to pay back your loan, what is your interest rate?
question
2%- They win 4%- You win
answer
If the bank gave you a 3% interest rate and they expected inflation to increase 3% over the time it takes you to pay back your loan, but inflation only actually rises 2%, who wins? What about 4%?
question
4%-1%= 3%
answer
In 2013, mortgage rates were 4% with a 1% inflation. Find the real interest rate.
question
Caused by rapidly printing money
answer
What is hyper-inflation?
question
3%/year
answer
Healthy inflation rate
question
Technology
answer
Labor Productivity will rise as __________________ improves.
question
Workers being more happy and productive
answer
Workforce Quality
question
More people need to get a higher education. Education helps firms.
answer
In order for labor productivity to increase, what needs to occur?



