KU Geography 105 – Lab Final – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
shows bigger area, less detail (map of world)
answer
Small Scale Map
question
shows smaller area, more detail (campus map)
answer
Large Scale Map
question
what part of the electromagnetic spectrum you're using. Size of Wavelength that its imaging.
answer
Spectral Resolution
question
Measure of how often data is collected. You need MULTIPLE images.
answer
Temporal Resolution
question
The amount of detail--> PIXELS. More pixels, more detail.
answer
Spatial Resolution
question
physically shoot something at it, comes back to you as colors, send out wavelength
answer
Active Resolution
question
getting the data. Taking a picture (wavelength is coming off as colors)
answer
Passive Resolution
question
- incoming solar radation - more insol. higher temp - Closer to the equator - seasonal variation --> seasons change as earth rotates
answer
Insolation
question
ex: florida, more insolation
answer
Latitudinal
question
- point with the most insolation that occurs on any given day - Migrates - tropic of cancer 23.5 North in summer// tropic of capricorn 23.5 South in winter - Moves up in our summer and down in our winter. -on tropic of capricorn
answer
Sub Solar Point
question
never moves, always at 0, most insolation always
answer
Equator
question
- migrates. Always follows sub-solar point - air coming together, low pressure - Climate: (low, rainbow) hot, rainy, tropical rainforest -Found: somewhere in the tropics, near equator - vegetation: tropical rainforest - low pressure, so the air rises
answer
ITCZ - intertropical convergent zone
question
N S, moves east to west
answer
Longitude
question
E W, but moves N to South - Tropic of Cancer --> 23.5 N S - Tropic of Capricorn --> 23.5 N S
answer
Latitude
question
63.5 N S
answer
Arctic Circle
question
depends on how earth is tilting, could be 24 hours of sunlight in summer or darkness in winter
answer
Antarctic Circle
question
2 sides to mountain: rainy side & side with rain shadow
answer
Orographic Mountains
question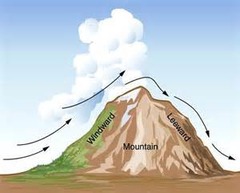
Direction of the wind goes up - cools down- getting closer to saturation - actual temp hits due point temp - at saturation - vapor condenses and turns into water (clouds) then it rains - go over mountain - no rain (rain shadow) - westerly winds affect it. (east side is wet, west side is dry)

answer
Orographic Uplift
question
rainy. Vegetation: trees
answer
Windward
question
dry vegetation: grass
answer
Leeward
question
- High Pressure - Climate: (high dry) Dry, worlds great deserts, grass, cacti - Found: 30 degrees N and S - grass, scrub, low precip.
answer
STH - Subtropical High
question
are blown toward the East. EVERYTHING GOES WEST TO EAST. affect orographic lift
answer
Westerly Winds
question
Temp where Relative Humidity = 100%
answer
Dew Point
question
Transition zone. Warm to cold air. (red)
answer
Warm Front
question
blue, will be having more rain, dew point higher, more humid, advancing cold air to warm air
answer
Cold Front
question
counterclockwise
answer
WINDS ALWAYS GOES
question
average of all the weather
answer
Climate
question
what's happening on any given day
answer
Weather
question
explains temp and precipitation
answer
Climograph
question
Atmospheric info when that snow landed. Gas bubbles tell you about climate
answer
Ice cores
question
Remember TREE STUMPS - Rainfall: big (thick) tree ring - Dry: thin tree ring -----Tree with with multiple rings, which one is bigger and which one is smaller??
answer
Dendrochronology
question
P: Pollen, Plants What kind of plants. What the climate was like. - Tree pollen: lots of rain - Grass pollen: forest fires
answer
Pollenology
question
Specific geographic pieces of land that have similar plants and animals
answer
Biomes
question
Transition between biomes. Has characteristics of both biomes. Ex: deserty grassland
answer
Ecotone
question
Take sediment and you lithify (transforms into stone), diagenesis (change of sediments) - must erode
answer
Sedimentary
question
- Intrusive (inside earth, big grains, shiny) extrusive (outside) - Magma cooling down
answer
Igneous
question
Extra heat pressure to rock - must melt magma
answer
Metamorphic
question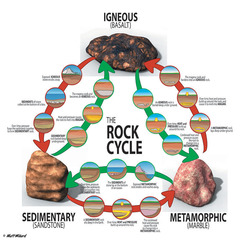
-Igneous --> Metamorphic --> sedimentary - Metamorphic --> sedimentary-->igneous - Sedimentary-->igneous-->metamorphic

answer
Rock Cycle
question
Sand, Silt, Clay
answer
Soil
question
Will not hold a lot of moisture or nutrients, low water holding capacity
answer
What if the soil is really sandy?
question
Holding a lot of water and nutriets tightly, plants cant get the nutrients because clay is hogging it, water is pooling up on top of clay
answer
What if it's clay soil?
question
Mixture of all types, WE WANT IT
answer
Loamy Soil
question
top of mountain: medium soil. middle of mountain: thinest soil - run off, erosion. Bottom of mountain: really thick soil. Most water logged conditions (remember the picture)
answer
Soil on a Slope
question
O - organic material A - top soil, lots of organic matter, where we grow things, dark colored E - leaching, eluviation - material that gets in this horizon gets flushed down B - zone of accumulation, illuviation, bringing in material C - unweathered parent material R - rock
answer
Soil Horizon
question
(COME TOGETHER) 2 converging continental tectonic plates coming together to make mountains and volcanoes. (where hot spots occur)--------->>>> Subduction. (fault boundary)
answer
Convergent Tectonics
question
(DIVIDE) pulling away (hand thing that he did) (mid oceanic ridges, large rift valleys)(fault boundary)
answer
Divergent Tectonics
question
nothing (fault boundary)
answer
Passive Tectonics
question
slide pass each other (fault boundary)
answer
Transform Tectonics
question
When one plate goes beneath other one. ex: oceanic plate is more dense than continental, so it will always be the one to go below it. --> trench Volcanoes, deep ocean trenches oceanic + ocean or continental + oceanic or continental = subduction ----- Plate goes beneath--> dips below--> crest gets low that it melts-->volcano
answer
Subduction
question
2 ends and compresses slowly (to not crack)--> start with something flat, starts to make squigly line, folds all layers underneath - Anticlines - at top of mountain -Synclines - at bottom
answer
Tectonic Folding
question
at the end of meandering stream, depositional - depositing water, dispersion: loss of energy, drop sediment
answer
Delta
question
at the bottom of meandering stream
answer
Oxbow Lake
question
erosional, cutting, wall will keep cutting, meandering stream moves with the cut bank
answer
Cut Bank
question
depositional, what it is?
answer
Point Bar
question
where river can erode to, where it eroded to prior. Reperian zone: vegetation along flood plains. Rivers help vegetation. Have trees along river--> more moisture
answer
Flood Plain
question
Delta, Oxbow Lake, Cut Bank, Point Bar, Flood Plain
answer
Meandering Rivers Contain
question
Q=Wdv - know what it means Q - discharge W- width D- depth V- velocity - If one side goes up, other side must go out - Anytime you change discharge, something on the other side must change to compensate - Equation must always be balanced
answer
Continuity Equation
question
Zone of Accumulation
answer
At the top of the mountain
question
altitude, ELA
answer
In the middle of the mountain
question
Zone of Ablation (ice melts)
answer
At the bottom of mountain
question
morains, dremlins, eksers, kettle lakes
answer
Depositional landforms
question
- Terminal - happens at the end of a glacier (know this - one the best) - Lateral - stuff melts off glaciar - Medial - inbetween 2 glaciers - Ground
answer
Type of Morains
question
- Big pile of sediment when you are in aired environment, infrequent rainstorms, sediment falls off - Will not have them if land is flat. Must have a slope or drop off - When water falls off cliff, disperses. Drop sediment, lose energy ◊ Course at the top, fine is at the bottom WHY? Course stuff is heavy so it gets dropped first. The second you disperse, you lose energy you drop all the big stuff. Little stuff doesn't take much energy so you take it all the way to the bottom ◊ Braided stream
answer
Alluvial Fans
question
not a lot of sand, strong wind comes from one direction
answer
Barchan Dune
question
anchored by vegetation, don't need a lot of sand
answer
Parabolic Dune
question
high sand supply, multiple wind directions, largest dunes in the world
answer
Star Dune
question
perfect ridges, squiggly lines, slow wind blows over
answer
Transverse Dune
question
how waves hit the beach at an angle, move sand along the beach which ever direction wind is going ----Spits ----Baymount bar
answer
Longshore drift
question
fingerlake projection that goes into ocean. Erosional, ex: snap bracelet --Can become sea cave--> sea stack --> erodes to nothing
answer
Headland
question
little pockets, get stuff that was eroded off headlands to make beach, behind headlands, get sand from headlands
answer
Pocket Beach
question
strip of sand that connects sea stack to main land, depositional
answer
Tombolo
question
in the summer and winter, earth is titled completely winter solstice - sometimes 24 hours of darkness summer solstice - 24 hours of sun
answer
Solstice
question
spring and fall
answer
equinox
question
air rises
answer
Low pressure
question
dry
answer
arid
question
all seasons (MN) - winters are super cold, summers are super hot
answer
temperate
question
hot, humid, moist - around the equator
answer
tropical
question
ITCZ & STH
answer
what are zones are complete opposites?



