IB Biology Topic 9: Plant Biology HL
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion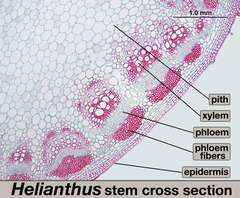
Xylem

answer
part of vascular bundle that is responsible for the transports water throughout the plant - no membrane or organelles are present.
question
Pores
answer
are present allowing water to leave the xylem to cells.
question
Lignen
answer
is laid down in rings around the cellulose cell wall. this adds strength (to resist pressure to the xylem)
question
Lumen
answer
is filled with sap (water + minerals).
question
Roots
answer
roots anchor the plants in the ground, and absorb minerals (by active transport) and water (osmosis) roots provide a large surface area due to branching and root hairs (extension of cells)
question
Absorption of minerals (roots)
answer
-there is usually a higher concentration of minerals within root cells than in the soil. - root cells use active transport to move minerals from the soil into the root cells. -there are lots of mitochondria in the root cells to produce ATP for active transport. - specific protein pumps are present in the plasma membrane of root cells, which actively transport the minerals into the cytoplasm.
question
Absorption of water
answer
-there is a high concentration of minerals in the cytoplasm of root cells due to active transport - water moves from the low solute concentration in the soil, through plasma membranes of root cells to the high solute concentration in the root cells's cytoplasm, by osmosis. - the water (and minerals) moves to the root xylem.
question
(Evapo) Transpiration
answer
the loss of water from leaves and other organs of the plant in the xylem
question
Stomata
answer
pores at the bottom surface of leaves which allow water to vaporise out of the leaf
question
The process of transpiration
answer
1) water evaporates from cells within the leaf. the water vapour diffuses out of the lead through stomata. 2) the leaf cells replace the water lost by taking water from the xylem. this reduces the water pressure in the xylem (creating a partial vacuum). 3) water is "pulled" up along the xylem from high pressure in the roots. This is known as transpiration pull. 4) the flow of water in the xylem ( transpiration stream( continues to flow because: a) water is cohesive (water is a polar molecule which forms hydrogen bonds) b) water adheres to the cellulose walls of the xylem. c) the lignified xylem walls are able to withstand pressure.
question
Abiotic factors affecting transpiration
answer
1) Temperature: as temp increases, the water particles gain kinetic energy and diffuse faster. 2) Humidity (concentration of water in the air): If humidity is low, the water diffuses quickly out of the leaf. If humidity is high, water diffuses slower. 3) Wind: increasing wind usually increases the rate of transpiration.
question
Xerophytes
answer
are plants that have been adapted to tolerate dry conditions (eg. cacti)
question
Xerophyte adaptations
answer
- water storage tissue - the leaves are modified into needles, decreasing surface area for transpiration - reduces number of stomata - vertical stems to allow them to absorb maximum sunlight during morning and evening. - thick waxy cuticles to prevent evaporation of water. - CAM physiology: a version of photosynthesis where the stomata open at night (to get CO2) but stay closed during the day.
question
Halophytes
answer
are plants adapted to survive in saline (high salt) conditions.
question
Phloem
answer
part of vascular bundle that transports the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant
question
Phloem structure
answer
photo ! - sieve tubes - sieve plates - companion cells - plasmodesmata
question
Translocation
answer
organic compounds (eg sugars + amino acids- are transported in plants from sources to sinks through the phloem.
question
Sieve plates
answer
between the sieve tube cells, which makes it easier for fluids to flow through the phloem
question
Plasmodesmata
answer
narrow companion cells and sieve tubes.
question
Companion cells
answer
- maintain the sieve tubes - have many mitochondria to produce ATP for active transport of organic compounds into sieve tubes.
question
Sources
answer
can be photosynthesising leaves, or storage organs (such as roots) releasing their store of nutrients.
question
Sink
answer
can be storage organs where nutrients are stored, growing leaves, flower, fruit.
question
Sieve tubes
answer
- form a column of cells - have a plasma membrane so that sugar concetration can be controlled. - does not have a nucleus and not many organelles, so that fluid can flow easily.
question
Process of translocation
answer
1) sucrose is produced in the leave (a source) by photosynthesis. The sucrose is actively transported into sieve tubes by companion cells. 2) water from the xylem moves into the phloem by osmosis (due to the high sucrose concentration, creating high pressure) 3) the water moving into the phloem;s sieve tubes pushes the water (containing sucrose) towards the sink. This occurs de to water being incompressible. 4)the fluid in the sieve tubes is pushed towards the sink. 5) the sucrose is then actively transported from the sieve tube into the source cells (eg. storage cells in the root) 6) the sucrose can be used for growth, converted to starch for storage, or respiration.
question
Tropism
answer
directional growth or movement of a plant towards or away from stimulus
question
Phototropism
answer
Directional growth of a plant towards or away from light.
question
Auxin
answer
plant hormone that promotes growth in the shoot of plants. auxin is produced by the shoot tips.
question
Process of photo tropism
answer
1) light is detected by pigments found in plants including phototropins. When these detect differences in (blue) light in the short tip, they trigger the movement of auxin by active transport. 2) Auxin efflux pumps are located in the plasma membrane of cells in the shoot. The auxin efflux pumps are used to actively transport auxin through cell from the light side of a plant to the shaded side. NOTE: auxin efflux pumps are moved to ensure that auxin is moved towards the shaded side 3) Auxin receptors (proteins) are found within the plasma membrane of cells. Auxin binds to the receptor. This causes changes within the cell that causes certain growth genes to be expressed. This results in the release of H+ into the cell walls. This loosens connections between cellulose, allowing the cells to grow.
question
Meristem
answer
- tissue in a plant consisting of undifferentiated cells which can differentiate into other plant cells, and undergo mitosis and cell division. - responsible for growth of a plant
question
Lateral meristem
answer
- tissue in a plant responsible for growth in width - found between xylem and phloem
question
Micropropagation of plants
answer
produces many genetically identical plants in a short period of time.
question
Flower structure
answer
Female [carpel] - anther - filament - petals Male [stamen] - stigma - style - ovary - sepals
question
carpel
answer
female reproductive organs of an angiosperm
question
anther
answer
male reproductive organs of a plant that produces pollen
question
filament
answer
stalk of stamen that holds up the anther
question
petals
answer
attract pollinators for pollination with colours
question
stamen
answer
???
question
sepal
answer
protect the developing flower while in the bud
question
style
answer
structure of carpel that holds up the stigma
question
ovary
answer
base of carpel in which the female sex cells develop
question
stigma
answer
sticky top of carpel on which pollen lands
question
Pollination
answer
- the transfer of pollen grains from the male anther to the female stigma. - the pollen contains sperm - often facilitated by animals, wind or water movement.
question
Fertilisation
answer
- fusion of the male gamete(sperm) with the female gamete(egg) to form a zygote. - In plants, pollen lands on the stigma. It germinates and grows down through the style to the ovary. - the zygote develops into a seed.
question
Seed dispersal
answer
when a seed, formed from a fertilised ovule, is moved away from the parental plant to reduce competition for resources.
question
Germination of seeds
answer
all seeds require oxygen (for aerobic respiration), water (most metabolic reactions occur in water) and a suitable temperature (required for the enzyme involved in germination) some seeds require other conditions such as light, fire, frost before they will germinate.



