GI – Liver: Cirrhosis, Cancer, PBC, PSC – PPT/Book – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Define liver cirrhosis.
answer
1. Slowly progressive. 2. Formation of fibrous and scar tissue that replaces hepatocytes. 3. Portal blood flow impaired.
question
Most of the clinical features of liver cirrhosis develop as a result of what 3 things?
answer
1. Portal hypertension. 2. Hepatocellular dysfunction. 3. Altered cellular differentiation.
question
3 most common causes of cirrhosis in industrialized nations.
answer
1. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 2. Alcoholic liver disease. 3. Hepatitis C.
question
True or False: Many people with cirrhosis at presentation have no readily identifiable cause.
answer
True.
question
Pathophysiology of cirrhosis.
answer
1. Hepatocytes die and release inflammatory markers. 2. Inflammatory markers cause stellate cells to differentiate to fibroblasts. 3. The fibroblasts lay down collagen/connective tissue in interspace of diss, resulting in fibrosis. 4. Sinusioid is compressed and gets smaller. 5. Nodules of fibrous tissue with foci of regenerating hepatocytes forms with rearrangement of blood vessels. 6. Disruption of normal hepatic lobular architecture and vascular bed leads to portal hypertension and shunting.
question
Fibrosis in the liver usually begins where?
answer
Around the portal area.
question
True or False: The symptoms of liver cirrhosis are often nonspecific in the early stages and progress to a wide array of signs and symptoms in various systems.
answer
True.
question
The diagnosis of liver cirrhosis can reliably be made by a combination of clinical, laboratory, and radiological findings in most cases. However, what is the gold standard?
answer
Liver biopsy. *However more often now doen to assess stage and severity of disease.
question
MRI findings supportive of cirrhosis.
answer
1. Relative enlargement of left hepatic and caudate lobes as a result of right lobe atrophy. 2. Surface nodularity. 3. Portal hypertension features such as ascites, intra-abdominal varices, and splenomegaly.
question
One of the many deficiencies in liver cirrhosisi will be deficient vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Which factors are these?
answer
II, VII, IX, X.
question
Bulging flanks and shifting dullness suggest what?
answer
Ascites.
question
Cirrhotic ascites is ultimately a result in what?
answer
An increase in total blood sodium and water.
question
What imaging is used to screen for ascites? Confirm it?
answer
*Ultrasound to screen. *Parecentesis to confirm.
question
What serum-asciteis albumin gradient [SAGG] level correlates with protal hypertension as the likely cause of fluid accumulation?
answer
Elevated SAGG >1.1 g/dL [calculated by serum albumin concentration - ascitic fluid albumin concentration].
question
Ascites becomes clinically detectable with fluid accumulation greater than what?
answer
500 mL.
question
Treatment of cirrhotic ascites if caused by portal hypertension.
answer
1. Diuretics to stimulate renal sodium loss. 2. Monitor diuresis closely for electrolyte disturbances and hypovolemia.
question
Refractory ascites will occur in what percent of cirrhotic patients despite maximal diuretic therapy?
answer
10%. *Must be treated with paracentesis, colloid expansion with albumin, TIPS, and eventually transplant.
question
2 scoring/classification systems for liver cirrhosis.
answer
1. Child-Turcotte-Pugh Classification 2. MELD score.
question
The Child's score takes into acount what 5 things?
answer
1. Encephalopathy. 2. Ascites. 3. Bilirubin. 4. Albumin. 5. PT/INR.
question
What are the Child classes for severity of Cirrhosis and what points correspond to each.
answer
Class A = 5-6 points, least severe. Class B = 7-9 points, moderately severe. Class C = 10 to 15 points, most severe. **Note, each criteria is scored 1 to 3 and then all scores are added.
question
Which is used more often, the MELD score or Child's Score?
answer
MELD score.
question
3 things used to calculate the MELD score.
answer
1. Bilirubin. 2. INR. 3. Creatinine concentration.
question
What does the MELD score specifically predict? How is it used?
answer
*30 day mortality. *Used to stratify those on the liver transplant list.
question
The MELD score ranges from 6 to 40. When are patients typically considered for liver transplantation?
answer
*15. *Average score at which patients undergo transplantation is age 20.
question
What is the 5 year survival rate for liver transplants?
answer
70-80%, usually with good quality of life.
question
What is the most common indication for liver transplant in the U.S.?
answer
Hepatitis C etiology.
question
What is the most common type of liver cancer?
answer
Hepatocellular carcinoma.
question
What is the cancer marker for hepatocellular carcinoma?
answer
Alpha-fetoprotein.
question
Prognosis with hepatocellular disease.
answer
*With transplant/resection - 70% 5 year survival. *Widespread, multifocal = 5% 5 year survival rate.
question
What is the most common benign tumor of the liver? What is it?
answer
Hepatomangioma: *Area of liver where the blood cells multiple and form a ball.
question
What is the most common benign, non-vascular liver tumor? What is it?
answer
Fibronodular hyperplasia: *Localized area of hyperplasia with cells becoming more numerous. *Secondary to vascular injury. *Central vein with fibrosis around it = central scar.
question
What is an adenoma of the liver? What is it associated with?
answer
*Enlarged liver cells that are highly vascular [don't biopsy]. *Associated with estrogen and BCP.
question
Primary biliary cirrhosis is associated with [intrahepatic/extrahepatic/both] bile duct involvement
answer
Intrahepatic. *Destruction of small and medium bile ducts.
question
Primary biliary cirrhosis is more common in [females/males].
answer
Females.
question
3 symptoms of PBC secondary to destruction of small bile ducts.
answer
1. Xanghoma from cholesterol back up. 2. Juandice from bilirubin back up. 3. Itching from bile salt back up.
question
What is the rule of 90's for PBC?
answer
90% female. 90% have isolated elevation of alk. phos. 90% have positive Anti-mitochondrial ab [AMA].
question
What is the onset of PBC?
answer
Insidious between age of 40 and 60.
question
A patient with PBC is usually [asymptomatic/symptomatic] at presentation.
answer
Asymptomatic. *Isolated elevation of alk phos might be only clue before the work-up.
question
True or False: There is no familial link for PBC.
answer
False. Like many autoimmune diseases there is an increase risk among first degree relatives.
question
4 risk factors for PBC.
answer
1. Family history. 2. Smoking. 3. Hormone Replacement Therapy.
question
Which other autoimmune disorders are highly correlated with PBC?
answer
1. Celiac. 2. CREST. 3. Sjogren's. 4. Autoimmune thyroid disease. 5. Calcinosis. 6. Raynauds. 7. Esophageal dysmotility. 8. Sclerdactyly. 9. Telangiectasia.
question
What is the hallmark serology finding for PBC?
answer
Positive AMA.
question
Elevated bilirubin is a[n] [early/late] finding of PBC.
answer
Late.
question
Diagnosis of PBC is confirmed how?
answer
Liver biopsy.
question
PBC can lead to what 2 things?
answer
1. Progressive cholestasis. 2. Cirrhosis.
question
4 stagese of PBC.
answer
1. Asymptomatic. 2. Symptomatic. 3. Cirrhotic stage. 4. Liver failure.
question
Treatment of PBC
answer
1. Suppression of underlying pathogenic process with ursodeoxycholic acid. 2. Management of symptoms and complications [naloxone for itching]. 3. Hepatoma surveillance. 4. Might also consider steroids and colchicine.
question
What is the only drug for PBC that has been shown to slow progression, increase survivial rate, and prolong time to transplant?
answer
Ursodeoxycholic Acid.
question
Primary Sclerosing cholangitis affects [extrahepatic/intrahepatic/both] ducts.
answer
Intra and extrahepatic ducts.
question
What is primary sclerosis cholangitis?
answer
Segmental inflammation leading to fibrosis of bile ducts.
question
PSC most commonly occurs in what demographic?
answer
Men younger than 45.
question
About 70% of PSC patients also have which other autoimmune disorder?
answer
Ulcerative colitis [which usually occurs first]
question
How is the diagnosis of PSC made?
answer
MRCP or ERCP.
question
Which autoimmune marker is elevated in PSC?
answer
PANCA antibody.
question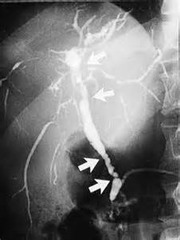
What is the characteristic pattern fibrosis in PSC?

answer
*Circumferential and segmental. *Leads to alternating areas of stricture and non-stricture, giving it a beaded appearance.
question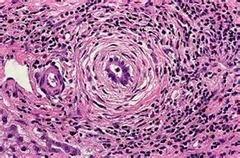
How can the histologic appearance of PSC be described?

answer
Onion skinning around the bile ducts.
question
What is the usual time to death from diagnosis in both PSC and PBC?
answer
About 12 years.
question
Most patients with PSC eventually progress to what?
answer
End stage liver disease.
question
3 complications of PSC.
answer
1. Cholestasis with biliary cirrhosis. 2. Recurrent cholangitis. 3. Colangiocarcinoma [30-40%].
question
What are lab abnormalities in PSC?
answer
1. Elevated alk phos. 2. AST/ALT mildly elevated. 3. pANCA [sensitive but not specific].
question
Symptoms of PSC.
answer
Similar to PBC: 1. Fatigue. 2. Pruritis. 3. Jaundice. *Most are asymptomatic at presentation.
question
True or False: No treatment for PSC slows disease.
answer
True.
question
Why is surgery avoided in PSC?
answer
Because it is segmental. [similar to Chron's].
question
Cholangitis associated with PSC can be treated how?
answer
Antibiotics and ERCP with stricture dilation.
question
What can be given to PSC patietns to help bind bile salts?
answer
Cholestyramine.
question
This drug is used in PBC, but can also improve lab values in PSC.
answer
ursodeoxycholic acid.
question
What is congestive hepatomegaly.
answer
Liver filled with blood.
question
What is steatotic hepatomegaly.
answer
Liver filled with fat.
question
What are the symptoms of hepatomegaly?
answer
Diffuse, dull discomfort in the RUQ secondary to stretching of the liver capsule.



