Genetics – Genetics Test Answers – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
genetics
answer
the study of heredity
question
heredity

answer
the passing of traits from one generation to the next
question
trait
answer
a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
question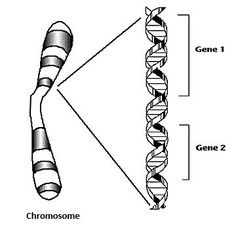
gene

answer
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
question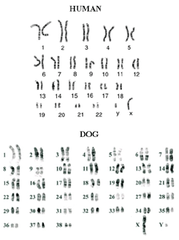
genome

answer
the entire "library" of genetic instructions in DNA that an organism inherits
question
Gregor Mendel

answer
father of genetics
question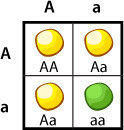
allele

answer
alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) located at a specific position on a specific chromosome (a letter)
question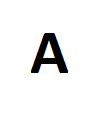
dominant allele
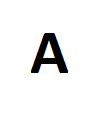
answer
an allele that produces the same phenotype whether its paired allele is identical or different (capital letter)
question
recessive allele

answer
an allele that produces its characteristic phenotype only when its paired allele is identical (lowercase letter)
question
genotype

answer
the combination of alleles located on homologous chromosomes that determines a specific characteristic or trait (the allelic combination such as Bb)
question
phenotype

answer
the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism, as determined by the genotype (the expressed trait such as brown eyes)
question
homozygous

answer
term used to refer to an organism that has two identical alleles for the same trait (ex. BB or bb)
question
heterozygous

answer
term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles for the same trait (ex. Bb)
question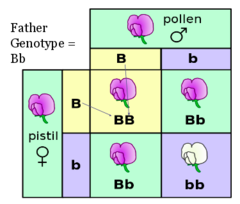
Punnett square

answer
diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross
question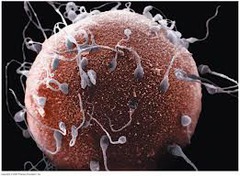
gamete (sex cell)

answer
specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction (sperm or egg)
question
probability

answer
the possibility of different outcomes (percentage or ratio)
question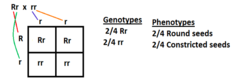
monohybrid cross

answer
a one-trait cross (ex. color)
question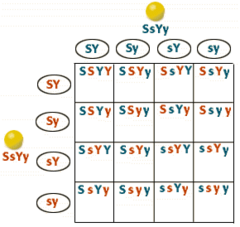
dihybrid cross

answer
a two-trait cross (ex. color & shape)
question
P generation

answer
parental generation is the first generation involving two individuals that are mated to predict or analyze the genotypes of their offspring
question
F1 generation

answer
first filial generation is the generation resulting immediately from a cross of the first set of parents (P generation)
question
F2 generation

answer
second filial generation is the generation resulting from a cross between two F1 individuals
question
purebred

answer
offspring that are the result of mating between genetically similar kinds of parents; opposite of hybrid; same as true breeding
question
hybrid

answer
offspring that are the result of mating between two genetically different kinds of parents; opposite of purebred
question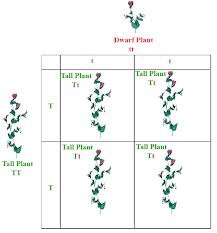
Principle of Dominance

answer
when individuals with contrasting traits are crossed, the offspring will express only the dominant trait
question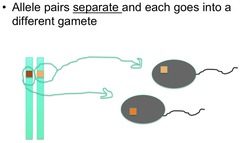
Law of Segregation

answer
states that allele pairs separate, or segregate, during gamete formation
question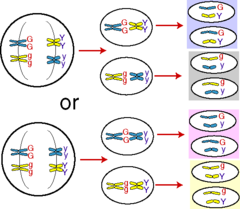
Law of Independent Assortment

answer
states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
question
non-Mendelian inheritance

answer
refers to any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws (ex. incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, sex-linked traits)
question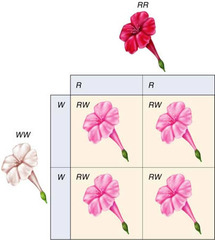
incomplete dominance

answer
when one allele is not completely dominant over the other, or blending occurs (ex. Red + White = Pink)
question
codominance

answer
occurs when BOTH alleles of a gene are expressed in an individual (ex. Black + White = Black & White Speckled)
question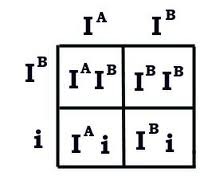
multiple allele traits

answer
traits that are controlled by more than two alleles (ex. ABO blood typing = A allele, B allele, & O allele)
question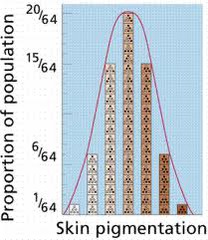
polygenic traits

answer
a trait controlled by two or more genes; produce a wide range of phenotypes
question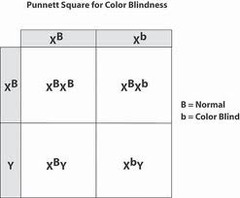
sex-linked traits

answer
a trait genetically determined by an allele located on the sex chromosome
question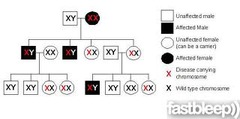
pedigree chart

answer
a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance or phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next
question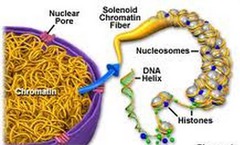
chromatin

answer
unraveled and long DNA (during interphase)
question
chromosome

answer
condensed, coiled, and shorted DNA (this occurs during mitosis and meiosis)
question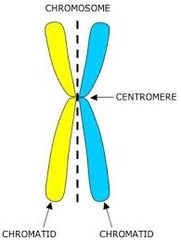
chromatids

answer
the two identical halves of a single replicated eukaryotic chromosome and joined at the centromere
question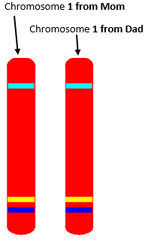
homologous chromosomes

answer
chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, with genes for the same characteristics at corresponding places (one homologous chromosome is inherited from the mother; the other from the father)
question
daughter cells

answer
new cells
question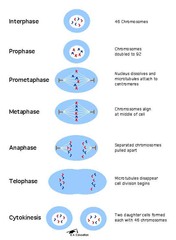
mitosis

answer
a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells each with the same number of chromosomes of the parent cell
question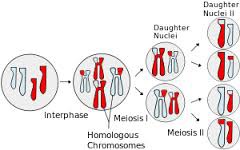
meiosis

answer
a type of cell division that results in four genetically different daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell (also known as reduction division)
question
sexual reproduction

answer
process by which two cells from different parent unite to produce the first cell of a new organism
question
asexual reproduction

answer
process by which a single parent reproduces by itself
question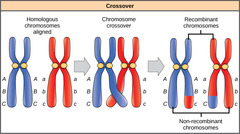
crossing over

answer
process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis (also called gene shuffling)
question
genetic variation

answer
genetic differences within a species
question
fertilization

answer
a process in sexual reproduction in which a sperm unites with an egg to make the first cell of a new organism, or zygote
question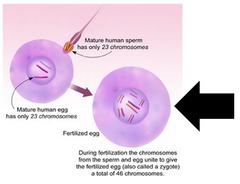
zygote

answer
fertilized egg
question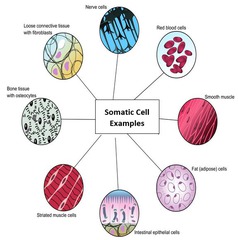
somatic cell

answer
body cell (non-sex cell)
question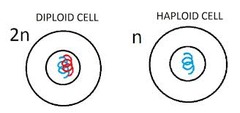
haploid (N)

answer
term used to refer to a cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes and therefore only a single set of genes (Humans N = 23)
question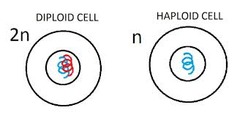
diploid (2N)

answer
term used to refer to a cell that contains both sets of homolgous chromosomes (Humans 2N = 46)
question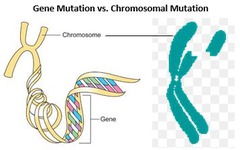
chromosomal mutation

answer
mutation that affects the number or structure of whole chromosomes
question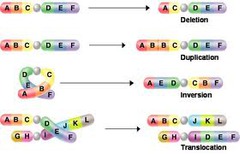
deletion chromosomal mutation

answer
a mutation that involves the loss of all or part of a chromosome
question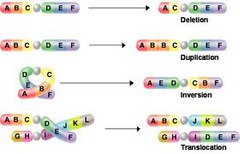
duplication chromosomal mutation

answer
a mutation that produces extra copies of parts of a chromosome
question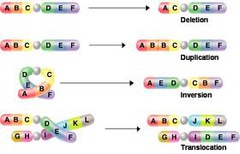
inversion chromosomal mutation

answer
a mutation that reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome
question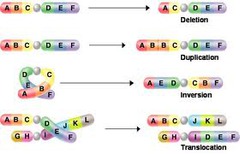
translocation chromosomal mutation

answer
a mutation that occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome
question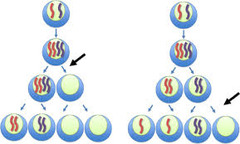
nondisjunction

answer
the most common error in meiosis and occurs when homologous chromosomes fail to separate
question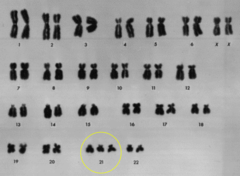
trisomy

answer
a condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nuclei, causing developmental abnormalities
question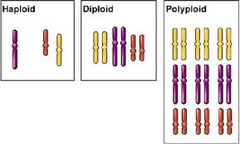
polyploidy

answer
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes because a complete set of chromosomes failed to separate during meiosis (ex. 3N or 4N)
question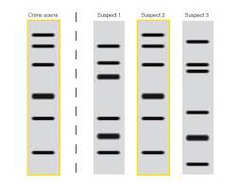
DNA fingerprinting

answer
an individual's unique sequence of DNA base pairs, determined by exposing a sample of the person's DNA to molecular probes
question
genetic engineering

answer
the process of making changes in the DNA code of living organisms
question
genetically modified organism (GMO)

answer
one that has artificially acquired one or more genes from the same or different species
question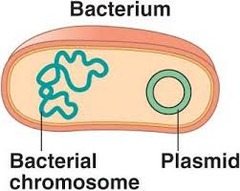
plasmid

answer
circular DNA found in bacteria
question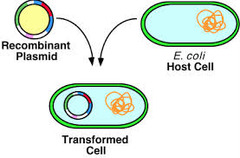
recombinant DNA

answer
DNA produced by combining DNA from different organisms (DNA is cut out of one organism and recombined with another organism's DNA)
question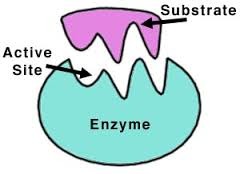
enzyme

answer
protein that speeds up chemical reactions in organisms
question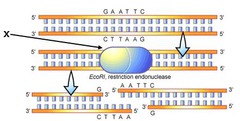
restriction enzyme

answer
DNA-cutting enzymes found in bacteria
question
biotechnology

answer
the use of living organisms or other biological systems in the manufacture of drugs or other products or for environmental management, as in waste recycling
question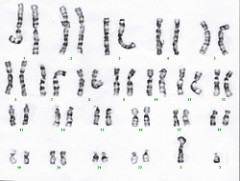
karyotype

answer
a picture of an organism's genome and can be used for chromosomal anlysis



