endocrine cancer/ diseases – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
pituitary adenoma
answer
benign -anterior pituitary funcional (hormones) or non functional nonfunctional - bitemporal hemianopsia, hypopituitarism, headache
question
prolactinoma
answer
females: galactorrhea and amenorrhea males: decreased libido tx: dopamine agonist to suppress prolactin (bromocriptine)
question
growth hormone cell adenoma
answer
children: gigantism adults: acromegaly -secondary diabetes mellitus tx: somatostatin analogue (octreotide)
question
hypopituitary
answer
dec ant pituitary hormones (FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, prolactin, GH) causes: 1) pituitary adenoma 2) sheehan syndrome (infarction during parturition) (poor lactation, loss of pubic hair, fatigue) 3) empty sella syndrome - congenital defect (herniation of arachnoid)
question
T1DM
answer
insulin defficiency -> hyperglycemia -autoimmune destruction of T lymphocytes (inflam of islets) -HLA-DR3 and DR4 symp: high serum glucose, weight loss, low muscle mass, polyphagia 3 P's (polyuria, polydipsia, glycosuria)
question
diabetic ketoacidosis
answer
excessive serum ketones -arrises with stress, epinephrine stimulates glucagon secretion -> inc lipolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis -causes increase ffa -> liver converts to ketone bodies symp: kussmaul respirations (trying to blow off metabolic acidosis), dehydration, naus/vom, fruity breath smell, mental changes
question
T2DM
answer
-end organ insulin resistance (Decreased number of insulin rec) -early on insulin levels inc -> Beta cell exhaustion -> amyloid deposits random glucose >200 fasting glucose > 126
question
central DI
answer
ADH deficiency symp: polyuria, polydipsia, hypernatremia, high serum osmolality, low urine osmolality -water deprivation test does NOT increase urine osmolality tx: desmopressin (ADH analog)
question
nephrogenic DI
answer
impaired renal response to ADH symp: polyuria, polydipsia, hypernatremia, high serum osmolality, low urine osmolality -water deprivation test does NOT increase urine osmolality DOES NOT respond to desmopressin
question
consequences of diabetes
answer
1) nonenzymatic glycosylation of vascular BM (atherosclerosis) large/med arteries ->cardio, peripheral vascular disease (hyaline arteriosclerosis) small arteries -> glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome (kimmelstiel-wilson nodules) 2) osmotic damage -glucose enters schwann cells -> aldose reductase converts glucose to sorbitol (peripheral neuropathy, blindness, impotence, cataracts)
question
pancreatic endocrine neoplasms
answer
1) insulinomas - episodic hypoglycemia w/ mental status change (inc insulin and c-peptide) 2) gastrinoma - zollinger ellison - peptic ulcers 3) somatostatinoma- achlorhydria, cholelithiasis w/ steatorrhea 4) VIPomas -watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, achlorhydria
question
SIADH
answer
-excessive ADH (ectopic production -small cell cancer) -retention of water symp: hyponatremia, low serum osmolality -mental status change and seizure (hyponatremia -> neuronal swelling -> cerebral edema) tx: water restriction, demeclocycline
question
hyperthyroid
answer
-increase basal metabolic rate -increase sympathetic nervous system activity ex: Grave's disease, multinodular goiter
question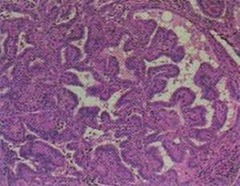
Grave's

answer
autoAb (IgG) to TSH receptor -> inc synthesis and release of thyroid hormone women 20-40 -thyroid hyperplasia, exophthalmos, -pretibial myxedema -irregular follicles, scalped colloid, chronic inflam lab: inc total and free T4, dec TSH, hypocholesterolemia, inc serum glucose
question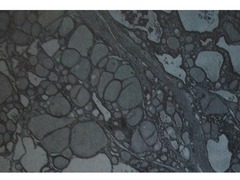
multinodular goiter

answer
enlarged gland w/ multiple nodules -due to iodine deficiency -usually nontoxic but may become TSH independent
question
cretinism
answer
hypothyroid (neonates and infants) -mental retardation, short stature, skeletal abnormalities, coarse facial features, enlarged tongue, umbilical hernia cause: maternal hypothyroid, thyroid agenesis, dyshormonogenetic goiter, iodine deficiency
question
myxedema
answer
hypothyroid (children or adults) -decreased basal metabolic rate and symp nervous system symp: accumulation of glycosaminoglycans in skin and soft tissue, results in deepening of voice and large tongue cause: iodine def, hashimoto's
question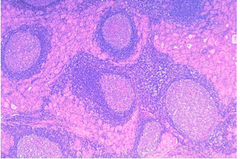
Hashimoto

answer
autoimmune destruction of thyroid (HLA-DR5) -initially can be hyperthyroid and then progresses to hypo -inflam w/ germinal centers and Hurthle cells labs: dec T4 and inc TSH
question
De Quervain (subacute granulomatous thyroiditis)
answer
-thyroiditis following a viral infection TENDER thyroid (self-limiting)
question
Riedel fibrosing thyroiditis
answer
chronic inflam w/ extensive fibrosis HARD "as wood" nontender thyroid
question
131 I radioactive uptake
answer
increased uptake: "hot nodule" - graves or nodular decreased uptake: "cold nodule" - adenoma and carcinoma
question
follicular adenoma
answer
benign -fibrous capsule -usually nonfunctional
question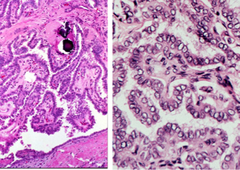
papillary carcinoma

answer
risk: radiation exposure, RET, BRAF -most common -orphan annie eye nuclei -nuclear grooves -psammoma bodies -often spreads to cervical nodes but good prognosis
question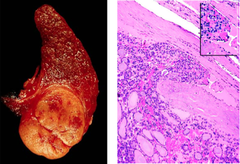
follicular carcinoma

answer
-malignant follicles surrounded by fibrous capsule w/ invasion through capsule -hematogenous metastasis
question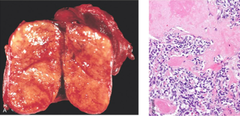
medullary carcinoma

answer
risk: MEN 2A and 2B (RET oncogene) -proliferation of parafollicular C cells (neuroendocrine cells - secrete calcitonin) -hypocalcemia (calcitonin inc renal excretion of Ca) -calcitonin deposits in tumor as AMYLOID -hematogenous spread
question
anaplastic carcinoma

answer
-elderly -invades locally -> dysphagia or respiratory compromise -undifferentiated poor prognosis
question
thyroglossal duct cyst
answer
remnant of thyroid tissue along migration path from base of tongue
question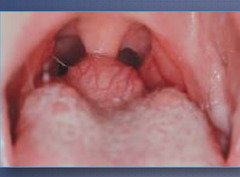
lingual thyroid

answer
persistence of thyroid at base of tongue -mass at base of tongue
question
parathyroid adenoma
answer
benign primary hyperparathyroidism -asymptomatic hypercalcemia -can have increased PTH and hypercalcemia problems 1) nephrolithiasis 2) nephrocalcinosis (calcification of renal tubules) 3) CNS disturbance 4) constipation, peptic ulcer, acute pancreatitis 5) osteitis fibrosa cystica (resorption of bone) inc PTH, Ca, urinary cAMP and alkaline phosphatase dec phosphate
question
hypoparathyroid
answer
low PTH causes: autoimmune damage, surgical excision, DiGeorge syndrome symp: low serum Ca -numbness and tingling -muscle spasm (trousseau or chvostek sign)
question
lymphoma
answer
assoiciated with hashimoto thyroiditis
question
Neuroblastoma
answer
-adrenal tumor of CHILDREN - N-myc -from neural crest cells --> occur anywhere along sympathetic chain symp: -abdominal distention, firm mass that can cross the midline -opsoclonus-myoclonus dx: -HVA and VMA in urine -homer-wright rosettes -bombesin and enolase +
question
pheochromocytoma

answer
-adrenal medulla tumor of ADULTS -NF1, MEN 2A, 2B, VHL -from chromaffin cells from neural crest symp: episodic HTN (Ep, Nep, Dopamine secretion) -5 Ps (pressure, pain, perspiration, palpitations, pallor) dx: inc catecholamins and metanephrines in urine (VMA) tx: a-antag (phenoxybenzamine) follow with b blocker
question
insulinoma
answer
pancreatic B cell tumor -overproduction of insulin --> hypoglycemia -increased C-peptide level whipple triad - low blood glucose, hypoglycemia (syncope, diplopia), resolution of symptoms after normalization of glucose tx: surgery
question
carcinoid syndrome
answer
-neuroendocrine -metastatic small bowel tumor to liver (secrete 5HT) symp: -diarrhea, flushing, wheezing, right side valve disease -rule of 1/3 -uniform shape and size w/ eosinophilic cyto and dense core granules in cytoplasm -rosettes dx: inc 5-HIAA, niacin deficiency (pellagra)
question
zollinger-ellison
answer
gastrin secreting pancreatic or duodenum tumor MEN-1 symp: -recurrent ulcers in duodenum/jejunum (refractory to therapy and beyond duodenal bulb (H pylori before)), abdominal pain, diarrhea dx: + secretin test (gastrin levels remain elevated)
question
MEN 1
answer
parathyroid, pituitary (prolactin, GH), pancreatic (zollinger, insulinoma, VIPoma, glucagonomas)
question
MEN 2A
answer
RET parathyroid hyperplasia, pheochromocytoma medullary thyroid carcinoma
question
MEN 2B
answer
RET pheochromocytoma medullary thyroid carcinoma, ganglioneuromatosis -marfan habitus
question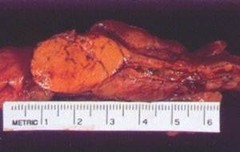
adrenocortical adenoma

answer
cause primary hyperaldosteronism (conn syndrome) -well defined yellowish tumor of the adrenal cortex symp: renal Na retention and loos of K and H --> HTN, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis (paresthesia and muscle weakness)
question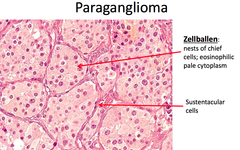
paraganglioma

answer
clusters of neuroendocrine cells -extra adrenal paragangliomas occur in head and neck nested zellballen pattern, benign but recur -may be familial (MEN) adrenal: pheochromocytoma (symp) nonadrenal: zucherhandle (symp) carotid body (parasymp)
question
thymoma

answer
primary mediastinum tumor -epithelial tumor w/ lymphocytes (T cells) -round or spindle cells -anterior mediastinal mass - paraneoplastic MG ** (AcH rec autoAb)
question
hyperaldosteronism
answer
HTN (inc Na expands plasma volume), hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis -no edema due to aldosterone escape cause primary: adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal adenoma (conn's) cause secondary: activation of renin-angio system
question
liddle syndrome
answer
decreased degradation of Na channels in collecting tubules -HTN, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis -low aldosterone and renin
question
cushing
answer
excess cortisol -muscle weakness, thin extremeties, moon facies, buffalo hump, truncal obesity, abdominal striae, HTN, high insulin, osteoporosis, dx: 24 hr urine cortisol, late night salivary cortisol (both increased) -late night dexamethasone suppression test (fails to suppress cortisol)
question
21-hydroxylase deficiency
answer
-aldosterone and cortisol decreased -androgens increased symp: hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, hypovolemia, salt wasting and life threatening hypotension -female neonates - genital ambiguity
question
11-hydroxylase deficiency
answer
-cortisol decreased -weak mineralcorticoids increased -increased androgens -low aldosterone and renin
question
17-hydroxylase deficiency
answer
-decreased cortisol and androgens -weak mineralcorticoids are increased -> HTN -renin and aldosterone are low -primary amenorrhea - lack of pubic hair in females or pseudohermaphroditism in males
question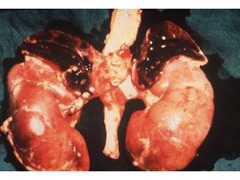
adrenal insufficiency

answer
1) waterhouse friderichsen - hemorrhagic necrosis (DIC with Neisseria Meningitidis) 2) chronic (Addison disease) - autoimmune, TB, metastatic carcinoma destruction of adrenal glands -hyperpigmentation and hyperkalemia (primary)



