Voltaic Cell with Electrolyte Solution
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
a device that sets up a spontaneous chemical reaction to produce electricity by using a barrier to separate the oxidation and reduction reactions.
answer
voltaic cell
question
a solid material that conducts electricity that must be present to provide a site for each half-reaction -commonly a meta immersed in an electrolyte solution containing a salt of the same metal
answer
electrode
question
the electrode at which OXIDATION OCCURS (loss of electrons)
answer
anode (-)
question
the electrode at which REDUCTION OCCURS (gain of electrons)
answer
cathode (+)
question
allows ions to flow so charge balance is maintained -electricity will not flow unless there is a complete circuit between the anode and the cathode.
answer
salt bride
question
process of passing electric current to cause a nonspontaneous redox reaction to occur *Used to stop corrosion*
answer
electrolysis (electroplating)
question
slow deterioration of metals due to interaction with the environment *odixation-reduction reaction*
answer
corrosion
question
diatomic metal (have nO fear....) atomic number: 8 atomic mass: O?- O?- electron configuration:
answer
atomic mass 16 oxygen ozone 1s² 2s² 2p?
question
What is the #1 abundant element in the universe? 75% typically found in compounds -pH scale (acidosis- excess/ alkalosis-deficient)
answer
hydrogen (H)
question
what is the #2 most abundant element in the universe
answer
Helium (He)
question
what is the #4 most abundant element in the universe? 2nd most abundant element in the human body common element of all known life -typically found in compounds (rarely atomic)
answer
Carbon (C)
question
diatomic metal (Have no fear....) atomic number: atomic mass: 1 H? electron configuration:
answer
Hydrogen atomic number: 1 atomic mass: 1 H?- hydrogent gas electron configuration: 1s¹
question
diatomic metal (have no fear...of ice Cold...) atomic number: atomic mass: 12 solid- graphite solid-diamond electron configuration:
answer
Carbon atomic number: 6 atomic mass: 12 H?- hydrogent gas electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p² (6 electrons mean 4 for bonding)
question
all gases have relatively ______ densities in comparison to liquids and solids, due to the large amount of empty space between molecules. how do we describe gases?
answer
low -by their density
question
the amount of force applied per unit area
answer
pressure
question
what are the factors that affect properties of gas (try and write out)
answer
vol, pressure, temperature, amount of particles (measured in mol)
question
relates gas volume and gas pressure, decreased volume creates increased pressure

answer
boyle's law
question
P?V?- ________ state P?V?-________ state If V is up than P is down (inspiration) if V is down and P is up (exhalation)
answer
starting resulting
question
as volume increases pressure ___________ and air flows _______ the lungs =______________
answer
decreases into inhalation
question
as volume _____________, pressure increases and air flows ______ the lungs = expiration
answer
decreases out
question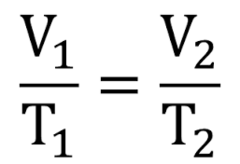
the relationship between the temperature and volume of gases *as the temperature increases, the volume increases* density inside lessens must use Kelvin for temperature.
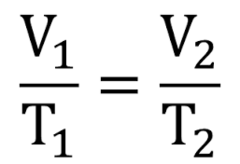
answer
Charles's Law p1
question
For a given amount of gas at a constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature on an absolute scale
answer
Charles's Law
question
gases combine in simple whole-number volume proportions at constant temperature and pressure
answer
Gay-Lussac's Law of Combining Volumes
question
The volume occupied by a gas at a given temperature and pressure is directly proportional to the number of gas particles and thus the moles of gas.
answer
Avogardo's hypothesis (Gay Lussac Law)
question
as the moles of gas increase the volume increases, direct linear relationship.
answer
Avogardo's hypothesis p2
question
at a given pressure and temperature, equal volumes of all gases contain equal number of moles or particles
answer
Avogardo's Hypothesis *most important*
question
Total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressure exerted independently by each gas in the mixture. (the partial pressure of each gas is directly proportional to its percentage in the mixture)
answer
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
question
Transfer of of Oxygen molecules from the lungs to the bloodstream is dependent on a pressure gradient. -pressure helps the oxygen molecules go across the alveolar membrane. *Higher the pressure gradient, the easier the molecule moves*
answer
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures, respiration
question
When a mixture of gases is in contact with a liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure. *as the pressure increases, the solubility increases* (soda is carbonated under high pressure)
answer
Henry's Law
question
When a gas is dissolved in a liquid, temperature increases, the solubility decreases
answer
Henry Law p1
question
CO2 most soluable O2 1/20th soluable of CO2 nitrogen is ______
answer
nitrogen practically insoluble in water
question
used to explain the behavior of gases and the properties of the gas laws
answer
kinetic molecular theory
question
-exist in all substances -it is the only intermolecular force present in NONPOLAR substances -result of temporary electron cloud distortions and temporary dipoles *All atoms and molecules*
answer
London Dispersion forces
question
polar molecules (permanent dipoles) attract one another *POLAR MOLECULES*
answer
dipole-dipole forces
question
two dipoles, one containing hydrogen bonded to an electronegative element, and the other containing electronegative containing element attract one and other.
answer
hydrogen bonding force
question
occurs when polar molecules containing unpaired electrons and a hydrogen bonded to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
answer
hydrogen bonding force 2
question
molecules with: H-F bonds H-O bonds H-N bonds
answer
hydrogen bonding force 3
question
What are the 6 main phase states- write them out
answer
1. evaporation 2. condensation 3. freezing 4. melting (fusion) 5. sublimation 6. deposition



