CSUS Nursing N113 MT1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Temperature - normal values
answer
97º-99ºF 36.1º-37.2ºC
question
Pulse - normal values
answer
60-100 bpm
question
Respiration - normal values
answer
12-20 breaths/min
question
BP - normal, elevated and HTN values
answer
<120/<80 - normal 120-129/ systolic OR 90 or > diastolic - HTN stage 2 >180 systolic and/or >120 diastolic - Hyptertensive crisis
question
Bradycardia vs. Tachycardia
answer
Low HR vs. High HR
question
Define "sounds of Korotkoff"
answer
Sound heard thru stethoscope applied to brachial artery distal to cuff of sphygmomanometer that changes with varying cuff pressure; used to determine systolic and diastolic BP
question
Why is it important to utilize the correctly sized BP cuff? How are results affected by a BP cuff that is too small? Too large?
answer
To obtain correct reading. If cuff too small, can cause systolic BP measurement to be higher than actual; too big can cause it to be lower than actual.
question
Identify changes in vital signs associated with aging.
answer
↑RR, ↑BP, ↓ temp,
question
PQRST
answer
Provokes - Quality - Radiates - Severity - Time
question
What is a general survey? What are 6 factors included?
answer
Descriptive impression of a patient including: 1) Overall health 2) Posturing 3) Grooming 4) Hygiene 5) Facial expression 6) LOC
question
What is purpose of ROM activities?
answer
Maintain joint flexibility to allow for optimal function and patient care.
question
Difference between AROM, AAROM and PROM?
answer
AROM = active range of motion; patients actively move joints AAROM = active assisted ROM; patients assisted in moving joints PROM = passive ROM; patients does not assist
question
Consequences of loss of ROM
answer
Loss of function; impaired function Increased risk of skin breakdown Poor hygiene
question
What are basic nursing assessments of musculoskeletal system?
answer
CMS, ROM, muscle strength Balance Coordination Upper and lower extremities
question
How does a nurse assess upper and lower extremities?
answer
Upper - RAM's (rapid arm movement) by patting hand to thigh, pronate and supinate rapidly. Lower - toe tapping; run heel down opposite shin
question
Normal posture
answer
Cervical - concave Thoracic - convex Lumbar - concave Sacral - convex
question
Abnormal posture
answer
Kyphosis - hunchback *ky -> shy = close yourself off Lordosis - swayback (ie pregnancy) Scoliosis - S-shaped curvature of spine https://healthsurgical.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/abnormal-curvature-of-the-spine.jpg
question
Abnormal gait types (5)
answer
Propulsive - leaning forward, fast-paced, short steps Scissor - legs cross, short steps Spastic - jerking movements Waddling - twisting foot movements Steppage - foot drop, foot does not pronate
question
Definition of death
answer
Complete cessation of respiration, BP and heart beat
question
Nursing duties upon death of patient
answer
1) Record TOD 2) Notify appropriate people, departments or agencies 3) Plan for religious or cultural practices desired by pt or family 4) If not a private room, transport other patient 5) Make itemized list of possessions; give to family (have them sign receipt) 6) Prepare body for family or transport to morgue
question
Post-mortem care of body
answer
1) Place body in supine position w/ pillow under head 2) Close eyes, replace dentures, place small towel under chin 3) Remove lines, tubes (except in autopsy) 4) Remove soiled dressings, place disposable pad under pt 5) Wrap body in shroud 6) Transport to morgue or leave in room until mortician arrives
question
What are the changes in a body after death?
answer
1) Livor Mortis (decomposed blood settles in lower body parts closes to ground) 2) Algor Mortis "coldness" 3) Rigor Mortis "stiffness" of muscles and joints (stage 3) 4) Skin indentation *Mortis = death
question
Swallow screen EXCLUSION criteria
answer
- coughing on saliva - excessive saliva/drooling - hx of dysphagia - slurred/garbled speech - pocketing of food in cheek Keep pt NPO, no PO meds, get order for SLP
question
List swallow difficulty behaviors (6)
answer
Cough Throat clearing Wet, gurgly voice Multiple swallows per bite or sip Runny nose Watery eyes
question
Define surgical asepsis
answer
Elimination of all microorganisms
question
What contaminates a sterile field?
answer
- Touching "clean" items - Touching "questionable" items - Falling below waist - Falling out of range of vision - Becomes wet (via capillary action or gravity) - Prolonged exposure to air
question
What supplies will you need to perform a dressing change?
answer
Dressing supplies Tape Clean (or sterile) gloves (will need 2-3 pairs)
question
What do you need to do BEFORE a dressing change?
answer
- Verify MD order - Pre-medicate pt per order - Gather supplies - Wash hands - Check pt ID x 3 criteria - Explain procedure to pt - Provide privacy
question
What supplies will you need to perform a wound irrigation?
answer
- Irrigating set - Solution - Chux - Dressing supplies - Tape - Sterile and clean gloves - sterile container for "wetting" solution - Small trash bag
question
How do you assess a wound? What do you look for?
answer
Pain Color Odor Temp of skin Edema Drainage Signs of healing Size
question
How do you assess drainage?
answer
Color Odor Amount Consistency
question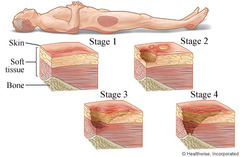
Describe a Stage I pressure ulcer

answer
Intact skin with non-blanchable redness of a localized area, usually over a bony prominence.
question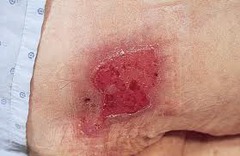
Describe a Stage II pressure ulcer

answer
Partial thickness loss of dermis presenting as a superficial, shallow open ulcer with a red pink wound bed, without slough. May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister.
question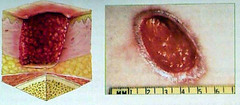
Describe a Stage III pressure ulcer

answer
Full thickness tissue loss. Subcutaneous fat may be visible but bone, tendon or muscle are not exposed. Slough may be present but does not obscure the depth of tissue loss. May include undermining (small opening, large wind under) and tunneling (narrow passage)
question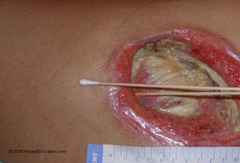
Describe a Stage IV pressure ulcer

answer
Full thickness tissue loss with expose bone, tendon or muscle. Slough or eschar may be present on some parts of the wound bed. Often include undermining and tunneling.
question
Debridement
answer
Removal of non-viable tissue from a wound
question
Dehiscence
answer
Failure of a wound to heal in which the surgical wound separates and opens to the fascial level
question
What factors contribute to wound dehiscence?
answer
Anemia, malnutrition, obesity and use of steriods.
question
Evisceration
answer
Failure of wound healing with total separation of the layers of the wound and protrusion of the internal organs through the wound.
question
What should the nurse do in the case of an evisceration in a pt?
answer
Cover the wound with a moist sterile saline dressing, notify surgeon immediately and prepare pt for emergent surgery.
question
Fistula
answer
An abnormal passage between two organs, or between an organ and the outside of the body.
question
Describe serous wound drainage
answer
Clear, watery plasma
question
Describe purulent wound drainage. What does this type of drainage indicate?
answer
Thick, yellow, pale green or white: indicates infection.
question
Describe serosanguinous wound drainage
answer
Pale, red, watery: mixture of serous and sanguineous
question
Describe sanguineous wound drainage
answer
Bright red: indicates active bleeding
question
Why does a wound heal best in a moist environment?
answer
Because it favors: 1) epithelial cell migration 2) promotes extracellular matrix formation 3) reduces fibrosis 4) decreases wound infection
question
What are dry gauze dressings primary used for?
answer
- Wound healing by primary intention with little drainage - Abrasions - Non-draining postoperative incisions
question
What are the disadvantages of dry gauze dressings?
answer
- Does not maintain a moist environment (unless wound is highly exudative) - Moisture evaporates quickly causing dressing to dry out - Increased infection rates
question
What is a "wet-to-moist" wound dressing? What is its purpose?
answer
Gauze moistened with appropriate solution. Primary purpose is to mechanically debride wounds
question
What types of wounds would you use a "wet-to-moist" dressing?
answer
- Full-thickness wounds healing by secondary intention - Wound with necrotic tissue
question
What is a transparent film dressing? Describe.
answer
A clear, adherent, non absorptive, polyurethane sheet. - Prevents tissue dehydration, allows for rapid, effective healing by speeding epithelial cell growth - Impermeable to fluids and bacteria
question
In what type of wound is a transparent film dressing appropriate?
answer
- Prophylaxis on high-risk intact skin - Superficial wounds with minimal or no exudate - Eschar-covered wounds when autolysis is indicated and safe - IV catheter insertion site - Secondary dressing to wound products (alginates and foam) -Stage 2 pressure ulcers
question
What type of tape is more likely to stay on an area that is moist?
answer
Plastic tape
question
What type of tape would you need to assess for an allergy before using?
answer
Plastic tape
question
What is purpose of Montgomery ties or straps over a dressing?
answer
To prevent skin breakdown due to frequent removal of dressings and tape
question
What type of dressing is generally used over a stage 2 pressure ulcer?
answer
Transparent dressing for easy wound inspection
question
What is the benefit of using gauze in a wound dressing that is healing by secondary intention?
answer
Absorbancy
question
What type of dressing is used for necrotic wounds?
answer
Moist-to-dry
question
When might packing strips be used in a wound?
answer
To fill a tunneled wound or fistula; to treat an infection
question
What does the "VAC" mean in Wound VAC? How does the Wound VAC work?
answer
Vacuum assisted closure It creates negative pressure in the wound, thus drawing the sides together
question
How is "slit" gauze dressing used around drain tubes? What other kinds of tubes are they used for?
answer
Place under and around wound drain tube to absorb, thus fitting better than a flat cause pad. Also used around tracheostomy tubes
question
How long after a surgical procedure can you expect sanguineous drainage?
answer
24-48 hours
question
What are the warning signs of melanoma?
answer
ABCDE Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving
question
List indicators of risk for pressure ulcers
answer
1) Decreased mobility 2) Impaired neurological functioning 3) Decreased sensory perception 4) Decreased circulation
question
Define "tissue ischemia"
answer
Decreased blood flow
question
Define "blanching"
answer
Normal red tones of skin are absent
question
What is normal reactive hyperemia?
answer
Redness due to local. blood vessel dilation (decreased blood flow to underlying tissues); redness blanches with fingertip pressure
question
What is abnormal reactive hyperemia
answer
Non-blanching tissue, remains red with fingertip pressure (tissue damage)
question
What are contributing factors to pressure ulcers?
answer
Shearing Friction Moisture Nutrition Infection Impaired peripheral circulation Obesity Age
question
What is "shearing"?
answer
Skin sticks to mattress, underlying tissue moves
question
What are general principles for heat and cold application?
answer
Check MD's order - type of application, body site, frequency and duration of tx Assess pt's response to tx during and after Document tx, length of time applied, pt response Nursing dx to keep in mind - high risk for injury when it's too hot, too cold or on too long
question
What are general principles for heat application?
answer
Apply only 15-30 minutes If applied >1 hour, vasoconstriction occurs
question
What are general principles for cold application
answer
Apply 15-30 minutes If applied >1 hour, reflex vasodilation occurs
question
Autolysis
answer
Natural, spontaneous process of revitalized tissue being separated from viable tissue.
question
Blister
answer
Collection of fluid underneath the epithelial layer; fluid may be clear to pink/red in color
question
Cellulitis
answer
Inflammation of tissues presenting as edema, redness, pain and heat, often with hardness of the tissues and a demarcation (definite boundary line) of the red area.
question
Colonisation
answer
Multiplication of micro-organisms without a corresponding host reaction
question
Dry
answer
Dehydration of the skin presenting as flaky, scaly or thick skin plaques.
question
Eczematous
answer
Acute or chronic inflammation of the skin presenting as redness, irritation, weeping, crusting or scaly area.
question
Epithelialisation
answer
The final stage of wound healing where epidermal cells migrate across the surface of the wound from the wound margins and the remaining hair follicles. These cells are pink/white in color at the wound edges or in islands over granulation tissue.
question
Erythema
answer
Redness of the skin caused by congestion of capillaries in lower layer of skin, maybe due to injury, infection, inflammation or hyperemia (increased/excess blood in blood vessels of organ/tissue)
question
Eschar
answer
Scab consisting of dried serum and revitalized dermal cells
question
Exudate
answer
Fluid that leaks out of wound
question
Foam
answer
Dressing made from polyurethane - a soft, open cell sheets in single or multiple layers. Non adherent, can absorb large amounts of educate and can also be used as secondary dressings. Can be impregnated with charcoal and with waterproof backing.
question
Granulation
answer
During proliferation phase of healing, bright red tissue formed from new capillary loops or "buds" which are red/deep pink and moist with a bumpy appearance.
question
Hydrocolloid
answer
Waterproof occlusive dressing that has mixture of pectins, gelatins and produces a gel when mixed with exudate.
question
Maceration
answer
Softening or sogginess of the tissue, owing to retention of excessive moisture which presents as moist, red/white and wrinkled.
question
Necrosis
answer
Local death of tissue, often black/brown in color and leathery in texture
question
Proliferation
answer
Granulation tissue is formed to replace lost volume. Epithelial cells grow around the wound or in islets, to form a new protective covering.
question
Slough
answer
Viscous yellow layer which often cover the wound and is a strong adherent to it. Its presence is related to end of inflammatory stage of healing when dead cells have accumulated in the exudate.
question
VAC
answer
Vacuum assisted wound closure that creates a hypoxic environment within the wound bed in which aerobic bacteria cannot survive.



