Cost Management Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cost Management Processes (3)
answer
- Estimate costs (PLANNING) - Determine the budget (PLANNING) - Control costs (M&C)
question
Cost estimating and cost budgeting
answer
On smaller scope projects, cost estimating and cost budgeting are so tightly linked that they can be viewed as a single process that can be performed by a single person over a relatively short period of time
question
When is the ability to influence cost the greatest?
answer
In the early stages of the project This is why early scope definition is so critical
question
Control Account
answer
On some large projects it might be more practical to estimate and control costs at a HIGHER LEVEL than the individual activities - this is CONTROL ACCOUNT Estimating and controlling costs at a level higher than the work package level in the WBS
question
Cost Management Plan
answer
aka BUDGET MGMT PLAN or BUDGET PLAN Created with the rest of the mgmt plans in DEVELOP PROJECT MGMT PLAN process in INTEGRATION MGMT May include the following: - Specifications for how estimates should be stated - Level of accuracy needed for estimates - Reporting formats to be used - Rules for measuring cost performance - Whether costs will include both direct costs (those directly attributable to the project) and indirect costs (e.g. overhead) - Establishment of a cost baseline for measuing against as part of project M&C - Control thresholds - Cost change control procedures
question
Cost thresholds
answer
The amount of variation allowed before you need to take action Part of the cost mgmt plan and an example of how PMs think in advance about how they will manage costs
question
Life Cycle Costing
answer
Looking at the cost of the whole life of the product, not just the cost of the project Ex: Not wise to design the product so the project costs are low but the maintenance costs are higher than the project cost savings
question
Value Analysis
answer
aka Value Engineering Finding a less costly way to do the same work (e.g. How can we decrease cost on the project while maintaining the same scope?) - Systematically identify all the required project functions, assign values to these functions and provide functions at teh lowest overall cost w/o loss of performance
question
Cost Risk
answer
Involves risk, procuement and cost managment - crosses several knowledge areas
question
7.1 Estimate Costs Process Group? Knowledge Area? Inputs (6)? T&T (9)? Outputs (3)?
answer
Process Group: PLANNING Knowledge Area: COST MGMT Inputs: .1 Scope baseline .2 Project schedule .3 Human resource plan .4 Risk register .5 Enterprise environmental factors .6 Organizational process assets T&T: .1 Expert judgment .2 Analogous estimating .3 Parametric estimating .4 Bottom-up estimating .5 Three-point estimating .6 Reserve analysis .7 Cost of quality .8 Project mgmt estimating software .9 Vendor bid analysis Outputs: .1 Activity cost estimates .2 Basis of estimates .3 Project document updates
question
Objective of ESTIMATE COSTS
answer
Coming up w/ cost estimates for each activity - Will be combined into one time-phased spending plan during DETERMINE BUDGET
question
Which costs should be estimated?
answer
Costs involved in all the efforts needed to complete the project: - Costs of quality efforts - Costs of risk efforts - Costs of the PM's time - Costs of the PM activities - Costs directly associated w/ the project, including labor, materials, training for the project, computers, etc. - Office expenses for physical office spaces used directly for the project - Profit, when applicable - Overhead costs, such as mgmt salaries and general office supplies
question
Fixed vs. Variable Costs
answer
Variable = costs change w/ the amount of production or the amount of work (e.g. cost of material, supplies, wages) Fixed = costs do NOT change as production changes (e.g. cost of set-up, rent, etc.)
question
Direct vs. Indirect Costs
answer
Direct = costs directly attributable to the work on the project (e.g. team travel, team wages, recognition, cost of materials used on the project) Indirect = Overhead items or costs incurred for the benefit of more than one project (e.g. taxes, fringe benefits, janitorial services)
question
Scope Baseline (INPUT)
answer
Provides the details of WHAT you are estimating - what is in scope - what constraints have been put on the project Scope baseline = scope statement + WBS + WBS dictionary
question
Project Schedule (INPUT)
answer
Schedule contains the activities, the resources assigned to complete the work and when the work will occur You need a schedule before you can come up w/ a budget: - The timing of whenyou buy something affects its cost - You need to develop a time-phased spending plan to control project expenditure so you know how much money will be spent during specific periods of time
question
Human Resource Plan (INPUT)
answer
Consider reward systems (increase productivity and ultimately save money) and labor rates
question
Risk Register (INPUT)
answer
Risk mgmt will save time and oney, but there are costs associated w/ the efforts to control risks
question
How is estimating done? (T&T)
answer
Same techniques described in the Time Mgmt chapter - One-point estimating - Analogous estimating - Parametric estimating - Three-point estimating (PERT) In addition, BOTTOM-UP ESTIMATING - Creating detailed estimates for each activity or work package - Estimates are rolled up into CONTROL ACCOUNTS and finally an overall project estimate - REQUIRES an accurate WBS
question
Reserve Analysis (T&T)
answer
ID which activities have significant risks and determining how much tiem and money to set aside to account for the risks if they occur Contingency reserves > known risks Management reserves > accommodate unknown risks or unidentified risks
question
Cost of Quality (T&T)
answer
Cost of work added to the project to accommodate quality efforts
question
Vendor Bid Analysis (T&T)
answer
Cost estimating may include analysis of what the project should cost, based on the responsive bids from qualified vendors
question
Accuracy of Estimates
answer
Estimates made early in the project will be less accurate than those made later, when more is known about the project Estimates should be in a range
question
Estimate Ranges - Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) estimate - Budget estimate - Definitive estimate
answer
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) estimate - Usually made during project INITIATING - Typical range for ROM estimates is + / - 50 percent from actual Budget estimate - Usually made during project PLANNING - Typical range of -10 to +25 percent from actual Definitive estimate - More refined estimate as the project progresses - Typical range or + / - 10 percent
question
Activity Cost Estimates (OUTPUT)
answer
Quantitative assessment of the probable costs required to complete project work
question
Basis for Estimates (OUTPUT)
answer
Amount and type of add'l details supporting the cost estimate Supporting detail: - Basis of the estimate (i.e. how it was developed) - Assumptions made - Known constraints - Range of possible estimates - Confidence level in final estimate
question
7.2 Determine Budget Process Group? Knowledge Area? Inputs (7)? T&T (5)? Outputs (3)?
answer
Process Group: PLANNING Knowledge Area: COST MGMT Inputs: .1 Activity cost estimates .2 Basis of estimates .3 Scope baseline .4 Project schedule .5 Resource calendars .6 Contracts .7 Organizational process assets T&T: .1 Cost aggregation .2 Reserve analysis .3 Expert judgment .4 Historical relationships .5 Funding limit reconciliation Outputs: .1 Cost performance baseline .2 Project funding requirements .3 Project document updates
question
Objective of Determine Budget
answer
PM calculates teh total cost of the project in order to determine the amount of funds the organization needs to have available for the project Meeting the cost baseline will be the measure of project success
question
How do RESERVES fit into the COST BASELINE and the COST BUDGET? Reserve Analysis (T&T)
answer
In estimating the total cost of a project, the PM must perform risk mgmt activities and include RESERVES in the estimate 2 types of reserves: - Contingency = Known risks identified during risk reponse planning - Management = Add'l funds set aside to cover unforeseen risks or changes to the project The COST BASELINE includes CONTINGENCY RESERVES and represents the funds the PM has aurhtority to manage and control COST BUDGET = cost baseline + MANAGEMENT RESERVES
question
Cost Aggregation (T&T)
answer
To create a budget - activity costs are rolled up to work package costs - work package costs are rolled up to control account costs - control account costs are rolled up to project costs - CONTINGENCY RESERVES are added to achieve COST BASELINE - MANAGEMENT RESERVES are added to achieve COST BUDGET
question
Funding Limit Reconciliation (T&T)
answer
Expenditure of funds should be reconciled w/ any funding limits on the commitment of funds for the project - a variance b/w FUNDING LIMITS and the PLANNED EXPENDITURE will sometimes necessitate the rescheduling of work to level out the rate of expenditures Check CASH FLOW (part of funding limit reconciliation) - funding may not be available when it is needed on the project, causing changes to other parts of the project iterations of the project docs or PM plan - the cost baseline, therefore, is time-phased and may be shown as an S-curve
question
Cost Peformance Baseline (OUTPUT)
answer
An authorized time-phased budget at completion (BAC) used to measure, monitor and control overall cost performance on the budget Developed as a summation of the APPROVED BUDGETS BY TIME PERIOD and is typically displayed as an S-CURVE
question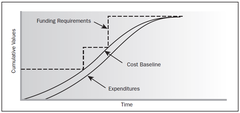
Project Funding Requirements (OUTPUT)

answer
Total funding requirements and periodid funding requirements (e.g. quarterly, monthly) are derived from the cost baseline Funding often occurs in incremental amounts that are not continuous - appear as steps
question
7.3 Control Costs Process Group? Knowledge Area? Inputs (4)? T&T (6)? Outputs (6)?
answer
Process Group: PLANNING Knowledge Area: M&C Inputs: .1 Project management plan .2 Project funding requirements .3 Work performance information .4 Organizational process assets T&T: .1 Earned Value Measurement (EVM) .2 Forecasting .3 To-complete performance index .4 Performance reviews .5 Variance analysis .6 Project management software Outputs: .1 Work performance measurements .2 Budget forecasts .3 Organizational process assets .4 Change requests .5 Project management plan updates .6 Project document updates
question
Progress Reporting - % complete - 50/50 rule - 20/80 rule - 0/100 rule
answer
On projects where work is not objectively measured, the estimate team members provide re: percent complete is simply a guess (and does NOt provide a reaslistic estimate of the project's progress) There are alternatives to asking for % complete when using a properly broken down WBS: - 50/50 rule = an activity is considered complete when it begins and gets credit for the last 50 percent only when it is complete - 20/80 rule = an activity is considered complete when it begins and gets credit for the last 80 percent only when it is completed - 0/100 rule = an activity does not get credit for partial completion; it only gets credit for full completion
question
Earned Value Measurement (EVM) (T&T)
answer
Method used to measure project performance against the SCOPE, SCHEDULE and COST BASELINES (aka the PERFORMANCE BASELINE) The measurements resulting from an EVM analysis indicate whether there are any potential deviations from teh scope, schedule or cost baselines EVM is BETTER than simply comparing planned to actual results: - Integrates cost, time and work done (or scope) - Can be used to FORECAST FUTURE PERFORMANCE and PROJECT COMPLETION DATES and COSTS
question
**PV
answer
PV = Planned Value As of today, what is the value of the WORK PLANNED TO BE DONE?
question
**EV
answer
EV = Earned Value As of today, what is the estimated value of the WORK ACTUALLY ACCOMPLISHED?
question
**AC
answer
AC = Actual Cost (total cost) As of today, what is the ACTUAL COST INCURRED for the WORK ACCOMPLISHED?
question
**BAC
answer
BAC = Budget at Completion (the budget) How much did we BUDGET for the TOTAL project effort?
question
**EAC
answer
EAC = Estimate at Completion What do we currently expect the TOTAL project to cost (a forecast)?
question
**ETC
answer
ETC = Estimate to Complete From this point forward, how much MORE do we expect it to cost to finish the project (a forecast)?
question
**VAC
answer
VAC = Variance at Completion As of today, how much over or under budget do we expect to be at the end of the project?
question
**CV (formula & interpretation)
answer
CV = Cost Variance Formula: EV - AC Interpretation: - NEGATIVE is over budget - POSTIIVE is under budget
question
**SV (formula & interpretation)
answer
SV = Schedule Variance Formula: EV - PV Intpertation: - NEGATIVE is behind schedule - POSITIVE is ahead of schedule
question
**CPI (formula & interpretation)
answer
CPI = Cost Performance Index Formula: EV / AC Interpretation: - We are getting $____ worth or work out of every $1 spent - Fund ARE or ARE NOT being used efficiently
question
**SPI (formula & interpretation)
answer
SPI = Schedule Performance Index Formula: EV / PV Interpretation: - We are (only) progressing at ____ % of the rate originally planned
question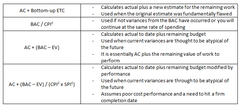
**EAC (multiple formulas & interpretation)

answer
EAC = Estimate at Completion Note: There are many ways to calculate EAC, depending upon the assumptions made. But the PURPOSE is to create FORECASTS base on past performance on the project Interpretation: - As of now, how much do we expect the total project to cost?
question
**TCPI
answer
TCPI = To Complete Performance Index Formula: (BAC - EV) / (BAC - AC) Interpretation: - Divides the remaining work to be done by the money remaining to do it - Answers the question "In order to stay within budget, what rate must we meet for the remaining work?"
question
**ETC
answer
ETC = Estimate to Complete Formula: - EAC - AC (How much more will the project cost?) - Reestimate (reestimate the reamining work from the bottom-up)
question
**VAC
answer
VAC = Variance at Completion Formula: BAC - EAC Interpretation: - How much over or under budget will we be at the end of the project?
question
ETC vs. EAC
answer
BOTH forecast future performance based on what actually occurred on the proejct, taking into account any variances from the plan the project has already experienced ETC - estimate of HOW MUCH MORE the REMAINING part of the project will cost to complete EAC - what the TOTAL PROJECT COST is forecasetd to be
question
**Understand and memorize the following related to EVM formulas
answer
- EV comes first in every formula - If it is a VARIANCE, the formula is EV minus something - If it is an INDEX, the formula is EV dividied by something - If the formula relates to COST, use AC - If the formula relates to SCHEDULE, use PV - For VARIANCE INTERPRETATION, negative is bad, positive is good - For INDICES INPERPREATION, great than one is good, less than one is bad
question
What is a formula for estimate at completion (EAC)?
answer
BAC / Cumulative CPI
question
What estimating method would use optimistic time estimates?
answer
Three-point estimate
question
"How much work should be done" has what earned value name?
answer
Planned value
question
What is the critical path?
answer
The longest duration path in the network; the shortest time to complete the project
question
The types and quantities of resources required are calculated in what part of time mgmt?
answer
Estimate activity resources
question
What does the schedule variance tell you?
answer
How far behind or ahead of schedule you are
question
What schedule network analysis technique involves crashing?
answer
Schedule compression
question
What does a finish-to-start relationship mean?
answer
One activity must finish before the next can start
question
What does the estimate at completion tell you?
answer
What we expect the total project to cost
question
Why would you crash a project?
answer
To shorten the project duration
question
The "what-if" scenario method of schedule network analysis primarily makes use of what technique?
answer
Monte Carlo analysis
question
What are sunk costs?
answer
Expended costs
question
What does a milestone chart show?
answer
Dates of significant events on the project
question
What is the duration of a milestone?
answer
Zero
question
What is analogous estimating?
answer
Top-down estimating
question
What are fixed costs?
answer
Costs that do not change with project activity
question
What are direct costs?
answer
Costs incurred directly by the project
question
What is the earned value name for "how much you have spent to date?"
answer
Actual cost
question
What is value analysis?
answer
Finding a less costly way to complete the work w/o affecting quality
question
What is a management reserve?
answer
An amount of time or money set aside to uncover unforeseen risks
question
What is the cost variance formula?
answer
EV - AC
question
Cost risk is greater for the buyer in what type of contract?
answer
Cost reimburseable
question
What schedule network analysis technique uses buffers?
answer
Critical chain method
question
What does present value mean?
answer
The value today of future cash flows
question
What is the formula for total float?
answer
LS - ES OR LF - EF This is the amount of time an activity can be delayed w/o delaying the project
question
Why would a project manager want to use resource leveling?
answer
The smooth the peaks and valleys of monthly resource usage consumed by the project
question
What does a benefit cost ratio of .25 mean?
answer
Benefits are 2.5 times the costs
question
A critical path activity will generally have how much float?
answer
Zero
question
What is parametric estimating?
answer
Using mathematical relationships found in historical info to create estimates (e.g. dollars per foot of material)
question
What is the range of accuracy with a definitive estimate?
answer
+ / - 10 percent



