Cholinergic Antagonists – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Muscarinic Antagonists & Prototype
answer
*Competitive Antagonists* at muscarinic receptors Prototype: Atropine (SUPER IMPORTANT FOR BOARDS!)
question
Sources of Atropine/Related Compounds

answer
Jimsom weed = related compound
question
Atropine - Structure, Mechanism, Common Contraindications
answer
STRUCTURE: No fixed charge, crosses BBB MECHANISM: Competitive antagonist at muscarinic receptors CONTRAINDICATIONS: Men w/BPH, glaucoma patients NOTE: Many drugs act as muscarinic antagonists and many drugs have atropine-like adverse effects. Overdoses of such drugs frequently produce effects that include those of atropine poisoning
question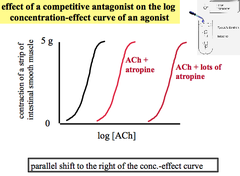
Experiment: Effect of Competitive Antagonist (Atropine) on Agonist (ACh)

answer
A piece of intestine (smooth muscle) is sitting in a salt solution. When it contracts it pulls on something allowing the force of contraction to be measured. *Parallel Shift to the Right = Competitive Agonist*
question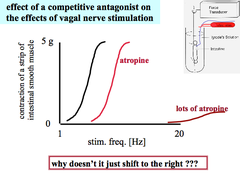
Experiment: Competitive Antagonist (Atropine) on Effects of Vagal Nerve Stimulation

answer
Stimulate Vagus nerve that travels to the piece of intestine to cause smooth muscle contraction. Result: 1. Eventually your body runs out of ACh and there is none left to compete with the Antagonist. 2. Eventually the axons will become refractory (can only conduct so many APs so quickly)
question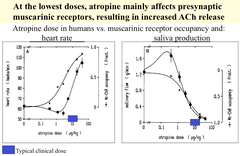
What happens when Atropine is given at very low doses?

answer
Initially, Atropine will block Presynaptic Muscarinic Receptors, resulting in increased ACh release (due to lack of feedback inhibition). This will produce an initial Parasympathetic Effect, until Atropine levels are raised. RESULT: May clinically observe slight bradycardia before heart rate increases as drug is being absorbed.
question
Most Prominent Atropine Effects Going from Low to High Dose

answer
Above Line = common doses Below Line = large doses
question
Scopolamine - Structure, Mechanism, Uses, "Other" Effects, Adverse Effects
answer
STRUCTURE: Tertiary Amine MECHANISM: Muscarinic Antagonist; greater CNS effects than Atropine USES: *Motion* Sickness (Anti-Nausea Effects) "OTHER" EFFECTS: Sedation, amnesia, dreamless sleep (no longer used for these now- there are better drugs) ADVERSE EFFECTS: Dry mouth, drowsiness, blurred vision, dilation of pupils
question
Glycopyrrolate - Structure, Mechanism, Uses
answer
STRUCTURE: Quaternary Amine MECHANISM: Muscarinic Antagonist USES: Various, often as pre-anesthetic agent (used to dry secretions in URT)
question
Ipratropium - Structure, Mechanism, Use
answer
STRUCTURE: Quaternary Amine - can't cross BBB MECHANISM: Muscarinic Antagonist USE: Inhalation to treat asthma
question
Benztropine - Mechanism, Use
answer
MECHANISM: Muscarinic Antagonist USE: Parkinson's Disease; has a good ratio of CNS:peripheral effects
question
Tolterodine - Structure, Mechanism, Uses, Adverse Effects
answer
STRUCTURE: Tertiary Amine MECHANISM: Muscarinic Antagonist; somewhat selective for M3 receptors; blocks excessive stimulation of detrusor muscle USES: Overactive bladder, urinary frequency, urgency, incontinence ADVERSE EFFECTS: Dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, etc.
question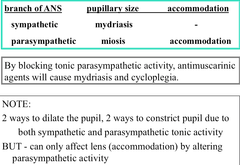
Ophthalmologic Effects of Muscarinic Antagonists

answer
By blocking tonic parasympathetic activity, antimuscarinic agents will cause mydriasis (dilation) and cycloplegia (inability to accommodate to see near)
question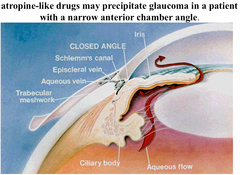
Why can't atropine be given to patients with narrow-angle glaucoma?

answer
Because it would cause pupillary dilation, closing the Canal of Schlemm even more, blocking outflow of aqueous humor ; increasing intraocular pressure.
question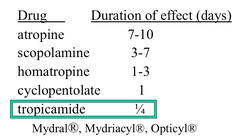
Comparison of Muscarinic Antagonists After Topical Application to the Eye

answer
Don't think we have to know this. Check Patch
question
Dimenhydrinate
answer
An Antihistamine that has prominent antimuscarinic activity and is used for *motion sickness*
question
Cardiovascular Uses of Muscarinic Antagonists
answer
Used in MI to treat bradycardia secondary to excessive vagal activity Rare patients with hyper-responsive vagal reflexes
question
Uses of Muscarinic Antagonists for GI Disorders
answer
Peptic Ulcer (no longer used- better drugs now) Diarrhea Irritable bowel syndrome "Anti-spasmodic"
question
Use of Muscarinic Antagonists to Treat Poisoning due to Muscarinic Agonist/Anticholinesterase
answer
Need a tertiary amine, such as Atropine May require "heroic" doses & repeated treatment ONLY used for effects of ACh at *muscarinic* receptors (no effect at nicotinic receptors)
question
Atropine Poisoning
answer
"Dry as a bone, blind as a bat, red as a beet, mad as a hatter" Dry mouth, skin, eyes, etc. Blurred vision Peripheral vasodilation CNS effects cause confusion Problems with thermoregulation; especially in infants & children hyperthermia may be prominent & lead to death REMEMBER: Many drugs have, as a 2nd action, atropine-like effects. So the signs of intoxication for some of these drugs are the same as Atropine.
question
Nicotinic Antagonists - Generalizations and Subtypes
answer
Most of the drugs are selective for either the nicotonic receptors at the NMJ or the autonomic ganglia. All are quaternary and do not cross the BBB and are not well-absorbed from the GI tract NMJ: Competitive Antagonists Depolarizing Blocker AUTONOMIC GANGLIA: Antagonist
question
Ganglionic Blocking Drugs - Selectivity, Prototype, Uses
answer
SELECTIVITY: Selective for Nicotinic Nn receptors BUT they *block BOTH arms of the CNS* PROTOTYPE: Hexamethonium USES: Formerly used for emergency treatment of hypertensive crisis (malignant hypertension) *Main use is to understand ANS*
question
Effects of Ganglionic Blockade
answer
Determined by the relative contribution of sympathetic & parasympathetic tone on various tissues at any given moment HR increases because of predominant vagal control. However, both reflex tachycardia & reflex bradycardia will be absent since both sympathetic & parasympathetic arms of the ANS will be blocked. GI tract will become non-active Drop in peripheral vascular resistance (why? patch)
question
Competitive Antagonists at Nicotinic Receptors of the Skeletal NMJ - Prototype, Structure, Mechanism & "Reversal"
answer
PROTOTYPE: Tubucurarine (Curare) STRUCTURE: *All are quaternary & have no CNS effects* MECHANISM:* Produces a non-depolarizing block* Effect can be antagonized with nicotinic agonist, or by increasing the acetylcholine concentration (not used clinically) with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
question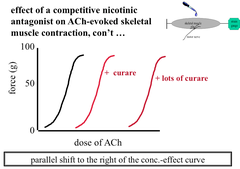
Effect of a Competitive Antagonist on an ACh-Evoked Skeletal Muscle Contraction

answer
Parallel shift to the Right - block can always be overcome with enough ACh
question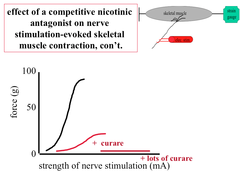
Effect of a Competitive Antagonist on Skeletal Muscle Contraction Evoked by Nerve Stimulation

answer
As stimulation increases, more & more motor units are recruited. Eventually the ACh runs out
question
Tubocurarine - Absorption, Effects, Use, Elimination
answer
ABSORPTION: It's not absorbed from GI tract ; doesn't cross the BBB. EFFECTS: Rapid onset of action after IV injection, weakness progressing to flaccid paralysis Small muscle involved in finely-controlled movements (e.g. eye muscles) are most sensitive. Large muscle are less sensitive & intercostal muscles & diaphragm are least sensitive. USE: Paralysis for surgeries ELIMINATION: Renal, Liver
question
Tubocurarine Limitations
answer
Relatively long DOA (50 min, bad because you want it to stop after surgery) Not completely selective; has some effect to inhibit transmission at autonomic ganglia Can cause release of histamine from mast cells
question
Atracurium - Elimination, Duration of Action, Selectivity, Adverse Effect
answer
ELIMINATION: Liver & spontaneous rxn (safer) DURATION OF ACTION: Short (20-35 min) [SELECTIVITY: No autonomic ganglia block, no effect at muscarinic receptors, Slight histamine release] ADVERSE EFFECT: One product of spontaneous breakdown can cause seizures
question
Mivacurium - Elimination, Duration of Action, Selecitivty
answer
ELIMINATION: *Plasma Esterase* DURATION OF ACTION: *Very short* (10-20 min) [SELECTIVITY: No autonomic ganglia block, no effect at muscarinic receptors, some histamine release]
question
Pancuronium - Elimination, Duration of Action, Selecitivty
answer
ELIMINATION: Renal DURATION OF ACTION: Moderate (>35 min) [SELECTIVITY: No autonomic ganglia block, moderate muscarinic receptor antagonism, no histamine release]
question
Vecuronium - Elimination, Duration of Action, Selecitivty
answer
ELIMINATION: Liver, renal DURATION OF ACTION: Short (20-35 min) SELECTIVITY: Most selective & most used clinically - no effects at other receptors
question
Succinylcholine - General Features
answer
MECHANISM: *Depolarizing blocker of NMJ transmission*. It acts as an *agonist at nicotinic receptors of NMJ*. Unlike ACh, it is NOT a substrate for Acetylcholinesterase. It produces a *depolarizing block* It has a*very rapid onset of action* and a *very brief duration of action* It has NO CNS effects
question
Succinylcholine - Mechanism
answer
Since it's an agonist, onset of action is marked by fasciculations. These can be limited by giving a low dose of a curare-like drug first. It produces depolarization block just like excess ACh. 2 phases: I. Depolarization - Voltage gated Na? channels locked in inactivated state II. Desensitization - End plate is repolarized but insensitive to ACh
question
Succinylcholine - Adverse Effects
answer
Lots of muscle contraction can result release of a lot of K? into the bloodstream, causing *Hyperkalemia*. *Malignant Hyperthermia*: rapid onset of extremely high fever with muscle rigidity, precipitated by exogenous agents in genetically susceptible individuals, especially by halothane or succinylcholine. (Medical Emergency) Succinylcholine action is intensified by anticholinesterase drugs and can make the depolarizing block even "worse"
question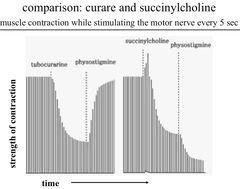
Experiment: Comparison of Curare ; Succinylcholine Effects on Strength of Muscle Contraction

answer
If more Tubocurarine was given, the strength of contraction could be brought down to 0. Physostigmine (anticholinesterase agent) - Rapid and complete recovery of ACh transmission; ACh is able to accumulate and counteract the effects of curare. Succinylcholine results in an initial increase in contraction, but it very quickly produces depolarization block. Physostigmine causes further loss of muscle contraction strength because ACh breakdown is blocked, so now there is ACh-mediated depolarization block on top of Succinylcholine-mediated depolarization block.
question
Succinylcholine - Pharmacokinetics***
answer
Short duration of action is due to hydrolysis by *plasma cholinesterase* (pseudocholinesterase). -In individuals with a genetically-determined abnormal plasma cholinesterase, succinylcholine has a much longer duration of action. -Many mutations have been identified *Psuedocholinesterase deficiency results in a delayed metabolism of succinylcholine* ; mivacurium. Heterozygous: slight prolongation of action Homozygous: may last many hours



