Childhood Cancer RAT – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
-ages 20 & younger -kids don't have the protein-binding ability because the muscles are beginning to grow -kids have quicker metabolic rate, going thru growth & development, need more fluid, smaller fat content -may have problems with infertility & cognitive functioning--depending on cancer & chemo

answer
Childhood Cancers
question
what are lasting effects of the cancer & chemo children hospitals--specialties higher risk of cancer return, or to get another cancer chemo affects the kidneys, lungs, & heart; chronic conditions

answer
Cancer Chart Slide
question
Wilms' Tumor Retinoblastoma Osteosarcoma Aplastic anemia Acute lymphobastic leukemia Ewing Sarcoma -most likely tested on -rare, but will see them as childhood cancers -96% favorable: more responsive to tx & have a better prognosis -93% unfavorable: large, distorted

answer
6 Cancers in PowerPoint
question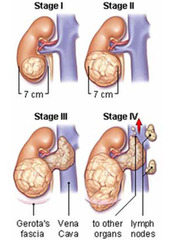
-nephroblastoma -named after Max Wilms in 1899 -often on the left kidney (but can be both kidneys) -slightly more common in girls -1 in 10,000 -peaks at age 3-4 -National Wilms Tumor Study good outlook for this tumor complicated to treat this cancer if unfavorable encapsulated in a thing, fragile covering, really easily torn -can cause cancer to spread into body can be favorable or nonfavorable-depends under a microscope

answer
Wilms' Tumor
question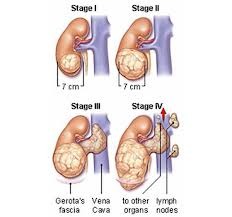
Stage 1: involves one kidney and removable with surgery Stage 2: extends beyond one kidney but can be completely removed with surgery Stage 3: cannot be completely removed beyond the one kidney but stays within the abdominal cavity Stage 4: metastasis to other organs Stage 5: involves both kidneys kidney dysfunction later, ex: renal failure kidneys affected: adrenals, BP, intra & extracellular fluid, dehydration, & cardiac problems may have increased or decreased BP than normal, changes when they change positions. Sx similar to shutting of SNS--anxious, can't sleep, losing weight, reved up all the time.

answer
Wilms' Tumor Staging
question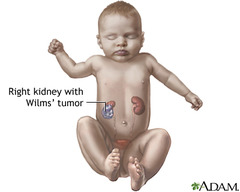
Sx -abdominal mass -abdominal pain -fever -hematuria usually ages 2-4 years upper left quadrant pain do not palpate, could rupture the capsule Diagnostic -ultrasound -CT -MRI -angiography of renal veins

answer
Wilms' Tumor Clinical Symptoms Diagnostic Tests
question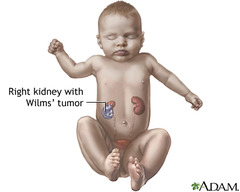
avoid palpation of the abdomen surgical removal chemotherapy -stages 1-3: actinomycin D and vincristine -stages 3-5: doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, etoposide and radiation understand meds: name, category, nadar, unique sx Stages 1-3: helps the cell stop dividing, but stops healthy cells too; sensitivity to light Stages 3-5: can be cardiac sx and can cause hemorrhagic cystitis. can be higher risk for kidney and heart problems as they age. vincristine: can cause hemorrhagic cystitis, mesna is antidote. increase fluids to filter out the kidneys.

answer
Wilms' Tumor Medical Management
question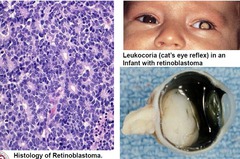
does run in families parents usually catch when they are holding their infants & the light hits their eye a certain way.

answer
Retinoblastoma
question
a malignant glioma of the retina usually unilateral occurs in young children frequently hereditary and known as germinal retinoblastoma (40%) can't find red reflex have white circle instead higher risk for developing other cancers x-ray will show it the smaller the tumor, the better the outlook.

answer
Retinoblastoma What is it
question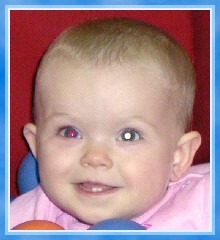
leukocoria or cat's eye reflex strasbimus red painful eye inward or outward turning of the eye visual impairment two different colored iris (heterochromia) won't be able to perform cranial nerve assessments if caught early, child may just have minimal vision problems. always investigate reason for 2 different colored eyes

answer
Retinoblastoma Symptoms
question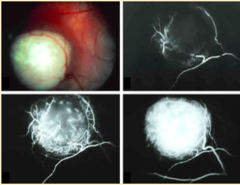
Grade A: small tumor located in retina; no seeding or detachment <3 mm Grade B: small tumor located in retina; no seeding or detachment <5 mm Grade C: localized seeding and some detachment Grade D: massive seeding and retinal detachment Grade E: no visual potential seeding=metastasize optic nerve is needed for sight

answer
Retinoblastoma Staging
question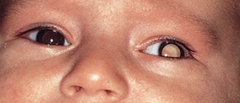
high beam radiation therapy: Cobalt 60, Radioactive Iodine 125 Cryotherapy for very small tumors Chemotherapy: carboplatin, vincristine, etoposide Enucleation (eye removal) after exhaustion of other treatments experimental injection of melphalan into ocular artery chemo does effect nervous system, could cause neuropathy enucleation used to do this often, not so much anymore melphalan interacts with guanine, kills cells, even healthy ones may have nystagmus (darting) or a lazy eye the rest of their life some cryotherapies are toxic to the kidneys could have renal failure, cardiac failure, and nervous system problems

answer
Retinoblastoma Medical Management
question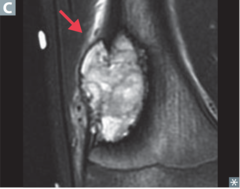
Tibial tuberosity: where the leg bones grow the quickest unusual, large, shiny area over a couple days=osteosarcoma end of the long bone=common cancer cells invade the bone structure, and crowd out all the normal cells becoming a mass; spreads to tissues; causing pain 50% of tumors are right below the knee 400-500 cases/year may have pain up to 6 months before osteosarcoma is suspected.

answer
Osteosarcoma
question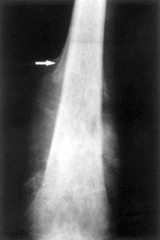
sarcoma originating in the bone at the growth points; shins, upper arm, and thigh most often during puberty twice as likely in boys familial retinoblastoma results in higher risk of osteosarcoma

answer
Osteosarcoma What is it
question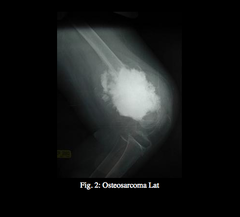
Sx -swelling upon flexion -night pain -shiny skin over tumor -cardiomyopathy Dx -CT -MRI -Biopsy -X-ray can be identified in athlete's when they are working out with weights heart muscles become affected if it metastasizes, worry about the lungs, kidneys, adrenals, and heart

answer
Osteosarcoma Symptoms Diagnosis
question
Chemotherapy -methotrexate -doxorubicin -cisplatin -ifosfamide -etopiside Amputation -only when necessary -limb sparing surgery where bone is replaced with a prosthetic or with bone from another area of the body Methotrexate is becoming a hallmark chemo agent; also used for rheumatoid arthritis and auto-immune diseases, stops the cell when it needs folic acid to divide amputation: used to do a lot of them body image issue may occur cisplatin: worry about ototoxicity, kidney toxicity, and cardiac toxicity methotrexate: two dose limiting factors: elevated liver enzymes and arachnoiditis (seizures and headaches)

answer
Osteosarcoma Treatment
question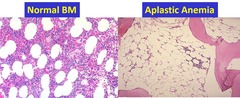
unique, all cells affected in bone marrow 4-5 cases per billion see a lot of immature RBC higher risk for infection, decreased WBC lower tissue perfusion, fatigue, pallor, SOB, decreased RBC

answer
Aplastic Anemia
question
also called pancytopenia or hypoplastic anemia suppression of the bone marrow of RBCs, WBC, and platelets RBCs are the last to show reduction in numbers more common in Asia hereditary form--Fanconi's anemia Acquired form--autoimmune disease 80% of cases acquired form; also exposed to environmental toxins: industrial chemicals Ex: benzene, arcinic; medications, ex: Dilantin, peridium

answer
Aplastic Anemia What is it
question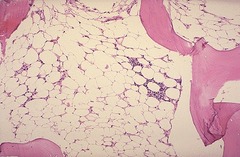
Sx -fatigue -SOB -rapid/irregular heart rate -pallor -frequent and prolonged infections -unexplained/easy bruising Dx -CBC -Bone marrow aspiration losing O2 ability=tachycardia

answer
Aplastic Anemia Symptoms Diagnosis
question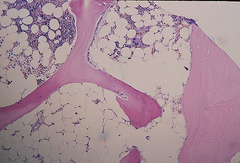
remove underlying cause if environmental RBC transfusions platelet transfusions bone marrow transplant immunosuppression: steroids, cyclosporine, antihymocyte globulin (thymoglobulin) to do bone marrow transplant, need to suppress immune system to reduce the risk of rejecting new bone marrow

answer
Aplastic Anemia Medical Management
question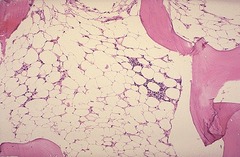
stem cell transplant to rebuild the bone marrow with stem cells from a donor may offer the only successful treatment option for people with severe aplastic anemia immunosuppressant for people who can't undergo a bone marrow transplant or for those whose aplastic anemia may be due to an autoimmune disorder bone marrow stimulants may help the bone marrow to produce new blood cells. Growth factors are often used in combination with immune-suppressing drugs. can try give erythropoietin to build more RBCs possibly treat aplastic anemia

answer
Aplastic Anemia more info
question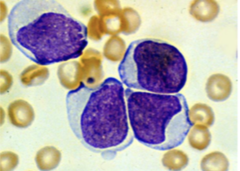
WBC get over-run 80% of leukemias they don't differentiate between the WBC, RBC, and platelets

answer
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
question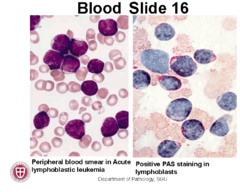
develops when there is an abnormal "error" in WBC production in the bone marrow cells allowing cells to keep dividing resulting in a large number of immature, lymphoblast (leukemic) cells which severely outnumber other blood cells. big blue cells in pathology=classic sign

answer
ALL
question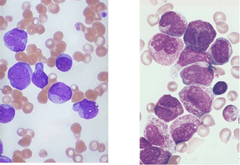
lymphoblasts crowd out RBCs and platelets lymphoblasts cross the blood-brain barrier as the RBCs die, the spleen and liver become engorged with cellular debris accounts for 80% of leukemia cancers peak age is at 2-3 years highest incidence in Hispanic children 95% remission rate usually a bone marrow transplant to cure

answer
ALL What is it
question
Change in bowel or bladder habits A sore that doesn't heal Unusual bleeding or discharge Thickening or lump in breast, testicles, or elsewhere Indigestion or difficulty swallowing Obvious change in size, color, shape or thickness of wart, mole, or mouth sore Nagging cough or hoarseness

answer
CAUTION s/s of cancer
question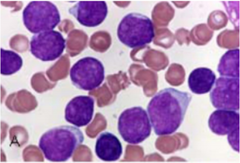
bleeding bone pain infections fatigue swollen lymph nodes bone marrow can't keep up Important to note the swollen lymph nodes: the ones in the thoracic area-clavicular, axillary, inguinal: usually never swell otherwise

answer
ALL Symptoms
question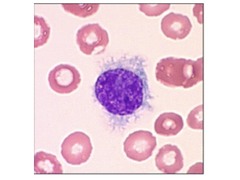
Chemotherapy -asparaginase -corticosteroids -cyclophosphamide -doxorubicin -methotrexate -cytarabine bone marrow transplant stem cell transplant tx option for kids who have a second remission after relapse: bone marrow transplant

answer
ALL Treatment
question
tx to cure some types of cancer, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma

answer
Stem Cell Transplant
question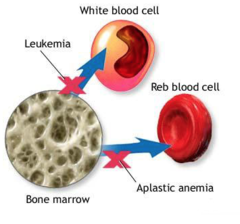
three types: allogenic, autologous, synergeneic allogenic: collected from donor autologous: pt's own blood-forming stem cells Synergeneic: the donor is an identical twin

answer
Stem Cell Transplantation
question
Stem cells are harvested from the iliac crest or bloodstream thru apheresis umbilical cord blood is an additional source stem cells are frozen the recipient is given high doses of chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide and busulfan) to destroy existing bone marrow--this takes weeks

answer
Stem Cells Info
question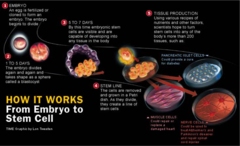
Stem cells are thawed and transfused to recipients stem cells travel to the bone marrow and establish themselves (engraftment); takes two to four weeks bone marrow becomes functional producing normal RBC, WBC, and platelets immunosuppressants are used to prevent graft-versus-host disease or stem cell rejection

answer
Stem Cell Therapy
question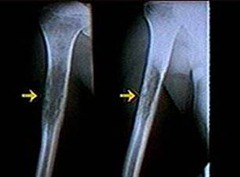
tends to appear in middle bones, most often in femur, pelvis, ribs, upper arms, and thigh educate parents about s/s of infection. teach quiet activities that integrate normal developmental socialization

answer
Ewing Sarcoma
question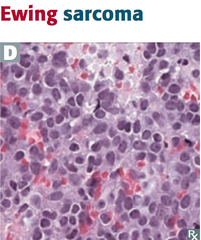
Represent one-third of all bone cancers in children chromosomes 11 and 22 abnormally exchange pieces (11:22 translocation) discovered by James Ewing in 1921 found in boys more than girls rare to be diagnosed after age 25 commonly 10-20 years of age nursing dx: impaired mobility dx: biopsy of bone lesion

answer
Ewing Sarcoma What is it
question
pain and swelling at tumor site bone pain or swelling respiratory distress spinal cord compression fever weight loss

answer
Ewing Sarcoma Signs and Symptoms
question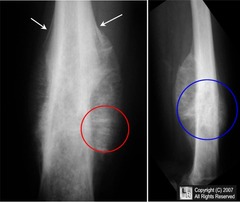
consists of 3 phases: Induction therapy: destroys leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow and to attempt a restoration of normal blood cell production; 30 day treatment (lumbar punctures to inject intrathecally to prevent central nervous system involvement) Consolidation therapy: destroys remaining leukemia cells in the body; 4-8 month treatment Maintenance therapy: prevention of further leukemic cell production; 1-2 years of treatment

answer
Ewing Sarcoma Medical Management
question
Septic Shock Hemorrhagic Cystitis Superior Vena Cava Syndrome DIC Hyperleukocytosis and leukostasis Spinal Cord Compression Tumor Lysis Syndrome

answer
Oncological Emergencies
question
confusion fever tachypnea decreased urinary output cold clammy skin

answer
Septic Shock Signs & Symptoms
question
bloody or painful urination

answer
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
question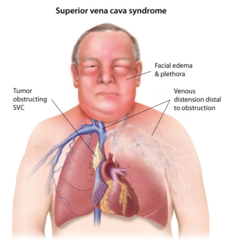
diminished blood return to the heart widening mass by the heart most common in lung cancers and Hodgkins lymphoma Increased ICP Sx: hoarseness, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, coughing up blood, swelling of veins in chest and neck, edema in arms, tachypnea, cyanosis

answer
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
question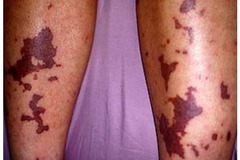
excessive thrombin generation due to sepsis or cancer common in leukemias common with use of asparaginase the proteins that control blood clotting become overactive S/S: chest pain, SOB, pain, redness, warmth and swelling, headaches, speech changes, paralysis, heart attack, lung and kidney problems

answer
DIC Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
question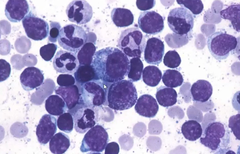
leukemias with counts higher than 100,000mm3 high counts cause sludging of the endothelial, bleeding and infiltrates in lungs hydroxyurea 1-3 grams every 6 hours S/S: coma, somnolence, altered mental status, agitation, seizures, papilledema, sluggish pupils, hypoxia, tachypnea, hemorrhage, thrombosis, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, enlarged lymph nodes, priapism

answer
Hyperleukocytosis and Leukostasis
question
fast growing mass that occludes spinal cord neuroblastomas in children; breast and prostate cancers in adults pain in thoracic area location identifies how symptoms progress S/S: weakness of neck flexion, reflexes preserved, ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, variable feeding problems, generalized weakness, shallow rapid respirations, scoliosis

answer
Spinal Cord Compression
question
Metabolic abnormalities: -hyperkalemia -hyperphosphatemia -hypocalcemia -hyperuricemia most common in leukemias S/S: lethargy, nausea & vomiting, oliguria, flank pain, pruritus, tetany, and altered LOC. Prevention: keep urine alkalized and maintain a low phosphate diet. Nursing Care: aloprim, monitor electrolytes, sometimes dialysis is needed

answer
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
question
nausea & vomiting alopecia extravasation mucositis diarrhea & constipation anemia thrombocytopenia neutropenia

answer
Side Effects of Cancer Treatment
question
22% LIVE at least 30 yrs and don't suffer from chronic health problems 34% DIE within 30yrs, 20% die in years 1-5 14% DIE in years 6-30 19% SURVIVE at least 30 years but suffer life-long life-threatening or disabling chronic health conditions 25% SURVIVE at least 30 years but suffer mild or moderate chronic health conditions
answer
Chart on Slide 2
question
anthracycline antibiotic Nadir: 10-14 days after dose dose limiting cardiotoxicity; turns urine red

answer
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) "red devil"
question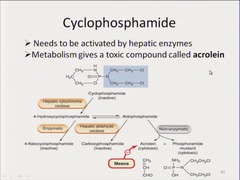
alkylating agent Nadir: 10-14 days after dose hemorrhagic cystitis--use MESNA

answer
Cyclophosphamide (Cyotoxan)
question
plant alkaloid Nadir: 7-10 days after dose peripheral neuropathy

answer
Vincristine (Oncovin)
question
plant alkaloid Nadir: 7-14 days after dose peripheral neuropathy; metallic taste; skin reaction
answer
Etoposide (Toposar)
question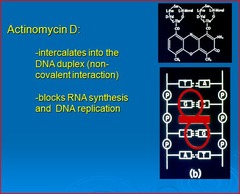
alkylating agent nadir: 14-21 days after dose sensitivity to sunlight

answer
Actinomycin D (Dactinomycin)
question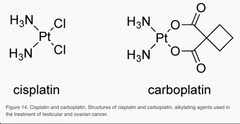
alkylating agent nadir: 21 days after dose ototoxicity; nephrotoxicity; cardiovascular events

answer
Carboplatin (paraplatin)
question
alkylating agent nadir: 8-10 (WBC) 27-32 (platelets

answer
Melphalan (Phenylalanine mustard)
question
antimetabolite agent nadir: 10 days after dose hemorrhagic cystitis

answer
Methorexate (Rheumatrex)
question
alkylating agent nadir: 10-14 days after dose hemorrhagic cystitis
answer
Ifasfomide (Ifex)
question
enzyme nadir: 14 days after IM dose stomach cramping; central nervous system toxicity (seizures, hallucination)

answer
Asparaginase (Lspar)
question
antimetabolite nadir: 7-10 days (WBC) 7-15 days (platelets) hand-foot syndrome; eye sensitivity
answer
Cytarabine (Cytosar-U)
question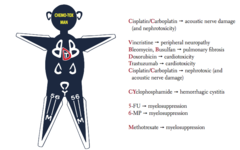
alkylating agent nadir: 14-21 days after pill dose adrenal insufficiency, busulfan lung-permanent lung damage and SOB

answer
Busulfan (Busulfex)
question
signal transduction inhibitor edema of feet, hands, and face; heart failure
answer
Imatinib (Gleevec: STI-571)



