Chemical Cycles and Organic Chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Liquid, solid, gas
answer
Forms of water
question
Turns water from a liquid to a gas, and the gas reenters the atmosphere
answer
Evaporation
question
When groundwater is taken up by plants and released from their leaves as a gas
answer
Transpiration
question
Gaseous water in the atmosphere cools at a certain rate
answer
Condensation
question
When liquid forms a large enough droplet in the atmosphere, and falls back to the surface
answer
Precipitation
question
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, freezing, melting, absorption/drinking (refer to water cycle diagram handout)
answer
Aspects of the water cycle
question
Sun, gravity, Earth's internal energy
answer
Driving force of the carbon cycle
question
Atmosphere/ocean, decomposers, consumers, producers, rocks, dead organisms/waste, fossil fuels
answer
Carbon reservoirs
question
Photosynthesis, cellular respiration, feeding, death and waste (detritus), burial and compaction, eruption, decomposition, burning (human impact), fossil fuel formation (refer to carbon cycle diagram handout)
answer
Carbon movement processes
question
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy = C6H12O6 + 6 O2
answer
Photosynthesis symbol equation
question
Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight = glucose + oxygen (reverse of cellular respiration)
answer
Photosynthesis word equation
question
Chloroplast
answer
Photosynthesis occurs in which plant organelle
question
Glucose + oxygen = Carbon dioxide + water + Chemical energy (ATP; Reverse of photosynthesis)
answer
Cellular Respiration word equation
question
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 = 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + energy (ATP)
answer
Cellular Respiration symbol equation
question
The amount of matter is always constant. No matter can be added (more atoms) and none can be removed. Matter can only change forms
answer
Law of Conservation of Matter
question
Mitochondria
answer
Cellular Respiration occurs in which organelle
question
The change overtime of rocks into sediments
answer
Weathering and erosion
question
When sedimentary and igneous rock is put under extreme heat and pressure (chemical process)
answer
Formation of metamorphic rock
question
Cooling off of magma (chemical process)
answer
Formation of igneous rock
question
Compaction and cementation of sediments (physical process)
answer
Formation of sedimentary rock
question
Earth's core, sun, gravity
answer
What is the driving force of the rock cycle
question
Sedimentary rock
answer
What type of rock are fossils found in
question
Molecule that can be linked to other monomers to create polymers; There are a small number of monomers used by living things, but livings things differ in the way that the monomers are put together to make macromolecules
answer
Monomers
question
Macromolecules
answer
Similar species make similar ___
question
Very large number of molecules that are bonded together in a specific pattern
answer
Macromolecules
question
Any molecule in a living system, containing carbon; carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
answer
Organic Molecules
question
Carbon
answer
All living things contain ___
question
Can create larger, more complex molecules
answer
Carbon
question
Polysaccharides (monosaccharides), nucleic acid (nucleotides), proteins (amino acids), lipids (glycerols)
answer
What do organic macromolecules include?
question
A molecule containing a very large amount of molecules
answer
Macromolecule
question
Lipids
answer
Which organic molecule does not form polymers?
question
A collection of monomers
answer
Polymer
question
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
answer
Elements of Carbohydrates
question
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen
answer
Elements of Proteins
question
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
answer
Elements of Lipids
question
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
answer
Elements of Nucleic Acid
question
Monosaccharide (glucose)
answer
Monomers of Carbohydrates
question
Amino Acids (20 total - different R groups)
answer
Monomers of Proteins
question
Glycerol and fatty acid chains
answer
Monomers of Lipids
question
Nucleotide (5 carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base)
answer
Monomers of Nucleic Acid
question
Polysaccharide
answer
Polymer of Carbohydrates
question
Polypeptide
answer
Polymer of Proteins
question
NONE
answer
Polymer of Lipids
question
Nucleic Acid
answer
Polymer of Nucleic Acids
question
SHORT term energy storage, structural component (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
answer
Function of Carbohydrates
question
Metabolism (enzymes), structural support (collagen), transport (in cell membrane), defense (antibodies), regulation (hormones), motion (muscle contraction)
answer
Function of Proteins
question
LONG term energy storage, structural component (cell membrane), insulation, prevention of water loss, steroids (hormones and cholesterol)
answer
Function of Lipids
question
Store and transmit genetic information (contains the code for proteins)
answer
Function of Nucleic Acids
question
Sugars, starches, fruits, milk
answer
Examples of Carbohydrates
question
Found in muscle, bone, hair, nails; lean meat, nuts, beans
answer
Examples of Proteins
question
Fats, steroids, phospholipids
answer
Examples of Lipids
question
DNA, RNA; found in nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast
answer
Examples of Nucleic Acids
question
The bonding of monomers by removal of a water molecule (H and OH)
answer
Dehydration Synthesis
question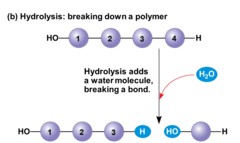
The separation of monomers through the addition of water molecules (H and OH)

answer
Hydrolysis
question
Chemical reactions in which simpler substances are combined to form complex molecules (ex. dehydration synthesis); store energy
answer
Anabolism
question
Chemical reactions in that result in the break down of more complex organic molecules into simpler substances (ex. hydrolysis); release energy that is used chemical reactions
answer
Catabolism
question
consist of one or more polypeptides, most are globular (3D), each has a unique sequence and number of amino acids
answer
Proteins
question
Long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
answer
Polypeptide
question
20 different amino acids (all have the same carboxyl and amino group, R group differs (ionized, polar, nonpolar)
answer
Amino acids
question
Function depends on specific sequence of amino acids and shape
answer
Protein molecules
question
chain of amino acids covalently bonded to form a polypeptide bond
answer
Primary structure
question
Hydrogen bonding between amino acids, forms alpha helix or pleated sheet, results in 3D shape
answer
Secondary structure
question
The unique overall 3D shape of a polypeptide due to hydrogen bonding between R groups
answer
Tertiary structure
question
When two or more polypeptide chains (tertiary forms) combine
answer
Quaternary structure
question
It is due to the number and type of amino acids it is composed of
answer
Why does each protein fold into a specific shape
question
While some cells have the same proteins, the differences of proteins ultimately makes cells (and organisms) different
answer
Unity and diversity of proteins
question
Proteins can have any combination of amino acids, and a possible infinite number of amino acids in a chain
answer
Why are an infinite number of different protein shapes possible?
question
Molecules must randomly collide in order for reactions to occur
answer
Random collision
question
Involve changes in chemical bonds that join compounds; involve changes in energy; energy is released or absorbed whenever chemical bonds form or are broken
answer
Chemical reactions
question
Energy needed to get a reaction started
answer
Activation energy
question
The chemical processes that occur within an organism in order to maintain life
answer
Metabolism
question
Photosynthesis, respiration, digestion, and synthesis of organic molecules
answer
Metabolic Reactions
question
To absorb energy, and pass it on to other organisms to keep life continuing on earth
answer
Purpose of Photosynthesis
question
To break down sugar and turn it into energy that organisms can use to help us function and live
answer
Purpose of Respiration
question
To help the body absorb and break down nutrients
answer
Purpose of digestion
question
Most common type of protein; used by cells for chemical reactions; not changed by reactions, reusable; catalyze (speed up) the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the amount of energy required
answer
Enzyme
question
A substance that increases the rate of chemical reactions without going under any chemical change
answer
Catalyst
question
Lowering the activation energy, allowing the reactions to occur faster
answer
Catalyzing
question
It lowers the amount needed
answer
How does an enzyme change activation energy?
question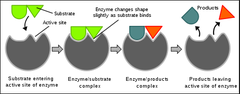
Enzymes are specific to their substrates (lock and key) and catalyze only one reaction

answer
Enzymes and substrates
question
Usually derived from the reaction it catalyzes (lactASE breaks down lactose)
answer
Enzyme name
question
Found in saliva, breaks down starch
answer
Amylase
question
Found in the stomach, works on digestion
answer
Pepsin
question
Breaks down hydrogen peroxide
answer
Catalase
question
Some enzymes break down nutrient molecules (fats, proteins, carbohydrates) during digestion. They also can guide the broken down molecules into the bloodstream. (Also involved in storage and release of energy and many other processes)
answer
General Role of Enzymes in Metabolic Processes
question
Enzymes require specific environmental conditions to work and are most effective at optimal conditions; factors influencing enzyme reactions are pH, temperature, and amount of substrate
answer
Optimal Conditions for Enzymes
question
When the pH of an environment where enzymes are is changes, the H+ ions or OH- ions that are added may break the ionic bonds within the enzymes by bonding to the an ion, thus ruining the structure of the enzyme (denaturing it). This may cause the active site to become deformed, which causes the enzyme to not be able to react with a substrate. (no structure, no function)
answer
pH affect on Enzymes
question
Low Temp: reactions are too slow; high Temp: can permanently alter the structure of most proteins, making it denatured; causes hydrogen bonds to break which changes the structure (usually changing the activation site) and giving it no function
answer
Temperature affect on Enzymes
question
When a protein's secondary or tertiary structure is altered, but the primary structure stays in tact
answer
Denatured
question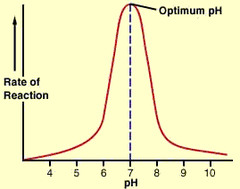

answer
Enzyme Activity pH graph
question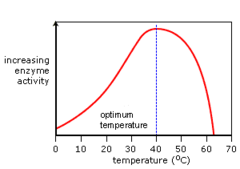

answer
Enzyme Activity Temperature graph



