Chapter 3 Outline and Packet – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Hydrogenation is a chemical process that.......
answer
-turns liquid oil to solid fats
question
Fats are major constituents of......
answer
-cell membranes
question
Typical fat molecules have _________ chain(s)
answer
-3
question
A single atom of carbon may form up to ___________ covalent bonds with other atoms
answer
-4
question
Although carbon dioxide contains carbon, it is not considered an "organic" compound because.......
answer
-the carbon atom is not bonded to at least one hydrogen atom
question
A hydrolysis reaction results in.....
answer
-bond breakage of a macromolecule
question
An -OH group is a __________ group
answer
-hydroxyl
question
An -NH2 group is an __________ group
answer
-amine
question
A figure with 3 unbonded glucose molecules in the top row and 3 bonded glucose molecules in the bottom row (bonded with O in the middle) illustrates a ______________ reaction that produces two ________ and a ____________
answer
-condensation -water molecules -polymer
question
What kind of reaction produces large molecules by linking small molecules?
answer
-condensation
question
Monosaccharaides may be characterized by.......
answer
-a ketone group -carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio -a backbone of five to six carbon atoms -one carbonyl group
question
Fructose and glucose are......
answer
-both monosaccharaides and six-carbon sugars
question
Oligosaccharides include....
answer
-both sucrose and lactose
question
Glucose and fructose......
answer
-contain the same number of hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl groups
question
Glucose an sugars in DNA and RNA.....
answer
-are monosaccharaides
question
Sucrose is composed of.....
answer
-a molecule of fructose and molecule of glucose
question
Glycogen is a polysaccharide used for energy storage by.....
answer
-animals
question
Cellulose is......
answer
-a polysaccharide found in cell walls of plants
question
What describes some aspect of polysaccharide?
answer
-energy storage -straight or branched chain -glucose subunits -contain only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
question
What is true about polysaccharides?
answer
-composed of many linked polysaccharides -may be straight or unbranched or highly branched -most likely made of glucose molecules if they are one of the natural polysaccharides -may by insoluble because of their large size and structure
question
Which of the following does not belong? -phospholipids -polysaccharides -unsaturated fats -steroids -saturated fats
answer
-polysaccharide
question
Triglycerides are.....
answer
-neutral fats
question
The honeycomb on which the bee is standing is made up primarily of what?
answer
-lipids
question
The dotted areas between the glycerol group and each of the three chains to make a fatty acid indicates where _____________ reactions will occur to produce _________ and ________-
answer
-condensation -covalent bonds -water molecules
question
Steroids characteristics....
answer
-have no fatty-acid component -consist of four rings -may have different numbers, types, and positions of functional groups attached to them -are a specialized type of lipid
question
Cholesterol characteristics....
answer
-has a rigid backbone of four carbon rings -is the most common steroid in animal tissue -is a lipid without a fatty-acid component -is needed to produce sexual development and maturity
question
____________ are long-chain fatty acids attached to long-chain alcohols
answer
-Waxes
question
Polyunsaturated fats.....
answer
-have fewer hydrogen atoms than to saturated fats
question
Lipids do not....
answer
-yield less energy per gram than do carbohydrates -include cartilage and chitin -include fats consisting of one fatty-acid molecule and three glycerol molecules -are composed of monosaccharaides
question
All steroids have....
answer
-four rings of carbon to which other atoms are attached
question
The sequence of amino acids is the __________ structure of proteins
answer
-primary
question
Amino acids are linked by what kind of bonds to form the primary structure of a protein?
answer
-peptide
question
The interaction of several polypeptide chains in a hemoglobin molecule is its __________ structure
answer
-quaternary
question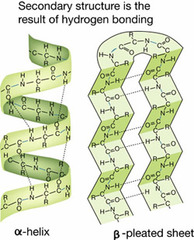
The figure on the other side illustrates one possible ______________ structure of _____________

answer
-secondary -proteins
question
Denaturation of proteins may result in.....
answer
-breakage of hydrogen bonds -loss of three-dimensional structure -alteration of enzyme activity -endangerment of a cell's life
question
What is found in every nucleotide?
answer
-a phosphate group -a single-ring base -a double-ring base -nitrogen
question
Enzymes....
answer
-affect metabolic reaction rates
question
Glucose....
answer
-a six-carbon sugar
question
Nucleotide....
answer
-found in DNA and RNA
question
Phospholipids.....
answer
-principal components of cell membranes
question
-NH2
answer
-the amine group -the group on the amino-terminal end of proteins
question
-COOH
answer
-the carboxyl group -the group that is acidic -the group on the carboxyl-terminal end of proteins
question
-CH3
answer
-the methyl group
question
-OH
answer
-the hydroxyl group
question
-PO4
answer
-the group typical of energy carriers such as ATP
question
Amino acid....
answer
-the basic unit of proteins -the monomers of a polypeptide chain
question
Nucleotide
answer
-the basic unit of DNA -the basic unit of RNA
question
Glucose....
answer
-the basic unit of cellulose -the basic unit of glycogen -the basic unit of starch
question
Which units combine in various ways to form lipids?
answer
-glycerol and fatty acids
question
A _________ is a term given to a macromolecule (large molecule) made up of individual subunits
answer
-polymer
question
Write the empirical formula for a carbohydrate
answer
-for every carb there are twice as many hydrogen -CH2O
question
A denatured protein has lost its ______________
answer
-shape and function
question
A lipid ________________ is the most common conformation of the membrane of living systems
answer
-bilayer
question
In biology, many complementary process exist. Explain how condensation reactions are complementary to hydrolysis reactions
answer
-both involve water -hydrolysis breaks down -condensation builds
question
What property of phospholipids allows them to form cell membranes?
answer
-polarity -hydrophobic and hydrophilic
question
Explain why vigorous exercise in warm weather could be hazardous to your enzymes
answer
-the enzymes overheat and then lose their shape and funciton
question
Describe how trans fats originated
answer
-Proctor and Gable Co. developed a partially hydrogenated soybean oil in 1908 as a substitute for expensive solid animal fats they had been using to make candles -electricity started to hurt the candle business -Proctor and Gamble Co. noticed that trans fats looked a lot like lard -Proctor and Gamble began marketing it as a new food in 1911
question
List foods that contain trans fats
answer
-manufactured and fast foods -French fries, butter substitutes, cookies, crackers, cakes, pancakes, peanut butter, pies, doughnuts, muffins, chicken nuggets, etc
question
Pros of trans fats
answer
-longer shelf life, mild flavor, lower cost than butter or lard
question
Cons of trans fats
answer
-raises the level of cholesterol in our blood and directly alter the function of our arteries and veins -atherosclerosis, heart attack, diabetes
question
Define organic
answer
-describes a compound that consist primarily of carbon and hydrogen atoms
question
Describe how the bonding behavior of carbon lends to the variety of compounds it forms
answer
-carbon can covalently bond with up to 4 other atoms, these atoms become polar or nonpolar depending on the other element -organic compounds have a backbone of carbon to which other compounds attach, these chains form 2 long rings, this versatility leads to the different structures
question
List the different types of molecular models
answer
-structural models -ball and stick models -space filling models
question
Structural Models
answer
-often very complex, often simplified by using polygons as symbols for rings, omitting the labels for some atoms
question
Ball-and-Stick Models
answer
-shows the arrangement of atoms in 3-D
question
Space-Filling Models
answer
-shows a molecules overall shape
question
Define monomer
answer
-molecules that are subunits of polymers
question
Define polymer
answer
-molecule that consist of multiple monomers
question
Define condensation reaction
answer
-process by which enzymes build large molecules from smaller subunits; water also forms
question
Define hydrolysis reactions
answer
-process by which an enzyme breaks a molecule into smaller subunits by attaching a hydroxyl group to one part and a hydrogen atom to the other
question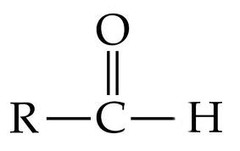
Aldehyde Group

answer
*Not the R*
question
Define cellulose
answer
-polysaccharide -major structural material in plants
question
Define disaccharide
answer
-polymer of two sugar subunits
question
Define glycogen
answer
-polysaccharide -energy reservoir in animal cells
question
Define monosaccharide
answer
-simple sugar -monomer of polysaccharide
question
Define polysaccharide
answer
-polymer of many monosaccharaides
question
Define starch
answer
-polysaccharide -energy reservoir in plant cells
question
Describe the purposes of carbohydrates in nature
answer
-quick energy -structure -soluble in water
question
Define mono-
answer
-one
question
Define oligo-
answer
-a few
question
Define poly-
answer
-many monosaccharaides
question
Role of glucose in nature
answer
-fuel to drive cellular processes, structural material to build larger molecules, starting material that is remodeled into other materials
question
Role of fructose in nature
answer
-a popular sugar in soda and juices
question
Role of amylose in nature
answer
-a common polysaccharide found in plants
question
Role of glycogen in nature
answer
-a common polysaccharide found in animals
question
Role of cellulose in nature
answer
-a common polysaccharide found in plants
question
Properties of lipids in nature
answer
-fatty, waxy, or oily organic compounds, all hydrophilic, many incorporate fatty acids
question
Purposes of lipids in nature
answer
-long term energy -structure (in cells) -water repellent (wax on leaves) -insulation -signals hormones
question
Define saturated
answer
-contains no carbon-carbon bonds
question
Define unsaturated
answer
-contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in its tail
question
Structure of fatty acids
answer
-organic compound that consist of a chain of carbon atoms with an acidic carboxyl group at one end
question
Structure of glycerol
answer
-attaches to a fatty acid by its carboxyl group head, the fatty acid then loses its hydrophilic character
question
Structure of triglycerides
answer
-a fat with three fatty acid chains
question
Structure of phospholipids
answer
-lipid with a phosphate group in its hydrophilic head and two nonpolar fatty acid tails, main constitute of eukaryotic cells
question
Structure of steroids
answer
-type of lipid with 4 carbon rings and no fatty acid tails
question
Structure of waxes
answer
-water repellent mixture of lipids with long fatty acid tails bonded to long chain alcohols or carbon rings
question
Properties of amino acids in nature
answer
-small organic compound that is a subunit of proteins -consist of a carboxyl group, an amine group, and a characteristic side group (R), all typically bonded to the same carbon atom
question
Define primary structure of proteins
answer
-consist of a linerar sequence of amino acids (a polypeptide chain)
question
Define secondary structure of proteins
answer
-arises as a polypeptide chain twists into a coil (helix) or a sheet held in place by hydrogen bonds between different parts of the molecule
question
Define tertiary structure of proteins
answer
-occurs when a chain coils and sheets fold up into a functional domain such as a barrel or pocket
question
Define quaternary structure of proteins
answer
-in which two or more polypeptide chains associate as one molecule
question
Define globular proteins
answer
-form chemically active pockets that can make or break bonds of other molecules
question
Define fibrous proteins
answer
-contribute to the structure and organization of cells and tissues
question
Structure of glycoproteins
answer
-molecules that allow a tissue or a body to recognize it's own cell, cells that help cells interact in immune responses
question
Structure of lipoproteins
answer
-form when enzymes covalently bond lipids to a protein -are aggregate structures that consist of variable amounts and types of proteins and lipids, carry fats and cholesterol through bloodstream
question
Factors of proteins that can cause denaturation of proteins
answer
-disruption of hydrogen bonds and other interactions that heat, some salts, shifts, in pH, or detergents
question
Describe the mechanism by which a prion infection operates
answer
-begins with a protein that occurs normally in mammals, this protein misfolds (not a big deal), but when it misfolds again it becomes a prion
question
Name several nucleotides
answer
-ATP
question
Recognize the structure and functions of nucleic acids
answer
-has a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and phosphate groups



