Cervical Cancer: Brachytherapy Techniques – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Most common applicator for intracavitary brachy
answer
Fletcher-Suit intrauterine tandem and ovoids or tandem and ring
question
Proper position of flange
answer
Flush against cervical surface
question
Proper position of tandem
answer
Should bisect angle of colpostats,unrotated,midline
question
Proper position of colpostats
answer
Hi in fornices along cervix
question
Flange position represents
answer
Cervical os
question
Where are marker seeds placed
answer
1cm above position of flange
question
What positions are marker seeds
answer
2, 5, 8, 11 o'clock positions or just one for depth
question
What holds positions of tandem of ovoids
answer
Proper packing
question
Improper packing does what
answer
Increases doses to rectum/bladder but rectal shield part of nucleotron applicator may reduce the need for packing
question
Insertion techniques for intracavitary applicators
answer
US and fluoroscopic guidance
question
Advantage of Smit sleeve
answer
May facilitate applicator placement;+risk of perf
question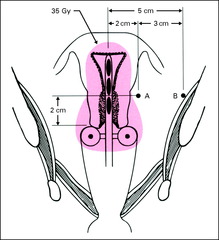
Point A

answer
2cm cephalad from cerv os, 2 cm lat to uterine canal We prescribe to this point
question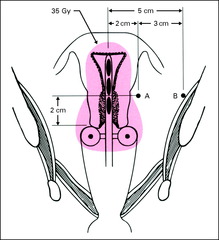
What does point A represent

answer
Med parametrium/lat cervix (ureter/uterine art cross)
question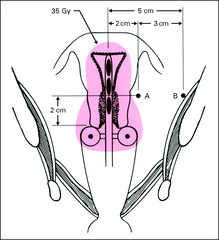
Point B

answer
5 cm lat to center of pelvis at same level as point A
question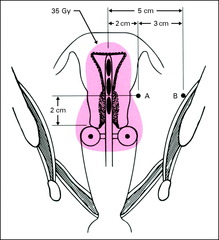
What does point B represent

answer
Obturator nodes/lat parametrium
question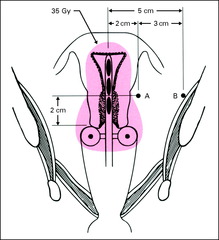
Point B receives what% of Point A dose

answer
1/3 to 1/4
question
What does point C represent
answer
Pelvic sidewall dose
question
Point C receives what% of Point A dose
answer
1/5
question
Point P
answer
most lateral point of bony pelvic sidewall
question
What does point P represent
answer
Minimal dose to ext iliac nodes
question
Point H
answer
2 cm above ovoid level, 2 cm lat line bisecting ovoids
question
Significance of point H
answer
recommended rx point by ABS
question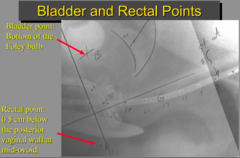
Bladder point

answer
post surface foley on lat film/middle of foley on AP
question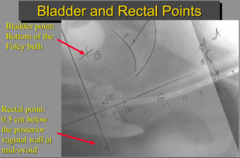
Rectal point

answer
5mm behind vag wall@last intrauterin tandem source
question
Vaginal point
answer
lat edge of ovoid on AP/mid-ovoid on lat
question
Historically point A used for
answer
Tolerance dose
question
Now point A is used for
answer
Prescription point
question
Dose for stage IB-IIA cervical CA
answer
80-85 Gy to point A (85 Gy more accepted) We use 7Gy x 4 after 45Gy/25fx but can use 6Gy x 5fx
question
Dose for more advanced stage disease
answer
85-95 Gy to point A (assuming EBRT to 50.4/28fx)
question
Problem w/ prescribing to point A
answer
empirical point (does not reflect tumor dose)
question
ICRU recommendation instead of rx to point A
answer
determine tissue volume in 60 Gy isodose sur
question
American working group developed system
answer
Prescribe to 3 separate CTVs
question
High risk CTV
answer
GTV prior to xrt + entire cervix (80-90 Gy)
question
Intermediate risk CTV
answer
Hi risk CTV + 0.5-1.5 cm margin (60 Gy)
question
Low risk CTV
answer
Tumor volume covered by ext beam
question
Onset of brachytherapy at what time point
answer
No later than week 6 Can be given during EBRT, but avoid chemo day
question
Total duration of xrt should be no more than
answer
<8 wks, as there is benefit to shortening the treatment interval - local control and survival is affected by 1% a day, (Perez, IJRBOP, 1995; Girinsky, IJROBP 1993) from RTOG 90-01
question
Tandem/ring has what dose distribution
answer
Narrow dose distribution, cover ant/post lip of cvx
question
Tandem/ovoid has what dose distribution
answer
Pear shaped, covers upper vagina
question
Tandem/cylinder has what dose distribution
answer
Narrow distribution, tx entire vagina, <5mm
question
Interstitial implant has what dose distribution
answer
Covers distal vagina >5mm
question
Mini-ovoids
answer
Unshielded This applicator was designed for the patient with a narrow vault. The medial area of the ovoid is flattened to accommodate a very small anatomy.
question
Advantage of tandem/ring
answer
Reproducible geometry; easy to insert
question
When is tandem/ring used
answer
When vaginal fornices absent/asymmetric
question
When is interstitial implant used
answer
Vag narrowing, absent fornices, vag extension
question
When is tandem/cylinder used
answer
Need interstitial implant but not available
question
Disadvantage of tandem/cylinder
answer
Lower parametrial doses,higher bladder/rectal doses
question
For deep or thick vaginal involvement consider this brachy tehcnique
answer
Interstitial
question
What kind of gauze should be used for cervical cancer brachy packing
answer
Triple-sulfate soaked gauze for LDR and KJ-Jelly for HDR
question
What should the brachy implant look like during anterior plain film evaluation:
answer
ant film: tandem bisects ovoids and tandem not rotated; phlange close to cervical marker seeds: ovoids high in fornices <1cm from marker seeds with 0.5-1cm spacing between them.
question
What should the brachy implant look like during lateral plain film evaluation:
answer
tandem bisects ovoids and is midway between sacrum and bladder, at least 3 cm from asacral promontory;, sufficient andterior and posterior packing, foley balloon firmly pulled down.
question
Dose constraint for HDR to bladder and rectum?
answer
<70% of point A dose
question
Dose constrain for LDR to bladder and rectum?
answer
limit rectal point to <70Gy and bladder point to <75Gy
question
What are the constraints for the vagina for brachy?
answer
Upper vaginal mucosa <120Gy Midvaginal mucosa <80-90G Lower vaginal mucosa <60-70Gy
question
What dose can cause fibrosis and stenosis of the vaginal canal?
answer
50+ Gy
question
What dose should the uterus be limited to ?
answer
<100Gy
question
What dose should the ureters be limited to?
answer
<75Gy
question
What dose should the femoral heads be limited to?
answer
<50Gy



