Breast – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
birads features of a mass
answer
space occupying lesion seen in two different projections convex outward contour denser center than periphery
question
birads mass features that are important to note
answer
size location density shape margins interval change
question
implications of mass size
answer
size does not predict malignancy size affects management large palpable masses can be biopsied with palpation
question
implications of mass location
answer
quadrant location does not predict malignancy mass within the skin cannot be a primary breast carcinoma air halo is an artifact from a skin mass
question
implications of mass density
answer
fat density and mixed density masses are benign
question
breast masses containing fat
answer
oil cyst lipoma galactocele
question
mixed density masses
answer
hamartoma fibroadenolipoma lymph node
question
birads descriptors of mass shape
answer
round oval lobular irregular (suspcious)
question
birads descriptors of mass margins
answer
circumscribed (well defined, only margin that is probably benign) microlobulated (50% chance of cancer) obscured indistinct spiculated (very suspicious)
question
how much of a margin must be seen to be able to call it circumscribed
answer
>75%
question
workup of breast mass
answer
spot-compresion magnification
question
implications of interval change in a mass
answer
prior films are always helpful worrisome changes are newly apparent lesion, interval enlargement, more lobular or indistinct borders, apparent calcifications
question
how to work up breast masses that contain multiple features
answer
always base management on most suspcious feature
question
management strategy of masses
answer
identify benign masses ultrasound to identify cysts biopsy or follow-up for solid masses that are not clearly benign
question
indications for following a mass (BIRADS 3)
answer
round, oval, or lobular shape circumscribed margin if a mass is stable for at least 2 years, call it benign (BIRADS 2) other solid masses should be biopsied
question
types of asymmetries
answer
asymmetry global asymmetry focal asymmetry developing asymmetry
question
definition of an asymmetry
answer
formerly called a density fibroglandular density visible only on one view 80% are superimposition of normal tissue
question
global asymmetry
answer
substantially greater volume of fibroglandular tissue in one breast than in the corresponding location in the contralateral breast must occupy more than one quadrant should not have suspicous mass, calcifications, or architectural distortion almost always normal variant further workup indicated if associated mass, grouped microcalcifications, architectural distortion, or palpable
question
focal asymmetry
answer
fibroglandular tissue asymmery occupying less than one quadrant visible on two views but does not have convex outward contours or conspicuity of a mass may be focal normal tissue, especially when there is interspersed fat <1% chance of malignancy if no associated mass, calcifications, architectural distortion, or palpable correlate easy way to work up is repeating to identify summation--repeat same view, change obliquity slightly, roll view, spot compression, targeted ultrasound if no mammographic, sonographic, or palpable abnormality, call it BIRADS 3; BIRADS 2 when stable at least 2 years
question
developing asymmetry
answer
focal asymmetry that is new, larger, or denser than prior uncommon 13-27% chance of malignancy BIRADS 4 unless proven to be simple cyst
question
general classification of asymmetries
answer
asymmetry BIRADS 1 global asymmetry BIRADS 2 focal asymmetry BIRADS 3 developing asymmetry BIRADS 4
question
typically benign calcifications (BIRADS 2)
answer
calcifications with radiolucent center milk of calcium vascular coarse or popcorn-like large, rod-like (duct ectasia) round injection granulomas
question
calcifications with radiolucent center
answer
lucent centered calcifications eggshell and rim calcifications skin and dystrophic calcifications may have lucent center but do not have to
question
lucent centered calcifications
answer
variable size round or oval with smooth surfaces, lucent center wall is usually thicker than rim or eggshell type may be due to fat necrosis or calcified debris or oil cyst
question
eggshell calcifications
answer
very thin, usually <1mm thick calcium on surface of sphere some fat necrosis and oil cyst
question
skin calcifications
answer
usually along inframammary fold or parasternal axilla and areola can confirm with tangential view
question
dystrophic calcifications
answer
usually in irradiated breast or following trauma irregular but coarse usually >0.5 mm often lucent center
question
common clinical history with retroalveolar dystrophic calcifications
answer
prior breast surgery, usually reduction
question
milk of calcium calcifications
answer
sedimented calcification in macro or microcysts on lateral, more clearly defined, semilunar and dependent on cc, less evident, fuzzy and round most important feature is change in shape on projections
question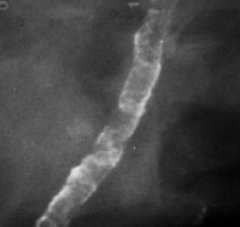
vascular calcifications

answer
parallel tracks linear calcifications associated with a tubular structure may want to report them in women <50 due to risk of CAD
question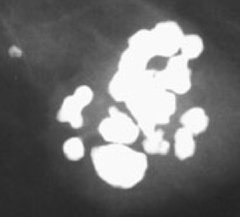
coarse or popcorn like calcifications

answer
usually large, >2-3mm involuting fibroadenoma
question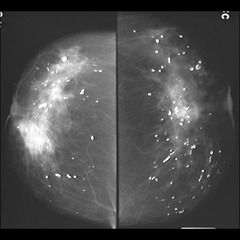
rod-like calcifications (duct ectasia)

answer
can form solid or smooth linear rods may have lucent center if calcium is in duct wall that becomes solid when secretions calcify follow ductal distribution, radiate to nipple may branch often bilateral usually women >60
question
round calcifications
answer
variable size (small or punctate) scattered cluster may warrant close surveillance or biopsy if new or ipsilateral to cancer
question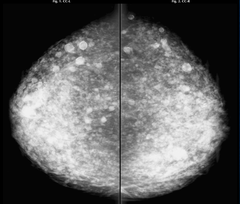
foreign body injection calcifications

answer
characteristic appearance should have obvious clinical history illegal to inject in the US multiplicity and bilaterality helps
question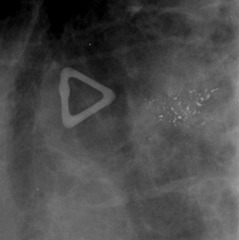
amorphous or indistinct calcifications

answer
BIRADS 4 unless can be demonstrated as benign small or hazy morphology difficult to discern distribution is very important diffuse is usually benign--magnification views can help clustered, regional, linear, or segmental may warrant biopsy
question
coarse heterogeneous calcifications
answer
irregular, conspicuous usually >0.5mm often coalesce but not right size for dystrophic calcifications can be due to malignancy, fibroadenoma, fibrosis, or prior trauma, so BIRADS 4
question
fine pleomorphic calcifications

answer
BIRADS 4-5 variable size and shape usually <0.5mm
question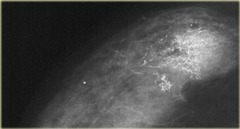
fine linear or fine linear branching calcifications

answer
BIRADS 4-5 thin, linear or curvilinear irregular calcifications can be discontinuous can be smaller than 0.5mm wide appearance suggests ductal involvement
question
BIRADS 4-5 calcifications
answer
amorphous 4 fine pleomorphic 4-5 fine linear 4-5
question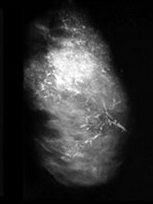
diffuse/scattered calcification distribution

answer
random through breast punctate and amorphous calcifications with this distribution are usually benign usually bilateral
question
regional distribution of calcifications
answer
scattered in a large volume >2cc of breast tissue not conforming to a ductal distribution
question
grouped or clustered calcification distribution
answer
at least five calcifications occupying a small space <1cc of tissue BIRADS 4-5
question
linear distribution of calcifications
answer
arrayed in a line may be suspicious for malignancy if represents a duct BIRADS 4-5
question
segmental calcification distribution
answer
worrisome suggests deposits in ducts and branches in a lobe or segment of the breast BIRADS 4-5
question
BIRADS 3 calcifications
answer
round or puncate and clustered linear or segmental distribution makes BIRADS 4
question
zonal anatomy for breast ultrasound
answer
subcutaneous (premammary)--subcutaneous fat, suspensory ligaments, vessels mammary zone--ducts, fat, fibrous tissue retromammary zone--fat, few cooper's ligaments, superficial pectoralis
question
reason cancers tend to be taller than wide
answer
TDLU points in that direction
question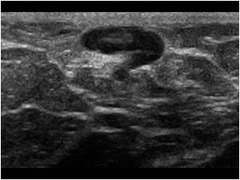
lymph node on ultrasound

answer
oval, reniform, notched circumscribed margins hyperechoic hilum, hypoechoic cortex may show increased through transmission may see hilar flow on color
question
positioning for breast ultrasound
answer
ipsilateral arm abducted, hand under head supine to contralateral posterior oblique or decubitus degree of dependency depends on lesion location
question
transducer selection for breast ultrasound
answer
highest frequency available usually linear high resolution (7MHz and higher) coupling agent is warm gel or stand-off pad for superficial or suspected skin lesion
question
utility of doppler in breast ultrasound
answer
helpful to determine solid versus cystic hyperemia in an infected cyst wall hilar flow in node duplex doppler (spectral and color) can show true flow vs noise avoid excessive compression that can occlude flow
question
uility of power doppler fremitus in breast ultrasound
answer
have patient hum normal tissues vibrate and light up with color signal true solid masses will not vibrate with the fat
question
limitations of doppler in breast ultrasound
answer
PSV, RI, S/D, PI, pattern of flow are not helpful in predicting malignancy grayscale is better for predicting need for biopsy
question
elastography
answer
measures differences in tissue stiffness (elasticity) superimposed strain images benign lesions get smaller on elastic overlay image malignant lesions get larger
question
required annotations for breast ultrasound
answer
side clock face position distance from nipple scan plane orientation depth in tissue is optional
question
mass characteristics to describe on ultrasoud
answer
size orientation margin lesion boundary echo pattern posterior acoustic appearance surrounding tissues
question
indications for breast ultrasound
answer
first line imaging technique for evaluation of palpable masses in women under 30, lactating or pregnant further evaluation of mammographic findings identification and characterization of palpable and non-palpable clinical symptoms evaluations of problems associated with implants guidance of interventional procedure treatment planning for radiation
question
palpable mass in young women <30
answer
start with ultrasound young breasts are very susceptible to radiation effects perform mammogram if no correlate to palpable finding mammogram when suspicious ultrasound needing further evaluation
question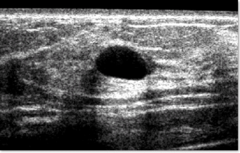
features of a benign simple cyst on ultrasound

answer
anechoic (internal echoes can be seen with high resolution probe) round or oval sharply marginated thin edge shadow artifact posterior acoustic enhancement no color flow
question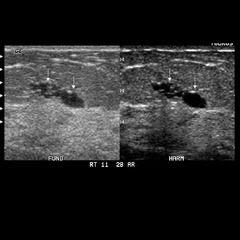
cluster of benign cyst

answer
clustered microcysts correspond to dilated TDLUs cluster of 2-3mm cysts without discrete solid component BIRADS 2
question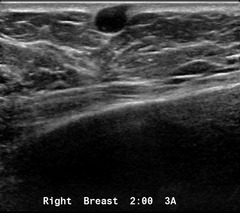
skin cysts

answer
sebaceous and epidermal inclusion cysts claw sign shows skin is origin turning on the lesion may demonstrate a hair follicle sebaceous cysts are hypoechoic and show a gland neck epidermal inclusion cysts are heterogeneous and show concentric echogenic layers neither have flow on doppler
question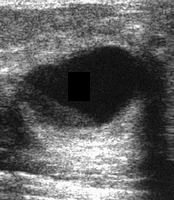
complicated breast cysts on ultrasound

answer
fibrocystic change, galactocele, lipid cyst internal echoes--mobile, ring-down, debris, protein, milk, cholesterol crystals, foam cells, apocrine cells uniformly thick walled is ok fluid-filled and fat-fluid levels circumferential wall calcifications are passable all these are BIRADS2
question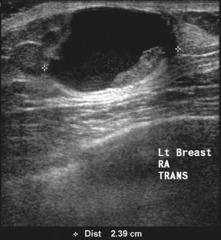
complex mass

answer
cystic lesion wth solid components usually papillary neoplasms eccentric wall thickening, mural nodules, fibrovascular stalk, or thick septations may have microcystic appearance or microlobulated contour these are all BIRADS 4 and require biopsy
question
BIRADS of breast cysts on ultrasound
answer
simple and skin cysts BIRADS 2 clustered microcysts or complicated cysts BIRADS 2-3 possibly solid mass (cannot confirm cystic) or complex mass BIRADS 4 when planning biopsy, ultrasound guidance should only be considered if a clip can be placed if a clip cannot be placed, excision should be performed
question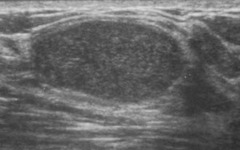
benign features of solid breast masses on ultrasound

answer
hyperechoic compared to fat ellipsoid shape 3 or fewer gentle lobulations thin, echogenic pseudocapsule absence of any malignant features
question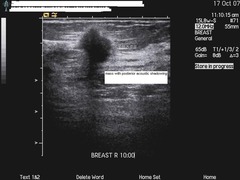
malignant features of breast masses on ultrasound

answer
spiculation taller than wide (nonparallel) angular margins shadowing branch pattern markedly hypoechoic calcification duct extension microlobulation disruption of tissue planes
question
two features most predictive of malignancy in solid lesions on breast ultrasound
answer
spiculation taller than wide
question
requirements for BIRADS 3 classification of a solid breast mass
answer
mammographically and sonographically benign appearance not new or growing personal audit <2% malignancy rate
question
how to manage mammographically visible mass without ultrasound correlate
answer
BIRADS 3 if well circumscribed, not new or growing, no suspicious features, or it is possibly a lymph node
question
mammographic findings necessitating ultrasound evaluation
answer
asymmetry focal asymmetry architectural distortion calcifications dilated ducts on targeted ultrasound look for correlate, determine benign vs malignant features, and assess if a lesion is amenable to ultrasound-guided biopsy
question
clinical symptoms nescessitating ultrasound evaluation of the breast
answer
palpable lump, ridge, thickening, skin changes, focal non-cyclical pain suspicious nipple discharge--unilateral spontaneous clear or bloody cellulitis (rule out abscess)
question
how to manage palpable finding with no mammographic or sonographic abnormality
answer
always defer to clinician/surgeon consider aspiration by palpation if indicated 4% of women with breast cancer have no imaging finding
question
saline and silicone implants on ultrasound
answer
hypoechoic when intact two echogenic lines when single lumen; three when double palpable masses may represent radial fold, herniation, or valve capsular contraction can cause changes in breast size
question
rupture of implants on ultrasound

answer
evident clinically with saline implants, ultrasound shows parallel echogenic lines representing collapsed implant silicone implants show snowstorm with extracapsular rupture, stepladder with intracapsular silicone can be seen migrating into echogeic granulomas or nodes
question
second-look ultrasound following breast MRI
answer
appropriate for suspicious MR finding not seen on intial mammogram or ultrasound reassess for ultrasound findings determine if lesion is amenable to ultrasound guidance for biopsy
question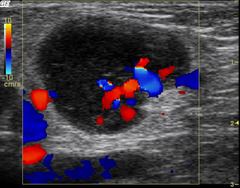
malignant ultrasound features in lymph nodes

answer
diffuse, globular, or irregular cortical thickening abnormal node adjacent to a normal node increased peripheral flow, as opposed to hilar with a normal node
question
indications for breast MRI
answer
evaluation of extent of disease axillary lymphadenopathy with unknown primary one time screen of contralateral breast in a patient with newly diagnosed breast cancer evaluation of treatment response in neoadjuvant population screening of high risk patients
question
patients with risk high enough for MRI screening
answer
>25% risk of cancer risk calculators available, although true calculation should be left to experts
question
indicators of high risk for breast cancer
answer
BRCA1/BRCA2 untested patient with primary relative who is mutation carrier very strong family history prior chest radiation therapy histologic diagnosis of LCIS/atypia personal history of breast cancer
question
breast MRI technique
answer
closed systems are better than open higher field strength better need dedicated breast coil prone positioning dynamic contrast-enhanced T1 active fat-suppression or subtraction T2
question
benefits of prone positioning
answer
minimizes motion degradation breast stabilized feet-first entry reduces claustrophobia
question
components of breast MR report
answer
overall composition--almost entirely fatty...mostly fibroglandular tisue presence of implant background enhancement description of abnormal enhancement overall summary BIRADS category
question
description of abnormal enhancment on breast MRI
answer
mass size, location, modifiers, kinetics non-mass-like enhancement--size, location, morphology, distribution small focus too small to characterize
question
appearance of pectoral muscle invasion on MRI

answer
enhancement along the muscle in addition to mass abutting the muscle
question
hormonal enhancement
answer
hormonal fluctuation causes variability in parenchymal enhancement most pronounced during second half of menstrual cycle optimal time to scan is between days 3 and 14 (UCSF policy 4-11)
question
classic MR appearance of DCIS

answer
clumped ductal enhancement extending towards the nipple extent of DCIS should be proven by biopsy
question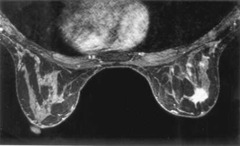
classic MR appearance of invasive ductal cancer

answer
spiculated mass rapid contrast uptake rapid contrast washout increased T2 signal morphology trumps kinetics
question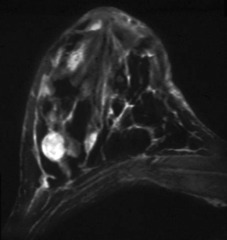
classic MR appearance of fibroadenoma

answer
bright on T2 FSE enhances uniformly persistent or increasing kinetics biopsy may be needed for proof
question
breast MRI for implants
answer
different protocol, no contrast in report, note that study does not evaluate for cancer silastic elastomer shell contains silicone, linguini sign when shell breaks and collapses when intracapsular rupture, silicone is contained by a fibrous capsule when extracapsular rupture, silicone leaks outside capsule and into parenhcyma
question
when to biopsy a breast mass
answer
whenever >2% chance of malignancy BIRADS 4 or 5
question
concordance
answer
pathology results make sense in light of imaging findings
question
features of fine needle aspiration of breast lesions
answer
least traumatic can be performed in office for palpable lesions done best with cytologist to assess immediately often insufficient tissue to completely diagnose
question
features of core biopsy of breast lesions
answer
tissue obtained rather than just cells architecture can be assessed histological underestimation common--DCIS may become invasive ductal, etc.
question
borderline pathology lesions
answer
not clearly malignant or atypical papillary lesion, lobular neoplasia (LCIS, ALH), radial scar when in doubt, excise surgically
question
borderline pathology lesions that should always be excised
answer
atypia/ADH radiologic-pathologic discordance any time pathologists recommends
question
biopsy of calcifications
answer
sometimes will be visible on ultrasound--specimen x-ray still needed stereotactic biopsy now most common for biopsy of calcifications representative sample of calcifications need to be removed to consider the biopsy satisfactory--specimen x-ray!
question
how many cores should be taken in a breast biopsy?
answer
six cores with 14G needle
question
benefits of larger core sizes
answer
more calcification less underestimation the entire lesion may be removed, so a marker clip is important to leave
question
biopsy of complicated breast cysts
answer
diffuse internal echoes otherwise fulfill criteria for simple cyst aspiration can establish that a complicated cyst is not a hypoechoic cancer
question
needle localization
answer
when all biopsy modalities cannot be performed used when a known impalpable finding needs surgery can be placed by any modality
question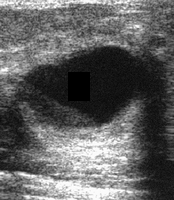
complicated breast cyst

answer
meets all criteria for simple cyst except for internal echoes
question
complex mass

answer
complex mass that contains cystic components
question
steatocystoma multiplex

answer
numerous skin-based oil cysts bilaterally hypoechoic abutting or within dermis on ultrasound distinctive appearance on physical exam
question
comments to make on surgical technique used for breast implants
answer
silicone verus saline prepectoral or retropectoral
question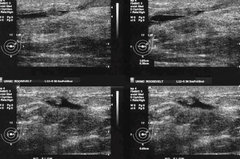
most common cause of spontaneous bloody discharge

answer
intraductal papilloma
question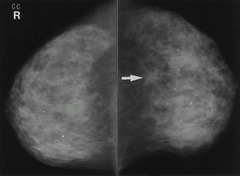
malignancy most likely to present as asymmetry or architectural distortion rather than a mass

answer
invasive lobular carcinoma
question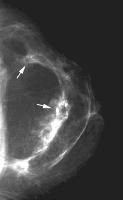
swirled appearance with undulating fibroglandular components bilaterally

answer
reduction mammoplasty will often have dystrophic calcifications too
question
likely true pathology when a lesion previously diagnosed pathologically as fibroadenoma grows
answer
phyllodes
question
differential diagnosis of a complex mass
answer
phyllodes ductal carcinoma complex fibroadenoma PASH lactational adenoma abscess
question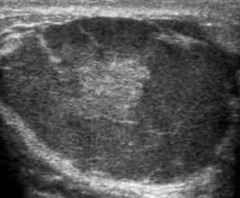
lactational adenoma

answer
complex mass, often cystic components usually young lactating woman often still requires biopsy because of appearance
question
signficance of bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy without a known primary
answer
50/50 chance of malignancy collagen vascular disease, sarcoid, infection can cause this lymphoma, leukemia, and mets possible call BIRADS 2 if known benign cause of nodes call BIRADS 4 and biopsy if no known underlying process
question
unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy without a visualized breast mass
answer
<1% of all breast cancers present as isolated unilateral lymphadenopathy breast cancer and mets are possible benign processes include mastitis, breast abscess, upper extremity infection, and granulomatous infection
question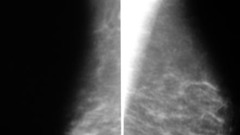
poland's syndrome

answer
unilateral absence of the pectoralis
question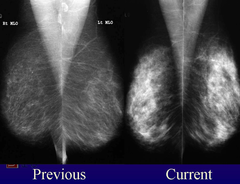
reasons for increasing fibroglandular prominence over time

answer
exogenous hormones endogenous hormones (pregnancy/lactation) weight loss
question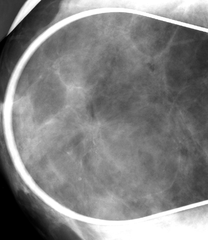
radial scar

answer
complex sclerosing lesion not truly a scar indeterminate lesion although technically benign need to excise because associated with atypia and malignancy mammo shows long thin radiating spicules, central radiolucency, and architectural distortion, but findings are not specific enough for diagnosis
question
three types of enhancing lesions on breast MRI
answer
focus (<5mm) mass non-mass-like enhancement
question
enhancing foci on breast MRI
answer
<5 mm tend to have type 1 curves on enhancement considered part of normal parenhcymal background can be expected to be stable on follow-up
question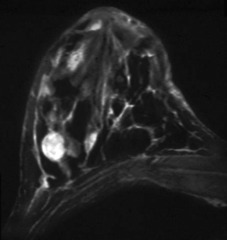
expected appearance of fibroadenoma on MRI

answer
lobulated mass with non-enhancing septations unconcerning dynamics
question
rate of malignancy with an irregular margin on MRI
answer
~1/3
question
rate of malignancy with spiculated margins on MRI
answer
0.8
question
lesions with containing fat on MRI
answer
lymph nodes fat necrosis hamartomas benign unless rapidly growing
question
lesions with bright signal on T2 with fat sat
answer
cysts lymph nodes fat necrosis exception to rule of benignity is colloid carcinoma
question
breast lesions with moderate T2 signal
answer
invasive lobular DCIS fibrocystic change
question
breast lesions with low T2 signal
answer
invasive ductal sclerotic fibroadenoma scar
question
six enhancement patterns of breast lesions
answer
homogeneous heterogeneous rim dark internal septations enhancing septations central enhancement
question
lesions causing rim enhancement on MRI
answer
high-grade invasive ductal fat necrosis inflammatory cysts 40% chance of malignancy if not a typical cyst
question
lesions with dark internal septations
answer
fibroadenoma septations do not enhanceme
question
type 1 kinetic curve
answer
slow rise that continues with time 6% malignant rate
question
type 3 kinetic curve
answer
rapid initial rise followed by drop (washout) 30-80% malignant rate
question
type 2 kinetic curve
answer
slow or rapid initial rise followed by plateau plateau definition allows variance within 10% indeterminate finding, meaning malignancy is between 6 and 30%
question
optimum timing for breast MR
answer
days 7-10 of the menstrual cycle limits background enhancement
question
best indication that a lymph node is involved with metastases
answer
morphology all lymph nodes demonstrate rapid wash in and out, so this is not helpful helpful to compare with prior mammo/usg to assess for changes
question
which phase of contrast is used for subtraction on MRI?
answer
phase 1 we want to identify lesions with rapid wash in
question
features of male breast cancer
answer
increased risk with klinefelter, liver disease, XRT, occupational heat exposure, testicular atrophy, family history gynecomastia is not a risk factor usually firm painless retroareolar or upper outer mass may cause swelling, bloody nipple discharge, retraction usually unilateral, more common on left 1/2 have enlarged axillary nodes at presentation typically delayed diagnosis, so often advanced treated with surgery, hormonal manipulation
question
sclerosing adenosis

answer
not a risk factor or precursor for cancer focally can show a cluster or microcalcifications or focal dense tissue mimicking a nodule or spiculated lesion diffusely will often show diffusely scattered calcifications
question
atypical lobular hyperplasia
answer
proliferation of round cells of LCIS type grows along terminal ducts in permeative fashion no mammographic correlate
question
atypical ductal hyperplasia
answer
low grade intraductal proliferation partial or incompletely developed features of noncomedo DCIS frequently calcifications present
question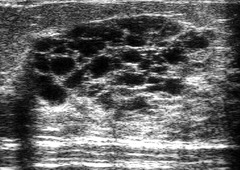
juvenile papillomatosis

answer
1-8 cm tumor with aggregated cysts calcfications common mean age 23 years localized firm tumor, no nipple discharge often familiy history of breast cancer ill-defined mass seen with multiple small peripheral cysts may have calcifications marked enhancement with benign dynamic curve on MR treated with complete excision
question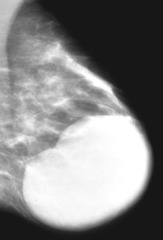
juvenile fibroadenoma

answer
hyperplasia and distortion of normal lobules due to hormonal imbalances usually adolescents, often african american rapidly enlarging, well-circumscribed nontender mass dilated superficial veins, may stretch skin and eventually cause ulceration may see cleftlike depressions and tiny cysts like phyllodes tumor strong enhancement on MR with sharp demarcation
question
paget disease of the breast
answer
uncommon manifestation of breast cancer infiltration of the nipple epidermis by adenocarcinoma can see nipple erythema, scaling, erosion, ulceration, retraction may cause bloody discharge and itching 1/3 have extensive invasive cancer; 2/3 DCIS in one duct
question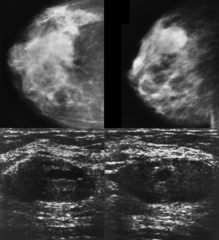
pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia

answer
PASH benign, hormonally stimulated myofibroblastic proliferation of mammary stroma tumoral form typically presents in 30-40s well defined mass with pseudocapsule single palpable movable painless firm rubbery mass, may grow rubbery dense, noncaclified, well circumscribed on ultrasound hypoechoic solid mass with long axis parallel to chest wall echotecture usually slightly heterogeneous, possibly with small cystic areas no posterior enhancement or shadowing excised when symptomatic or growing
question
common pathological results that often underestimate disease and necessitate excision
answer
ADH DCIS fibroepithelial lesions
question
columnar cell lesions
answer
controversial, involves alteration of ductal epithelium previously referred to as columnar alteration, blunt duct adenosis, peritubular hyperplasia, CAPSS, ELUCA 3/4 have intraluminal calcifications often clustered amorphous or pleomorphic calcifications on mammo typically non-circumscribed mass with irregular margins on US nonspecific finding with spectrum of atypia
question
breast lumps in men
answer
most commonly gynecomastia no benign masses occur in men <1% will be cancer imaging features are similar to those in women, although calcifications rarely occur 85% are IDC same prognosis, although tend to diagnose later in disease than women 1/2 have axillary adenopathy at diagnosis
question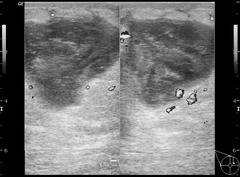
BIRADS for clinically suspected abscess

answer
2 for young, lactating women 3 for premenopausal non-lactating women--3-6 month follow up to evaluate for resolution 4 for post-menopausal--biopsy, with excision indicated if does not resolve with antibiotics since tumor necrosis cannot be excluded
question
suspicious types of nipple discharge
answer
unilateral bloody or clear from a single duct spontaneous not suspicious when bilateral, milky, green, yellow, or non-spontaneous



