Breast and Prostate Cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cancer Statistics

answer
Very common, not a death sentence, depends on the stage and treatment getting better
question
Cancer Cases and Deaths

answer
Breast cancer most common Men can get breast cancer 1% Prostate only for male
question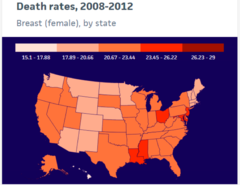
Breast Cancer Death Rates

answer
Not equal with higher mortality rates and states of diagnosed Access to care??
question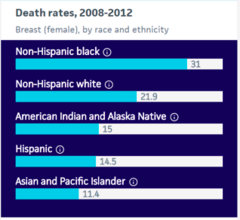
Breast Cancer Race and Ethnicity Death Rates

answer
Disparity in health care
question
Prostate Cancer Race and Ethnicity Death Rates

answer
Disparities based on race and region
question
Breast Cancer Signs and Symptoms
answer
Signs & Symptoms Often asymptomatic(do not know they have it, no lump or symptoms) Breast lump, pain Edema in affected arm Weight loss - significant metastases Bone pain -significant metastases Can have unilateral edema
question
Breast Cancer Risk Factors (Non-Modifiable)
answer
Risk Factors (Non-Modifiable) Gender-Women 99% Age-Older Family and/or personal history - first degree relative mother, sibling, or reoccuring Genetic (BRCA1/2) - genetic mutations that when present significantly increase ovarian and prostate cancer Ethnicity - more common among non Hispanic whites and JEWS Menarche before 12 - period for women Menopause after 55
question
Breast Cancer Risk Factors (Modifiable)
answer
Risk Factors (Modifiable) First pregnancy after 30 or nulliparity(never giving birth) EtOH - related with breast caner HRT (>4yrs combined HRT) - estrogen progesteron, perimenopause(menopause transition, begins several years before menopause. It's the time when the ovaries gradually begin to make less estrogen) symptoms Obesity Inactivity Radiation
question
Nurses Health Study Links EtOH Use to Breast Cancer
answer
Women who drink 3-6 drinks a week have a 15% higher risk of developing breast cancer Women who drink 2 drinks a day have a 50% increased risk of developing breast cancer Safe amount of alcohol 1drink a day, 7 a week
question
Current ACS BCA Guidelines

answer
For screening you will want to know who to screen, how often, and what type of testing. See website (titanium) for USPSTF guidelines Controversies- evidence was not supporting original guidelines, not based on original stories but multiple Apply to women of average risk https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/UpdateSummaryFinal/breast-cancer-screening1
question
Current ACS Cervical CA Guidelines

answer
Main cause is HPV- sexually transmitted affection- strain more likely to cause cancer PAP and swabs Pap test - changes in cervical cells that suggest cervical cancer or changes that put you at risk This for people with Average risk Pap and HPV don't need to be done every year
question
Preventing Cervical CA
answer
HPV is the primary cause of cervical cancer (and can cause other cancers such as throat, vaginal, penile, and rectal). There are 3 FDA approved vaccines that prevent the most lethal forms of HPV which cause cervical cancers - can cause vaginal, penile, reticle, throat Recommended by CDC for kids at 11-12, up to age 26
question
Vaccines Prevent Cervical Cancer
answer
Three vaccines are approved by the FDA to prevent HPV infection: Gardasil, Gardasil 9, and Cervarix. All three vaccines prevent infections with HPV types 16 and 18, two high-risk HPVsthat cause about 70 percent of cervical cancers and an even higher percentage of some of the other HPV-associated cancers (9, 10). Gardasil also prevents infection with HPV types 6 and 11, which cause 90 percent of genital warts (17). Because Gardasil protects against infection with four HPV types, it is called a quadrivalent vaccine. Gardasil 9 prevents infection with the same four HPV types plus five additional high-risk HPV types (31, 33, 45, 52, and 58) and is therefore called a nonavalent, or 9-valent, vaccine. All three vaccines are given through a series of three injections into muscle tissue over a 6-month period. The FDA has approved Gardasil and Gardasil 9 for use in females ages 9 through 26 for the prevention of HPV-caused cervical, vulvar, vaginal, and anal cancers; precancerous cervical, vulvar, vaginal, and anal lesions; and genital warts. Gardasil and Gardasil 9 are also approved for use in males for the prevention of HPV-caused anal cancer, precancerous anal lesions, and genital warts. Gardasil is approved for use in males ages 9 through 26, and Gardasil 9 is approved for use in males ages 9 through 15. Females and males who have previously received Gardasil may be able to also receive Gardasil 9. FDA has information for patients about Gardasil 9 available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/UCM426460.pdf. The Cervarix vaccine is produced by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). It targets two HPV types16 and 18and is called a bivalent vaccine. The FDA has approved Cervarix for use in females ages 9 through 25 for the prevention of cervical cancer caused by HPV. In addition to providing protection against the HPV types included in these vaccines, the vaccines have been found to provide partial protection against a few additional HPV types that can cause cancer, a phenomenon called cross-protection. The vaccines do not prevent other sexually transmitted diseases, nor do they treat existing HPV infections or HPV-caused disease.
question
Gardasil, Gardasil9, Cervarix
answer
Gardasil - Human Papilomarvius Types 6,11,16,18 Gardasil 9 - Human Papilomarvius (-Valent Vaccine Recombinant Ceravix - Human Papilmovarius Bivalent Types 16 and 8 Vaccine Recombinant
question
Breast Cancer Subjective
answer
HPI/ROS: breast discomfort, breast mass, nipple discharge, breast enlargement (men), also asymmetrical enlargement in women PMH: previous breast dz, known genetic mutation, other related cancers (e.g. ovarian), surgeries Menstrual history Pregnancies FH: breast and other related cancers and what age Health maintenance: breast cancer screening EtOH, caffeine- certain types of breast masses firbonomas
question
When should you do a breast exam and what should you examine?
answer
When? When a patient has a specific complaint As part of a well-exam Before a mamogram What? Breast and axillae Primarily for identification of masses, vascular or skin changes that might indicate malignancy Tanner staging for children, abnormal breast development in males Hormonal imbalances Specific complaint- nipple discharge
question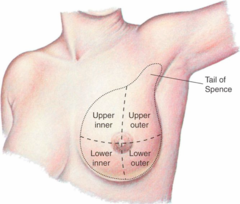
Breast Exam Quadrants

answer
4 quadrants Under arm area important- when metastases tends to go to under arm
question
Breast Exam Pressure

answer
Applying 3 levels of pressure, soft medium and hard Masses can be at different depths
question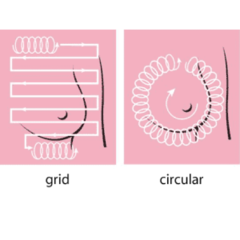
CBE Techniques

answer
Have to keep fingers on breast, cant lift up Planned fashion not missing section of breast tissue Never lift finger above tissue Can use vertical technique
question
Documenting a Breast Mass
answer
Location Size - based on what you feel Shape Consistency Tenderness Mobility Borders Retractions
question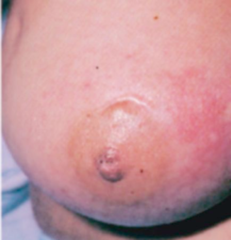
Erythema of Breast

answer
Infection, mastitis, Women who are breast fitting Warm and tender, erythema
question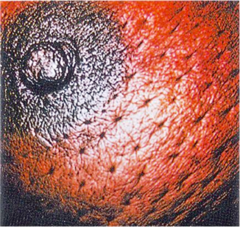
Peau d' Orange

answer
When breast tissue looks like an orange peel Associated with breast cancer
question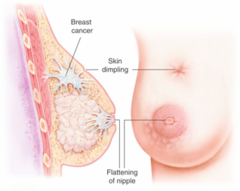
Nipple Retraction and Dimpling

answer
Unless reported for years and years Contraction of the skin - pretty common for undying malignancies
question
Supernumerary Nipples

answer
See nipples along the milk line Normal variant, nothing concerning about it Mistake for a mole
question
Paget's Disease

answer
Dermatologic finding, sign of underlying breast cancer, crusting of the skin
question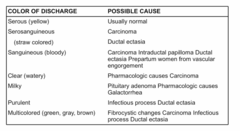
Discharge

answer
Pregnant or breast feeding or coming out on its own
question
Common Problems of the Breast
answer
Fibrocystic breast changes Fibroadeoma-A noncancerous breast tumor that most often occurs in young women. Galactorrhea- is a milky nipple discharge unrelated to the normal milk production of breast-feeding. Galactorrhea itself isn't a disease, but it could be a sign of an underlying problem. It usually occurs in women, even those who have never had children or after menopause Gynecomastia- Swollen male breast tissue caused by a hormone imbalance. Mastitis- A painful infection of the breast tissue. Breast cancer
question
Fibrocystic Breast Changes

answer
Multiple benign masses within the breast Etiology: ductal enlargement and cyst formation S ; S: one or more palpable masses which often fluctuate with the menstrual cycle Get bigger and smaller Tender and not tender Need further investigation in different stage of period Need ultra sound
question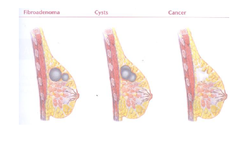
Fibroadenoma

answer
Benign breast mass Consists of both glandular and fibrous tissue Common in young women S ; S: unilateral mass, no fluctuation with menstrual cycle Usually a single mass Can be Increased by caffeine Needs to be investigated
question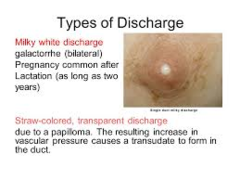
Galactorrhea

answer
Milky nipple discharge, unrelated to breast feeding Can occur in men or women Sign of an underlying problem Etiology: disorder of hypothalamus or pituitary (leading to increases in prolactin), medication SE, breast stimulation
question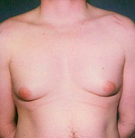
Gynecomastia

answer
Development of breast tissue in males Can occur in any age Often an indication of an underlying hormonal imbalance Psychosocial implications Treatment: 'watchful waiting', medication, surgery Talking about a young man - carries huge psychosocial implications How they are feeling
question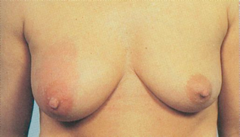
Mastitis

answer
Mastitis Infection of breast tissue Often bacterial (Staph aureus) Occur most frequently in women who are Breast feeding S/S: unilateral enlargement, pain, erythema, edema, warmth, fever and other systemic sxs, nipple d/c, enlarged axillary lymph nodes Women who have this can continue to breast feed, can help but will be very painful
question
Prostate CA Symptoms
answer
Signs/Symptoms Typically asymptomatic Urinary frequency Dysuria - discomfort with urine Hematuria - blood in urine Pain in low back, hips, or thighs - most common mastitis in bone
question
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
answer
Non-Modifiable RF Age - older you are Gender -Males Race/ethnicity (;common in black men, Asian men IN Asia lowest risk) Family/personal history - personal history of breast cancer Geography (sunlight) - closer you are to the equator less likely Modifiable Risk Factors Smoking, diet, sedentary lifestyle, BMI, occupation (farmer, tire plant, painter Diet- lots of vegetables and fruits, mediterranean diet no meat. Gave feeling of sense of control
question
ACS Prostate CA Screening Guidelines

answer
Truth current screening and blood test is not that good PSA, not specific to prostate cancer Can be elevated by BNH Need better tumor marker Know African American men and first degree relative Leaving up to individual to screen
question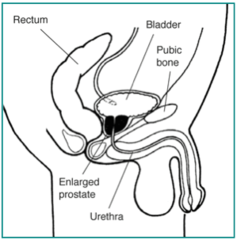
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)

answer
NOT cancer NOT associated with cancer IS very common, and occurs to some degree to all men if they live long enough May cause urinary problems due to pressure placed on urethra Symptoms: difficulty with urination, 'dribbling', incomplete emptying of bladder, nocturia, weak stream, incontinence, etc. (sxs similar to cancer) Normal change occurring with age As prostate enlarges can effected urethra - harder to empty bladder, go more frequently, quality of life issue
question
Reproductive System Sex life Subjective
answer
HPI/ROS: abnormal bleeding-heavy or light during menstration and outside of cycle, vaginal discharge, pain with intercourse, pain, vaginal discharge, PMS sxs, menopausal sxs, fertility/infertility, urinary sxs, menstrual history PMH FH: DM- can see urinary frequency and candida yeast infections, congenital problems, multiple pregnancies, related cancers Meds, include hormonal contraception - all the testing's Health maintenance: previous pelvic exams/ paps, HPV testing Sexual history and practices: partners, barrier protection, VD-Veneral Disease( An infection transmitted through sexual contact, caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.) EtOH, drugs, cleansing routines Un safe sex practices, sexual abuse
question
Types of STI's
answer
Gonorrhea- A sexually transmitted bacterial infection that, if untreated, may cause infertility., Chlamydia- A common sexually transmitted infection that may not cause symptoms. Herpes Simplex- A virus causing contagious sores, most often around the mouth or on the genitals. Syphilis- A bacterial infection usually spread by sexual contact that starts as a painless sore. HPV- An infection that causes warts in various parts of the body, depending on the strain. HIV - HIV causes AIDS and interferes with the body's ability to fight infections. HEP C - An infection caused by a virus that attacks the liver and leads to inflammation
question
Menarche
answer
First menstruation Average age of onset is 12, normal age range is 9 - 15 years of age. -Menarche before age 9, or after 15 should be evaluated. Childhood obesity thought to be r/t earlier age at menarche. --Eating disorders, competitive athletes more likely to begin menstruation at an older age. In each case, endocrine abnormalities should be considered. Often irregular and unpredictable for the first 1-2 years following menarche. Occurs earlier in girls, rising BMIS or exposure delay- eating disorder Can have irregular period for first couple of years
question
Menstruation
answer
Shedding of uterine lining Normal Menstrual Cycle -every 21-35 days, most commonly every 28 days 3-7 days duration, moderate flow-heavly flow- change tampon every hour, mild PMS symptoms- mood cramping, feeling tired Should inquire about frequency, duration, flow, associated symptoms. To quantify flow, ask about how often pt changes pad/tampon. Needing to change once an hour or more = heavy flow. Last menstrual period (LMP) refers to the first day of a woman's last menstrual cycle. Want to know how often have period, frequency first day of one period and first day of the next
question
Menopause
answer
Defined as no menses for 12 or more months (with no other biological or physiological explanation) Average age of menopause is 51 Increases in FSH - look at lab work Risks and benefits of HRT HRT(hormone replacement theary) can be used to alleviate peri-menopausal sxs such as hot flashes. Should be used at the lowest effective dose, for the shortest period of time possible in order not to ? one's risk for BCA and cardiovascular dz. - can cause breast cancer and heart disease. Helps for short period of time Lowest dose possible and shortest time When women stop having their period Vaginal draining, difficult sleeping, hot flashes, mood swings
question
Men Subjective Sex Life
answer
HPI/ROS: difficulty achieving/maintaining erection, penile discharge, dysuria, infertility, enlargement in inguinal area, testicular pain/masses- occurs in young men and not older- caught early mortality rates are low but remove testicle possible, PMH: STIs, related cancers, DM, cardiac dz, hernias Health maintenance: testicular self exam- younger men similar to breast exam mass in testicles, prostate cancer screening EtOH, drugs Heart disease goes along with erection, arteries leading to the penis Men can have STIs and be asystematic- spread and not knowing you have it
question
Signs of Sexually Transmitted Infections Men
answer
Ulcers Penile discharge Abdominal pain Systemic sxs (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis)
question
Signs of Sexually Transmitted Infections Women
answer
Ulcers Purulent vaginal discharge Abdominal/pelvic pain Dyspareunia - painful intercourse Infertility - Gonorrhea or Chlamydia- PID- pelvic disease Systemic sxs (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis)
question
Signs of Sexual Abuse Physical Complaints
answer
Physical Complaints Evidence of general abuse/neglect Evidence of trauma/scarring Presence of STI Anorectal pruritis, bleeding, pain, incontinence Vaginal bleeding, discharge, dysuria, UTIs
question
Signs of Sexual Abuse Behavioral Changes
answer
Problems in school Change in appetite/weight Change in sleep Depression Change in personality, aggression Avoidance of people/places



