Bone Tumors – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is the most common tumor of the bone? What is the most common bone sarcoma? What is the most common benign bone tumor?
answer
Metastatic Osteosarcoma Osteochondroma
question
Where in the bone does the following tumor occur? 1. Osteosarcoma 2. Giant cell tumor 3. Osteochondroma 4. Ewing's Sarcoma 5. Enchondroma 6. Chondrosarcoma The typical patient with a primary bone tumor is in what age group?
answer
1. Metaphysis 2. Epiphysis 3. Metaphysis 4. Diaphysis 5. Metaphysis/diaphysis 6. Metaphysis Young
question
What are the typical symptoms of a benign tumor? Malignant bone tumors are aggressive. What are some symptoms?
answer
Usually asymptomatic Pain, fractures, and metastasis.
question
Is grade or stage of a malignant bone tumor important in predicting the clinical outcome? Predicting the behavior? What indicates that a bone tumor is at the highest stage?
answer
Stage Grade Metastasis
question
A patient comes to your office complaining of nocturnal bone pain that is relieved when the patient takes aspirin. What is the first tumor you should suspect? What age would you expect this patient to be? Where does this type of bone tumor typically arise? What causes the associated pain?
answer
Osteoid osteoma Young, teens to early 20s. In the cortex of the long bones such as the femur. Small tumors release cytokines which lead to pain and the area is typically well innervated.
question
What umbrella condition is associated with an osteoma? Where do osteoma's typically develop? This condition presents with cortical type bone growing in the craniofacial bones. Why is this a problem?
answer
Garner's syndrome The craniofacial bones. This is mature bone growing in an abnormal place as this type of bone should only be seen in the shaft of long bones.
question
What condition is seen here? What age is typically affected by this condition? It typically occurs where in youth and where in the elderly? What conditions are associated with development of this condition in the elderly?
answer
Osteosarcoma It is a bimodal age distribution with the largest peak at an early age (children & young adults) and a second smaller peak in the elderly. Youth: Metaphysis of long bones Elderly: Flat bones Paget's disease of the bone and radiation.
question
Two characteristic features of what condition are seen here? Name and describe the characteristics. This condition can be associated with hereditary condition or sporadic development. Name the mutations. If the tumor is associated with heredity, what is the most common mutation?
answer
Osteosarcoma: Codman triangle - triangle peaks of growing bone lifting the periosteum Sunburst appearance - tiny bone fragments coming off of the area of tumor growth Hereditary: Li Fraumeni (p53 mutation) & Rb mutation (retinoblastoma gene) Sporadic: p53, MDM2, and Rb mutation (although this is rare) Rb mutation
question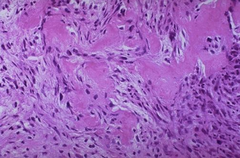
What condition is seen here? In teens this condition typically arises in the metaphysis. Where is it most commonly seen? Most osteosarcomas are high grade and require chemo and extensive treatment. Identifying the area of the bone affected helps to identify the grade. Based on the following location, name the grade of the tumor. 1. Intramedullary 2. Juxtacortical 3. Intracortical

answer
Osteosarcoma - pleomorphic cells that are producing osteoid The distal femur or proximal tibia (the knee area) 1. Low grade 2. Low grade or High grade 3. High grade
question
What is an osteochondroma? What types of bones does this develop in? What is seen at the growth plate in this condition? What is the suspected gene associated with this condition?
answer
A benign cartilage tumor of the metaphysis with an overlying cartilage cap. Those that undergo endochonral ossification (ie. long bones). Lateral projections of the growth plate. EXT gene family mutation - gene involved in growth plate regulation
question
What condition is seen here? It is a benign tumor of what type of cartilage? What area of the bone is most commonly affected and what bones are most commonly affected in solitary tumors?
answer
Enchondroma - punctate and ring like calcifications Hyaline and myxoid cartilage Medullary cavity which may cause erosion of the cortex but not invasion (as it is benign). Most commonly affected bones are those of the hands and feet.
question
Enchondromas are most commonly solitary. When they are seen in in multiples they are associated with which syndromes? What is the difference between the two disease? If associated with these conditions they have a 20% chance of developing into what? Patients with Marfucci's disease have a 100% chance of what?
answer
Ollier's or Mafucci's disease. Marfucci's disease is Ollier's disease with multiple hemangiomas. Chondrosarcoma Developing another extraskeletal malignancy such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or lung cancer.
question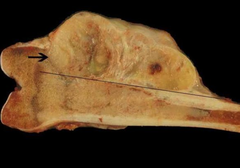
What condition is seen here? What age group is typically affected by this condition? Which bones are typically affected by this condition?

answer
Chondrosarcoma Older adults Pelvis, ribs, humerus, and proximal femur.
question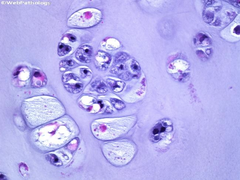
What condition is seen here and what helps to identify it? What is the typical clinical presentation of a patient with this condition? What does this type of tumor do to pre-existing bone?

answer
Chondrosarcoma showing lots of cartilagenous matrix with many cells in different stages of growth. Pain in the bone It entraps and invades the pre-existing bone.
question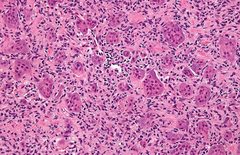
What bone tumor is seen here and what gives it away? is this type of tumor benign or malignant? What bones does this type of tumor typically occur on?

answer
Giant cell tumor of bone (osteoclastoma) - osteoclastic giant cells mixed with mononuclear histiocytes. Benign The ends of long bones and the pelvis.
question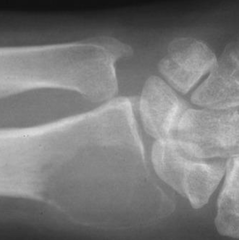
An X-ray of what condition is seen here and what is the characteristic name of the radiological appearance?

answer
Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Soap bubble appearance showing the expanding lytic lesion.
question
Ewing Sarcoma is what type of tumor? What is the appearance of the tumor cells? They are associated with what mutation? What is the prognosis for patients with this condition?
answer
Malignant proliferation of poorly differentiated cells derived from the neuroectoderm. Small blue cells that grow in sheets. t(11;22) & t(21;22) Poor without treatment but treatment with chemo significantly improves survival.
question
What are the most common primary sites for a metastatic tumor of the bone? Is this type of tumor blastic or lytic? What area of the skeleton is most often involved? What age group is associated with metastatic bone tumors?
answer
BLT & Kosher Pickle Breast Lung Thyroid Kidney Prostate It can be either or both. Axial skeleton on the vertebrae and diaphysis of some bones. Older patients
question
Are metastatic tumors of the bone commonly unifocal or multifocal? How do we determine the original site from which the tumor metastasized?
answer
Multifocal Morphology or immunohistochemistry can help to determine or provide a strong suggestion for the site of origin.



