Blood vessels and Circulation test – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Plasma is closest in composition to
answer
interstitial fluid
question
What is most abundant plasma protein?
answer
albumin
question
What is a large protein involved in molecule transportation, osmotic pressure and it's also a stock of amino acids? Albumin lactic acid steroids
answer
albumin
question
The percent fraction of formed elements relative to whole blood is the
answer
hematocrit
question
Which of the following is a function of the blood
answer
all of the answers are correct
question
Which of the following statements about blood is false
answer
the normal pH of blood is 6.8 to 7.0
question
Formed elements make up about what percentage of blood
answer
45 percent
question
The combination of plasma and formed elements is called
answer
whole blood
question
Whole blood for testing in a clinical laboratory is usually collected from
answer
a superficial vein
question
When checking the efficiency of gas exchange, it may be necessary to draw a blood sample from
answer
an artery
question
Consider these results from a blood lab test. Which value is most likely abnormal
answer
hemoglobin - 10.7 g/100ml
question
Each of the following is a characteristic of whole blood, except a
answer
viscosity about the same as water
question
The total volume of blood in the body of a 76-kg man is approximately __________ liters
answer
5.3
question
The most abundant component of plasma is
answer
water
question
A person who has a low blood volume is said to be
answer
hypovolemic
question
The chief differnce between plasma and interstitial fluid involves the
answer
concentration of proteins
question
A typical adult hematocrit is
answer
45
question
Which of these is not one of the formed elements of blood?
answer
antibodies
question
Plasma composes about _________ percent of whole blood and water composes _________ percent of the plasma volume
answer
55; 92
question
A hematocrit provides information on
answer
formed elements abundance
question
You are caring for an adult patient who weights 48 kg. What would her approximate blood volume be
answer
3.8 L
question
Thyroid-building globulin is an example of which kind of plasma protein
answer
hormone-binding
question
Transferrin is an example of which kind of plasma protein
answer
metalloprotein
question
Which plasma proteins trasports fatty acids and some hormones
answer
albumin
question
Which organ secretes most of the plasma proteins
answer
liver
question
The most abundant proteins in blood plasma are
answer
albumins
question
Plasma proteins essential in body defense are the
answer
immunoglobulins
question
A plasma protein essential for blood coagulation is
answer
fibrinogen
question
All the circulating red blood cells in an adult originate in the
answer
red bone marrow
question
Red blood cell production is regulated by the hormone
answer
erythropoietin
question
Mrs. Higgins needs to have major surgery. Two weeks before the surgery, her doctor prescribes EPO. Which of the following statements best explains his reason for doing this? By prescribing EPO, the doctor will decrease her hematocrit so that her blood is less likely to clot during surgery. By prescribing EPO, the doctor will be able to increase oxygen levels because EPO causes hemoglobin to bind oxygen more efficiently. By prescribing EPO, the doctor can stimulate Mrs. Higgins's body to produce an overabundance of RBCs, which can be harvested and saved for her surgery. After she takes EPO, Mrs. Higgins's risk of infection will go down because of increased production of WBCs.
answer
By prescribing EPO, the doctor can stimulate Mrs. Higgins's body to produce an overabundance of RBCs, which can be harvested and saved for her surgery.
question
Which of the following statements concerning red blood cells is false
answer
red cells are about 18 um in diameter
question
Which of these proteins functions to store or transport iron
answer
ferrritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin
question
The disease sickle cell anemia is an example of what can happen if
answer
a gene for adult hemoglobin is abnormal
question
When a person who lives at sea level vacations in the Rocky Mountains, you would expect a) a rise in hematocrit. b)an increase in red blood cell production. c)release of erythropoietin. d)a drop in atmospheric oxygen levels.
answer
all of the answers are correct
question
Surgical removal of the stomach could cause
answer
pernicious anemia
question
Mary is tested for the amount of hemoglobin in her blood. the test results indicate that her hemoglobin level is 16 g/dL of blood. This value indicates that
answer
her hemoglobin level is normal
question
An obstruction in blood flow to the kidneys would ultimately result in
answer
increased erythropoiesis
question
The level of erythropoietin in the blood would rise due to all of the following, except
answer
during periods of fasting
question
The average life span of a red blood cell is
answer
4 months
question
The function of red blood cells is to
answer
carry oxygen to the cells and then carry away carbon dioxide
question
Eileen is a strict vegan and therefore eats no animal products. She develops an anemia that her doctor thinks is caused by a nutritional deficiency. Which of the following is the likeliest candidate
answer
vitamin B12 deficiency
question
In adults, the only site of red blood cell production, and the primary site of white blood cell formation, is the
answer
red bone marrow
question
Each heme ring in hemoglobin encloses an atom of
answer
iron
question
Excess iron is stored in the liver and spleen as
answer
hemosiderin and ferritin
question
In which of the following situations would you expect the blood level of bilirubin to be evaluated
answer
an alcoholic with a damaged liver
question
If bile ducts are blocked
answer
more bilirubin appears in the plasma
question
More than 95 percent of the protein in a red blood cell is
answer
hemoglobin
question
The function of hemoglobin is to
answer
carry dissolved blood gases
question
_________ is a condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduction
answer
anemia
question
Pernicious anemia caused by a lack of intrinsic factor is specifically treated by
answer
injection of vitamin B12
question
Which of the following would you expect to see in increased numbers in a peripheral blood sample after donating a unit of blood
answer
reticulocytes
question
A red blood cell that contains normal amounts of hemoglobin would be called
answer
normochromic
question
A bruise appears as a greenish spot in the skin because
answer
the heme group in the hemoglobin has broken down in to biliverdin
question
Aged and damaged erythrocytes are broken down by macrophages in the
answer
spleen, liver, and bone marrow
question
The waste product bilirubin is produced from
answer
heme molecules lacking iron
question
Most of the iron that is removed from degraded hemoglobin is
answer
recycled to the red bone marrow
question
In adults, erythropoiesis exclusively takes place in
answer
red bone marrow
question
In adults, red bone marrow is located in the
answer
all of the answers are correct
question
The process of red blood cell production is called
answer
erythopoiesis
question
The developmental stage at which erythocytes enter the circulation is as
answer
reticulocytes
question
Except for __________, the following statements about blood are true. a.The viscosity is three to five times greater than water. b The pH is slightly acidic. c. It contains about 55% plasma. D. It contains dissolved gases.
answer
B
question
The formed elements of blood consist of _________. A. platelets B. red blood cells C. white blood cells D. All of these are formed elements of blood.
answer
D
question
Plasma makes up approximately what percentage of whole blood?
answer
55%
question
Except for the amount of __________, plasma and interstitial fluid differ little in composition. A. water B. protein C. glucose D. sodium ion
answer
B
question
The most abundant solute in plasma is __________.
answer
protein
question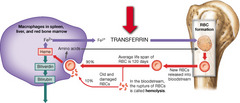
What is the role of transferrin in the cycle shown above?

answer
It transports iron ions in the plasma.
question
Which of the labels in the figure indicate a cell normally found in the circulating blood?
answer
reticulocyte
question
Red blood cells (RBCs) are removed from the circulation after about __________.
answer
120 days
question
Red blood cells carry __________ to the lungs and __________ to the tissues.
answer
carbon dioxide; oxygen
question
The most abundant protein in blood is __________.
answer
hemoglobin
question
Reticulocyte is a stage in the development of __________.
answer
red blood cells
question
The formed elements are largely produced within the __________.
answer
red bone marrow
question
__________ stimulates production of red blood cells.
answer
erythropoietin
question
What evidence in this figure indicates that this is not a first pregnancy?
answer
Presence of maternal anti-Rh antibodies Antibodies against Rh antigen are only generated after a first pregnancy.
question
People with type "O" blood are considered "universal donors" for transfusions because __________.
answer
their blood lacks A and B antigens
question
A person with a type A positive blood type can safely receive blood from all of these donors except __________.
answer
B positive
question
Which of these is not a surface antigen found on red blood cells? A. Rh B. A C. B D. O
answer
D
question
Which of these is characteristic of monocyte? A. Reduces inflammation B. Provides defense against specific antigens C. Releases cytotoxic enzymes D. Engulfs pathogens

answer
D
question
Which of these is characteristic of eosinophil? A. Release histamine B. Releases cytotoxic enzymes C. Provides defense against specific antigens D. Reduces inflammation
answer
B, D
question
Which of the formed element stem cells is developmentally the most different from the others?
answer
Lymphoblast Lymphoid stem cells differentiate separately from the myeloid stem cell, which gives rise to all the other blood cells.
question
The white blood cell type that most rapidly increases in number after a bacterial infection is the __________.
answer
neutrophils
question
Which of these statements about basophils is not true? A. They are abundant. B. They promote inflammation. C. They release histamine. D. They contain cytoplasmic granules.
answer
A
question
Granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) stimulates production of __________. A. lymphocytes B. neutrophils C. monocytes D. platelets
answer
B
question
The agranular leukocyte (agranulocyte) that is capable of phagocytosis is the __________. A. eosinophil B. lymphocyte C. monocyte D. neutrophil
answer
C
question
Granulocytes are produced in __________. A. white bone marrow B. the liver and spleen C. the lymph nodes D. red bone marrow
answer
D
question
The largest white blood cell in circulation is the __________. A. eosinophil B. lymphocyte C. neutrophil D. monocyte
answer
D
question
If a patient has thrombocytopenia, the best therapy is infusion of __________.
answer
purified platelets
question
An important function of thrombocytes is to __________. A. transport blood gases B. transport nutrients C. transport clotting factors D. transport thrombopoietin
answer
C
question
Megakaryocytes are the source of __________.
answer
platelets
question
Which of the pathways shown above will occur within a damaged vessel?
answer
Both the intrinsic and the common pathways
question
Most of the plasma proteins required in the coagulation process are produced by __________.
answer
the liver
question
During fibrinolysis __________.
answer
clots slowly dissolve
question
The common pathway in coagulation ends with __________.
answer
conversion of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin
question
The enzyme that dissolves fibrin is named __________.
answer
plasmin
question
The complex process that leads to the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen is called __________.
answer
coagulation
question
Which of these phases is not part of hemostasis? A. erythropoiesis phase B. vascular phase C. coagulation phase D. platelet phase
answer
A
question
Serum can't coagulate because the __________ has been removed.
answer
fibrinogen
question
Which blood type is called the universal donor?
answer
Type O
question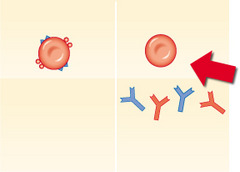
What blood type is indicated by the arrow?

answer
Type O
question
An individual whose blood type is AB negative can .
answer
receive any blood type except that with an Rh antigen
question
Which of the following is characteristic of all leukocytes? A. they are nucleated B. they have cytoplasmic granules C. they are phagocytic D. they are the most numerous elements formed in blood
answer
A
question
Tom's blood type is AB positive. What does this mean? A. antibodies to A and B are present in the plasma B. he can only receive blood from a donor who is AB positive C. there are no antibodies to A to B or to Rh antigens in the plasma D. his blood lacks the Rh factor
answer
C
question
Platelets .
answer
stick to damaged areas of blood vessels and help seal the break
question
Blood is classified as a(n) __________ tissue.
answer
Connective
question
Which of the following cells are NOT found in the blood? A. Lymphocytes B. Thrombocytes (platelets) C. Leukocytes D. Chondrocytes E. Erythrocytes
answer
D
question
Which type of cell functions to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body? Neutrophils Megakaryocytes Macrophages Basophils Erythrocytes
answer
Erythrocytes
question
Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood, is mainly composed of _________________. Protein Electrolytes (Na+, Cl-, K+, etc.) Lipids Hormones Water
answer
Plasma is 92% water.
question
Which of the following are functions of blood? Transport of nutrients, gases, ions, and wastes Coagulation Control of the chemical composition of interstitial fluid Immunity
answer
All are correct
question
Visible cytoplasmic granules are NOT present in .
answer
monocytes and lymphocytes
question
Visible cytoplasmic granules are present in .
answer
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
question
When viewing a blood smear under a microscope, the cells with the visible nuclei are ___________. platelets erythrocytes leukocytes none of the above
answer
leukocytes
question
Which white blood cells are first to arrive at the site of a wound?
answer
neutrophils
question
What white blood cells are most abundant in lymphoid tissue?
answer
lymphocytes
question
_________________ is the substance of the red blood cell (erythrocyte) that binds to oxygen and carbon dioxide.
answer
Hemoglobin
question
Mature red blood cells that are in circulation are multinucleate. True or False
answer
false. Mature red blood cells are anucelate. During the maturation process, red blood cells lose their nucleus.
question
Platelets, which are involved with blood clotting, are fragments of which cells?
answer
Megakaryocytes
question
Which of the following cells are classified as lymphocytes?
answer
T cells, B cells
question
When neither anti-A sera nor anti-B sera clump on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is Type .
answer
Type O
question
Which type of blood is considered to be the universal recipient?
answer
Type AB
question
Antibodies are proteins that can randomly bind to antigens. true or false
answer
false. Antibodies are protein molecules secreted by plasma B cells. Antibodies exhibit specificity and will bond only to certain antigens.
question
A patient with type A blood will naturally produce antibodies for the A antigen. true or false
answer
False A patient with type A blood will express type A antigen on the surface of the red blood cells. A person with type A blood will produce antibodies to type B antigen.
question
A person with which blood type is considered to be a universal donor?
answer
Type O- people with type O- blood can receive only type O- blood
question
Which of the following scenarios may induce erythroblastosis fetalis?
answer
Rh-negative mother; Rh-positive fetus
question
Administering _____________ can prevent an Rh-negative mother from producing anti-Rh antibodies (anti-D) following exposure to the Rh antigen.
answer
RhoGam
question
A ________________ measures the percentage of total blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells.
answer
Hematocrit test
question
A woman has a hematocrit of 25%. What does this indicate?
answer
Anemia normal hematocrit for a woman is between 37% and 47%
question
A low hematocrit would impair which bodily function?
answer
Oxygen transport
question
During coagulation, insoluble protein threads called ___________ trap platelets to help form a clot.
answer
Fibrin
question
What is heparin?
answer
An anticoagulant
question
A patient with a slower-than-normal coagulation time might be at risk for which of the following?
answer
Hemorrhage
question
A hematocrit primarily measures the volume of .
answer
red blood cells
question
What prevents blood from clotting?
answer
heparin
question
D
answer
Which plasma protein transports fatty acids and some hormones? A) translipin B) steroid-binding protein C) hormone-binding protein D) albumin E) gamma globulin
question
C
answer
The most abundant proteins in blood plasma are A) globulins. B) transport proteins. C) albumins. D) lipoproteins. E) fibrinogens.
question
C
answer
Bilirubin binds to ___________ and is transported to the liver for excretion in bile. A) Transferrin B) Ferritin C) Albumin D) Hemosiderin
question
D
answer
What are the major plasma proteins? A) Albumin and -Alpha-1 globulin B) Albumin -Alpha-2 globulin C) Beta globulin -Gamma globulin D) Albumin and Globulin
question
A
answer
___________________ constitutes 60% of plasma proteins A) Albumins B) Fibrogen C) Globulin D) Water
question
C
answer
Thyroid-binding globulin is an example of which kind of plasma protein? A) metalloprotein B) steroid-binding C) hormone-binding D) apolipoprotein E) transport albumin
question
C
answer
Plasma proteins essential in body defense are the A) albumins. B) fibrinogens. C) immunoglobulins. D) metalloproteins. E) lipoproteins.
question
B
answer
Which category of plasma proteins includes the antibodies? A)fibrinogen B)globulins C)albumin D)hormones
question
C
answer
___________________ constitutes 35% of plasma proteins A) Albumins B) Fibrinogen C) Globulin D) Water
question
B
answer
___________________ constitutes 4% of plasma proteins A) Albumins B) Fibrogen C) Globulin D) Water
question
C
answer
The combination of plasma and formed elements is called A) serum. B) lymph. C) whole blood. D) extracellular fluid. E) packed blood.
question
E
answer
Once plasma has lost its fibrinogen is is A) agglutinins B) agglutinogens C) T-cells D) erythrogens E) serum
question
A
answer
90% of plasma proteins are made by the A) liver. B) spleen. C) thymus. D) red bone marrow. E) yellow bone marrow.
question
B
answer
A plasma protein essential for blood coagulation is A) albumin alpha. B) fibrinogen. C) immunoglobulin A. D) metalloprotein D. E) lipoprotein C.
question
D
answer
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalyzed by the enzyme A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) factor VIII. D) thrombin. E) prothrombinase.
question
D
answer
________ involves a cascade of reactions leading to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. A) Vascular spasm B) The platelet phase C) Retraction D) Coagulation E) Fibrinolysis
question
B
answer
Which type of plasma protein serves as a carrier for the hormones T3 and T4? A)fibrinogens B)albumins C)antibodies D)apolipoproteins
question
A
answer
The process of hemostasis includes five phases. What is the correct order of the phases as they occur after injury? A) vascular, platelet, coagulation, clot retraction, clot destruction (fibrinolysis) B) coagulation, vascular, platelet, clot destruction (fibrinolysis), clot retraction C) vascular, coagulation, platelet, clot retraction, clot destruction (fibrinolysis) D )platelet, vascular, coagulation, clot retraction, clot destruction (fibrinolysis)
question
D
answer
Clot destruction involves a process that begins with __________. A)activation of the proenzyme fibrinogen, which initiates the production of fibrin B)activation of prothrombin, which initiates the production of thrombin C)activation of Cá+ to produce tissue plasmin D)activation of the proenzyme plasminogen, which initiates the production of plasmin
question
C
answer
The most abundant component of plasma is A) ions. B) proteins. C) water. D) gases. E) nutrients.
question
A
answer
Plasma composes about ________ percent of whole blood and water composes ________ percent of the plasma volume. A) 60-83; 92 B) 92-100; 7 C) 92-100; 5 D) 46-63; 90 E) 50; 50
question
C
answer
Which of these descriptions best matches the term B lymphocytes? A) adhere to collagen beneath endothelium B) helper cells are one type C) develop into plasma cells D) kill bacteria using hydrogen peroxide E) often elevated in allergic individuals
question
B
answer
You have spent 24 hours traveling from the U.S to New Zealand, on quite a few airplanes with many stops. Because of the stress, changes in time zones, and short blocks of time between planes, you find yourself tired with a headache when you arrive. You are severely dehydrated. A hematocrit value on your blood would be ________ than normal because ________. A) lower; more red blood are being made by the bone marrow B) higher; you have less blood plasma volume C) lower; the bone marrow is making fewer red blood cells due to the latitude of the airplanes D) higher; more plasma proteins are made by the liver
question
D
answer
The chief difference between plasma and interstitial fluid involves the concentration of A) water. B) electrolytes. C) nitrogen wastes. D) proteins. E) glucose.
question
B
answer
How is it that liver disorders can alter the composition and functional properties of the blood? A)The proteins synthesized by the liver are filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. B)The liver is the primary source of plasma proteins. C)The liver synthesizes immunoglobulins and protein hormones. D)The liver serves as a filter for plasma proteins and pathogens.
question
B
answer
In addition to water and proteins, what else is part of plasma? A)erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets B)electrolytes, nutrients, and organic wastes C)albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen D)None of the listed responses is correct.
question
B
answer
Production of formed elements of the blood in the red bone marrow is A) Leukospoiesis B) Hemopoiesis C) Forming blood D) Fibrinogenisis
question
B
answer
Approximately 45 percent of blood volume is composed of the A) clotting factors. B) formed elements. C) leukocytes. D) plasma. E) antibodies.
question
C
answer
Which of the following is not one of the formed elements of blood? A) RBCs B) platelets C) antibodies D) lymphocytes E) basophils
question
C
answer
A hematocrit provides information on A) blood type. B) clotting factors. C) formed elements abundance. D) plasma composition. E) sedimentation rate.
question
C
answer
___________________ constitutes 99% of formed elements. A) Platelets B) White Blood Cells C) Red Blood cells D) Water
question
D
answer
Formed elements make up about what percentage of blood? A) 55 percent B) 30 percent C) 60 percent D) 45 percent E) 20 percent
question
A
answer
The most numerous WBCs in a differential count of a healthy individual are A) neutrophils. B) basophils. C) lymphocytes. D) monocytes. E) leukocytes.
question
B
answer
_____________ develop into erythrocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes (all WBC and some RBC). A) lymphoid stem cells B) myeloid stems cells C) White blood cells D) Red blood cells
question
E
answer
Which of the following is true of eosinophils? A) Granules stain with eosin dyes. B) Allergic patients have many. C) They have bilobed nucleus. D) They constitute about 2 to 4 percent of WBCs. E) All of the answers are correct.
question
E
answer
Which of the following is true of basophils? A) constitute about 1 percent of WBCs B) granules contain heparin C) granules contain histamine D) attract other defense cells E) All of the answers are correct.
question
F
answer
Which of the following is true of eosinophils? A) React to parasites B) Allergic patients have many. C) They have bilobed nucleus. D) They constitute about 2 to 4% of WBCs. E) the are bright red in color F) All of the answers are correct.
question
E
answer
50-70% of circulating white blood cells are A) monocytes. B) lymphocytes. C) eosinophils. D) basophils. E) neutrophils.
question
B
answer
A small white blood cell with a large round nucleus would be a A) neutrophil. B) lymphocyte. C) monocyte. D) basophil. E) eosinophil.
question
C
answer
White blood cells that release histamine at the site of an injury are A) neutrophils. B) eosinophils. C) basophils. D) lymphocytes. E) monocytes.
question
A
answer
A patient has an infected puncture wound to her foot. Which type of white blood cell would you expect to be elevated in a differential white cell count? A) neutrophils B) eosinophils C) basophils D) lymphocytes E) monocytes
question
E
answer
________ are large phagocytic white cells that spend most of their time outside the blood as fixed and free phagocytic cells. A) Neutrophils B) Eosinophils C) Basophils D) Lymphocytes E) Monocytes
question
D
answer
In adults, the only site of red blood cell production, and the primary site of white blood cell formation, is the A) liver. B) spleen. C) thymus. D) red bone marrow. E) yellow bone marrow.
question
D
answer
Hormones called ________ are involved in regulation of white blood cell populations. A) erythropoietin B) bilirubin C) thrombopoietin D) colony-stimulating factors E) plasmin
question
B
answer
Lymphocytes account for __________ % of circulating white blood cells. A)20-50 B)20-30 C)10-15 D)less than 1
question
B
answer
What is the term for the characteristic of white blood cells whereby they are attracted to a specific chemical stimulus? A)polymorphism B)positive chemotaxis C)leukopenia D)phagocytosis
question
B
answer
Which type of white blood cell circulates in the blood for about 24 hours before entering the tissues and differentiating into a macrophage? A)lymphocyte B)monocyte C)neutrophil D)basophil
question
A
answer
Which type of white blood cell includes the B and T cells that are responsible for humoral and cell-mediated immunity? A)lymphocyte B)monocyte C)neutrophil D)basophil
question
B
answer
Which of the following types of white blood cells are involved in fighting parasitic infections, such as flukes and roundworms? A)neutrophils B)eosinophils C)basophils D)lymphocytes
question
D
answer
Which of the white blood cells is also known as a polymorph? A)basophil B)monocyte C)lymphocyte D)neutrophil
question
A
answer
A person whose platelet count is 1,200,000/µl is suffering from A) thrombocytosis. B) leukocytosis. C) hemocytosis. D) thrombocytopenia. E) leukopenia.
question
B
answer
During an infection, the white blood cell count may rise, a condition known as __________. A) thrombocytosis. B) leukocytosis. C) hemocytosis. D) thrombocytopenia. E) leukopenia.
question
B
answer
Myeloid stem cells will differentiate into progenitor cells, which give rise to all white blood cells EXCEPT __________. A)eosinophils B)lymphocytes C)neutrophils D)basophils
question
E
answer
The blood cells involved in specific immunity are the A) neutrophils. B) monocytes. C) basophils. D) erythrocytes. E) lymphocytes.
question
A
answer
During a bacterial infection you would expect to see increased numbers of A) neutrophils. B) eosinophils. C) basophils. D) reticulocytes. E) thrombocytes.
question
D
answer
All of the following are true of neutrophils except that they are A) granular leukocytes. B) phagocytic. C) also known as polymorphonuclear leukocytes. D) important in coagulation. E) active in fighting bacterial infections.
question
A
answer
Which of the following is not true of neutrophils? A) less abundant than lymphocytes B) can make hydrogen peroxide C) can exit capillaries D) can destroy bacteria E) attracted to complement-coated bacteria
question
E
answer
Reticulocytes complete their development into ________ in the circulation. A) neutrophils B) megakaryotes C) thrombocytes D) macrophages E) erythrocytes
question
A
answer
Which type of granular leukocyte can engulf up to two dozen bacteria and also produces a respiratory burst that creates harsh chemical agents such as hydrogen peroxide? A)neutrophil B)basophil C)eosinophil D)lymphocyte
question
A
answer
2-8% of circulating white blood cells are A) monocytes. B) lymphocytes. C) eosinophils. D) basophils. E) neutrophils.
question
D
answer
Macrophages of the ___________ play a role in recycling red blood cell components. These also detect and remove Hb molecules from ruptured RBC. A) spleen B) liver C) red bone marrow D) all of the above
question
E
answer
Aged and damaged erythrocytes are broken down by macrophages in the A) spleen. B) liver. C) bone marrow. D) digestive tract. E) spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
question
C
answer
Which of these descriptions best matches the term B lymphocytes? A) adhere to collagen beneath endothelium B) helper cells are one type C) develop into plasma cells D) kill bacteria using hydrogen peroxide E) often elevated in allergic individuals
question
B
answer
Which of these descriptions best matches the term T lymphocytes? A) adhere to collagen beneath endothelium B) are involved in cell mediated immunity C) produce antibodies in response to antigens D) kill bacteria using hydrogen peroxide E) often elevated in allergic individuals
question
B
answer
A small white blood cell with a large round nucleus would be a A) neutrophil. B) lymphocyte. C) monocyte. D) basophil. E) eosinophil.
question
E
answer
The blood cells involved in specific immunity are the A) neutrophils. B) monocytes. C) basophils. D) erythrocytes. E) lymphocytes
question
D
answer
The process of lymphopoiesis occurs mainly in the A) spleen. B) kidneys. C) lymph nodes. D) red bone marrow. E) thymus.
question
A
answer
Which of the following statements is FALSE concerning T cells and B cells? A)B cells differentiate into T cells and produce antibodies against foreign antigens. B)B and T cells are involved in the specific immune response. C)B cells and T cells are both types of lymphocytes. D)T cells complete their maturation process in the thymus.
question
C
answer
On average, 1 microliter of blood contains __________ erythrocytes. Á) 10-12 million B) 260-300 million C) 4-6 million D) 25-30 million
question
D
answer
Which blood cells are the most abundant? A)monocytes B)platelets C)neutrophils D)erythrocytes
question
C
answer
Reticulocytes account for about __________ percent of the erythrocyte population in the blood. A)0 B)5 C)1 D)zero
question
B
answer
One function of platelets is to assist in the A) destruction of bacteria. B) process called hemostasis. C) removal of worn out red blood cells. D) immune response during an infection. E) transport of blood gases such as oxygen.
question
B
answer
One function of platelets is to assist in the A) destruction of bacteria. B) release of chemicals for clotting process C) removal of worn out red blood cells. D) immune response during an infection. E) transport of blood gases such as oxygen.
question
C
answer
One function of platelets is to assist in the A) destruction of bacteria. B) removal of worn out red blood cells. C) reducing the size of a break in the vessel wall D) immune response during an infection. E) transport of blood gases such as oxygen.
question
D
answer
A person whose platelet count is 40,000/µl is suffering from A) thrombocytosis. B) leukocytosis. C) hemocytosis. D) thrombocytopenia. E) leukopenia.
question
A
answer
Which of the following descriptions best matches the function of platelets? A) adhere to collagen beneath endothelium B) helper cells are one type C) produce antibodies in response to antigens D) kill bacteria using hydrogen peroxide E) often elevated in allergic individuals
question
D
answer
A fibrin network that contains trapped blood cells and platelets is called a(n) A) platelet plug. B) rouleaux. C) agglutinin. D) blood clot. E) lysin.
question
E
answer
Which of the following statements is true about platelets? A) Platelets live for less than two weeks. B) The spleen is a storage organ for a large platelet population. C) Platelets are not cells. D) Platelets clump together at a site of injury. E) All of the answers are correct.
question
C
answer
In case of hemorrhage, platelets are stored as a reserve in A) the heart. B) the kidneys. C) the spleen. D) the thymus gland. E) bone marrow.
question
B
answer
An abnormally low platelet count is called __________. A)thrombocytosis B)thrombocytopenia C)leucopenia D)anemia
question
B
answer
The production of platelets, or ___________________, takes place in the red bone marrow. A) thrombocytosis. B) thombocytopoiesis C) hemocytosis. D) thrombocytopenia. E) leukopenia.
question
A
answer
______________ divide to produce the various classes of lymphocytes via the process of lymphopoiesis. A) lymphoid stem cells B) myeloid stems cells C) White blood cells D) Red blood cells
question
A
answer
Erythropoiesis is stimulated by a kidney-derived hormone called A) erythropoietin. B) bilirubin. C) thrombopoietin. D) colony-stimulating factors. E) plasmin.
question
C
answer
______________ is low oxygen level in tissues, which stimulates erythopoiesis. A) hyperchromic. B) normochromic. C) hypoxia. D) normocytic. E) macrocytic.
question
C
answer
An obstruction in blood flow to the kidneys would ultimately result in A) pernicious anemia. B) renal anemia. C) increased erythropoiesis. D) decreased erythropoiesis. E) increased sensitivity to vitamin K.
question
D
answer
The level of erythropoietin in the blood would rise due to all of the following except A) anemia. B) high altitude. C) as a consequence of hemorrhage. D) periods of fasting. E) when blood flow to the kidneys is disrupted.
question
C
answer
Jessica has just moved to Denver, Colorado, from Orlando, Florida. What condition is she experiencing now that is stimulating the production of erythropoietin and, consequently, more red blood cells? A)a change in diet, from deep-fried comfort foods to healthy organic meals B)a decrease in the number of existing white blood cells C)hypoxia caused by an increase in her elevation above sea level D)increased oxygen concentration in the atmospheric air
question
T
answer
Is this the correct order for the steps of erythropoiesis? 1)hemocytoblast 2)proerythroblast 3)normoblast 4)reticulocyte 5)erythrocyte T or F
question
D
answer
The condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is reduced, owing to a low blood hemoglobin concentration, is called A) thrombocytopenia. B) leukopenia. C) polycythemia. D) anemia. E) leukocytosis.
question
A
answer
A hormone that stimulates production of monocytes is A) M-CSF. B) G-CSF. C) GM-CSF. D) multi-CSF. E) thymosin.
question
B
answer
A hormone that stimulates production of granulocytes is A) M-CSF. B) G-CSF. C) GM-CSF. D) multi-CSF. E) thymosin.
question
C
answer
A hormone that stimulates production of granulocytes and monocytes is A) M-CSF. B) G-CSF. C) GM-CSF. D) multi-CSF. E) thymosin.
question
D
answer
A hormone that stimulates the production of granulocytes, monocytes, platelets, and red blood cells) A) M-CSF. B) G-CSF. C) GM-CSF. D) multi-CSF. E) thymosin.
question
Each hemoglobin contains
answer
4 iron atoms
question
A
answer
When plasma oxygen levels are low, hemoglobin releases oxygen, making the carbon dioxide levels elevated. The process of the alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin binding then binding the carbon dioxide is called______________, which is carried to the lungs to be expelled. A) carbaminohemoglobin B) oxyhemoglobin C) deoxyhemoglobin D) hemoglobinuria
question
B
answer
Each heme unit holds an iron ion in such a way that the iron can interact with an oxygen molecule, forming ______________. Associates easily w/ oxygen A) carbaminohemoglobin B) oxyhemoglobin C) deoxyhemoglobin D) hemoglobinuria
question
B
answer
A bruise appears as a greenish spot in the skin because A) hemoglobin has leaked from the blood into the injury and hemoglobin has a green color. B) the heme group in the hemoglobin has broken down into biliverdin. C) bilirubin from iron recycling has built-up in the bruise. D) red blood cells are green when they leave circulation. E) dead white blood cells accumulate at the site of injury.
question
C
answer
More than 95 percent of the protein in a red blood cell is A) albumin. B) porphyrin. C) hemoglobin. D) immunoglobulin. E) fibrinogen.
question
C
answer
Which of the following does not influence hemoglobin saturation? A) temperature B) DPG C) nitric oxide D) carbon dioxide
question
C
answer
A hemoglobin molecule whose iron is not bound to oxygen is called _________________. Disassociates easily with oxygen. A) carbaminohemoglobin B) oxyhemoglobin C) deoxyhemoglobin D) hemoglobinuria
question
C
answer
Each heme ring in hemoglobin encloses an atom of A) magnesium. B) calcium. C) iron. D) sodium. E) copper.
question
D
answer
Consider these results from a blood lab test. Which value is most likely abnormal? RBCs—5.2 million/µl B) platelets—280,000/µl C) leukocytes—8600/µl D) hemoglobin—10.7 g/100 ml E) hematocrit—44 percent
question
D
answer
Most of the iron that is removed from degraded hemoglobin is A) excreted by the kidneys. B) excreted by the liver. C) excreted by the intestines. D) recycled to the red bone marrow. E) stored in yellow bone marrow.
question
D
answer
The condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is reduced, owing to a low blood hemoglobin concentration, is called A) thrombocytopenia. B) leukopenia. C) polycythemia. D) anemia. E) leukocytosis.
question
E
answer
Which of these proteins functions to store or transport iron? A) hemoglobin B) ferritin C) hemosiderin D) transferrin E) ferritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin
question
E
answer
Excess iron is stored in the liver and spleen as A) transferrin. B) hemosiderin. C) ferritin. D) hemoglobin. E) hemosiderin and ferritin.
question
E
answer
The yellow color that is visible in the eyes and skin in jaundice results from A) excessive amounts of bilirubin in the plasma. B) extensive breakdown of RBCs. C) destruction of hemoglobin. D) the recycling of hemoglobin. E) All of the answers are correct.
question
E
answer
The process of the destruction of RBCs so that hemoglobin is liberated. A) Polycythemia B) Leukemia C) Anemia D) Leukopenia E) hemolysis
question
A
answer
The function of hemoglobin is to A) carry dissolved blood gases. B) carry bicarbonate ion. C) aid in the process of blood clotting. D) produce antibodies. E) stimulate erythropoiesis.
question
C
answer
The waste product bilirubin is produced from A) globin chains of hemoglobin. B) heme molecules plus iron. C) heme molecules lacking iron. D) iron found in hemoglobin molecules. E) abnormal proteins found in red blood cells.
question
A
answer
A red blood cell that contains excessive amounts of hemoglobin would be called A) hyperchromic. B) normochromic. C) hypochromic. D) normocytic. E) macrocytic.
question
C
answer
The disease sickle cell anemia is an example of what can happen if A) the diet is deficient in iron. B) there is insufficient heme in the hemoglobin. C) a gene for adult hemoglobin is abnormal. D) red blood cells bind too much oxygen. E) hemolysis is prevented by a mutated gene.
question
C
answer
Each hemoglobin molecule contains A) four alpha chains. B) one alpha and one beta chain. C) four iron atoms. D) one heme group. E) a molecule of oxygen and a molecule of carbon dioxide.
question
E
answer
Mary is tested for the amount of hemoglobin in her blood. The test results indicate that her hemoglobin level is 16 g/dL of blood. This value indicates that A) she is suffering from anemia. B) she has fewer red blood cells than normal. C) her hematocrit is probably lower than normal. D) she may be suffering from a form of leukemia. E) her hemoglobin level is normal.
question
A
answer
Hemoglobin molecules released into the bloodstream by the breakdown of RBCs by hemolysis will be excreted in the __________. A)kidney B)small and large intestine C)skin D)tears
question
B
answer
A change in the amino acid sequence of DNA coding for one of the globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule results in a condition known as __________. A) thalassemia B) sickle cell anemia C) leukemia D) leukopenia
question
B
answer
The iron extracted from heme molecules during hemoglobin recycling is stored in the protein-iron complexes __________. A)transferrin and porphyrin B)ferritin and hemosiderin C)biliverdin and bilirubin D)urobilin and stercobilin
question
B
answer
Each hem unit is stripped of its iron and converted to A) albumin B) biliverdin C) stercobiln D) ferritin
question
C
answer
Biliverdin is converted to ____________, and released into the bloodstream A) Transferrin B) Ferritin C) Bilirubin D) Hemosiderin
question
C
answer
Bilirubin binds to ___________ and is transported to the liver for excretion in bile. A) Transferrin B) Ferritin C) Albumin D) Hemosiderin
question
B
answer
It is an illegal practice for Olympic competitors to receive doses of which hormone, which stimulates the production of red blood cells? A)thyroxine B)erythropoietin C)calcitonin D)renin
question
D
answer
The rate of megakaryocyte activity and platelet formation is regulated by __________. A)multi-CSF B)interleukin-6 C)thrombopoietin D)All of the listed responses are correct
question
D
answer
A person's blood type is determined by the A) size of the RBCs. B) volume of the RBCs. C) chemical character of the hemoglobin. D) presence of specific glycoproteins on the cell membrane. E) shape of the RBCs.
question
B
answer
People with type AB blood are considered the "universal recipient" for transfusions because A) their blood cells lack A and B antigens. B) their blood lacks A or B agglutinins. C) their blood is plentiful in A and B agglutinins. D) they usually have very strong immune systems. E) they are usually Rh negative.
question
D
answer
Blood type is identified primarily by A) the Kahn blood group. B) the HB blood system. C) the Rh blood group. D) both the ABO and Rh blood groups. E) the ABO blood group.
question
C
answer
Type AB blood has which of the following characteristics? A) RBCs have the Rh positive antigens and the anti-D plasma antibodies. B) RBCs have no surface antigens and both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma. C) RBCs have both the A & B surface antigens and no ABO plasma antibodies. D) RBCs have the A and the B surface antigens and the plasma has anti-A and anti-B antibodies. E) RBCs have the A antigen and the plasma has the anti-B antibody.
question
B
answer
Anti-D antibodies are present in the blood of A) all individuals with type AB blood. B) Rh negative individuals who have been exposed to the D surface antigen. C) all Rh positive individuals. D) Rh positive individuals who have been exposed to the D surface antigen. E) all Rh negative individuals.
question
C
answer
Which of the following combinations may result in the hemolytic disease of the newborn? A) mother Rh positive, baby Rh negative B) mother Rh negative, baby Rh negative C) mother Rh negative, baby Rh positive D) mother type A+, baby type O+ E) None of the answers is correct.
question
E
answer
Which of the following statements is true regarding the ABO blood types and the Rh blood types? A) Rh disease in the newborn occurs when the mother is Rh+ and the baby is Rh-. B) Rh disease is worse in male offspring because it is a hereditary disease. C) A person with O- blood type has blood cells with O antigens, but no Rh antigens. D) Those with AB blood type can receive blood from other AB people only, no other blood type can be given. E) An Rh- person has to be exposed to Rh+ blood in order to produce anti-Rh.
question
C
answer
Type A blood has ________ antibodies in the blood plasma. A) anti-A B) anti-D C) anti-B D) anti-Rh E) anti-O
question
D
answer
Type _____blood has both A and B surface antigens and does not contain anti-A or anti-B antibodies. A) A B) B C) O D) AB E) Rh-
question
C
answer
What type of blood can be transfused into a person with type O blood? A) A or B B) B C) O D) AB E) Rh-
question
A
answer
A cross-match test is performed between donor blood and recipient blood, even though the ABO and Rh blood types match between the two because A) there are many more surface antigens on red blood cells other than A, B and Rh. B) all antibodies of the donor blood and the recipient blood must be identified. C) coagulation can occur even in a small percentage of cases. D) one has to make sure that the same agglutinogens have to be on both donor and recipients red blood cells. E) errors are commonly made by the clinical staff regarding donor-recipient matches.
question
A
answer
Jane has Type A blood; therefore, she A) has antibodies to B agglutinogens. B) can give blood to other people with Type A blood only. C) can receive blood from other people with Type A blood only. D) makes anti-A without ever having been exposed to Type A blood. E) has B antigen on her RBCs.
question
A
answer
If a person has type A and Rh surface antigens on the blood cells and anti-B antibodies in the plasma, what is that person's blood type? A)A-positive B)B-negative C)A-negative D)B-positive
question
C
answer
What type of blood would cause a cross-reaction when given to a person with type A-positive blood? A)type A-positive B)type O-positive C)type B-positive D)type O-negative
question
C
answer
What is the most common blood type among Americans? A)type B B)type AB C)type O D)type A
question
F
answer
If Misty is type A and needs to receive transfusions of blood during a surgery, which blood type(s) could she receive? A)A B)B C)AB D)O E)A and AB F)A and O
question
C
answer
The extrinsic pathway of coagulation is initiated by the A) sticking of platelets to damaged tissue. B) activation of Factor VII exposed to collagen. C) release of tissue factor by damaged endothelium. D) release of heparin from the liver. E) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
question
B
answer
The intrinsic pathway of coagulation is activated by the A) sticking of platelets to each other. B) activation of Factor XII by platelet factors. C) release of tissue factor (Factor III) by damaged endothelium. D) release of heparin from the liver. E) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
question
B
answer
The intrinsic pathway of coagulation is activated by the A) sticking of platelets to each other. B) Platelet Factor (PF-3) C) release of tissue factor (Factor III) by damaged endothelium. D) release of heparin from the liver. E) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
question
D
answer
The common pathway of coagulation begins with the A) sticking of platelets to damaged tissue. B) activation of a proenzyme exposed to collagen. C) release of tissue factor by damaged endothelium. D) activation of Factor X, production of prothrombin activator. E) conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
question
D
answer
________ involves a cascade of reactions leading to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. A) Vascular spasm B) The platelet phase C) Retraction D) Coagulation E) Fibrinolysis
question
A
answer
People who suffer from hemophilia A fail to produce a functional Factor VIII; as a result, A) they lack a functional intrinsic pathway. B) they lack a functional extrinsic pathway. C) they lack a functional common pathway. D) their coagulation times are much longer than normal. E) their coagulation times are too quick.
question
B
answer
The clumping of red blood cells, when the specific antibody against the antigen on the cells is added, is called A) coagulation. B) agglutination. C) hemostasis. D) vascularization. E) areolation.
question
B
answer
Antigens of the surface of red blood cells are also called ________ and antibodies in the blood plasma are also called ________. A) agglutinins; agglutinogens B) agglutinogens; agglutinins C) T-cells; B-cells D) erythrogens; antibiotics E) serum; plasma
question
A
answer
Opposing antibodies attach to surface antigens, which causes _______________, and then hemolysis. A) agglutination B) agglutinogination C) cellular breakdown D) erythrogenosis E) serumulois
question
A
answer
When antibodies attack, foreign cells _________________, or clump together. A) agglutinate B) agglutinoginate C) cellular breakdown D) erythrogenis E) serumulois
question
D
answer
Most of the chemicals involved in the coagulation pathways are A) electrolytes. B) lipids. C) vitamins. D) proteins. E) carbohydrates.
question
B
answer
How would removal of calcium ions from a blood sample affect coagulation? A) The coagulation pathway would be more sensitive to activation. B) Coagulation would be prevented. C) There would be no important effect because magnesium can substitute for calcium. D) Coagulation would occur only in Rh positive individuals. E) More blood cells would be produced.
question
C
answer
In which phase of hemostasis does local contraction of the injured blood vessel occur? A)fibrinolysis B)coagulation phase C)vascular phase D)platelet phase
question
B
answer
In which phase of hemostasis is fibrin deposited, creating a solid blood clot? A)fibrinolysis B)coagulation phase C)vascular phase D)platelet phase
question
D
answer
Which of the following affect almost every aspect of the clotting process? A)sodium ions and vitamin D B)calcium ions and vitamin C C)potassium ions and vitamin B12 D)calcium ions and vitamin K
question
A
answer
Which of the following factors does NOT restrict the coagulation process? A)thromboxane Á B)alpha-2-macroglobulin C)heparin D)antithrombin III E) prostacyclin
question
T
answer
Is this the correct order for clotting to occur? B. Endothelial cells contract and expose underlying basal lamina to bloodstream D. Endothelial cells release local hormones and chemical factors, causing them to become "sticky" F. Platelets attach to exposed surfaces (platelet adhesion) E. Formation of a platelet plug C. Coagulation phase A. Blood clot formed and bleeding stopped T or F
question
C
answer
Which of the following precursor cells give rise to agranular leukocytes? a. Proerythroblast b. Megakaryoblast c. Lymphoblast d. Myeloblast e. None of the selections are correct.
question
T
answer
Order of events occurring during the recycling of a red blood cell. A. After approximately 120 days, a macrophage consumes a red blood cell. B. Heme is broken down, iron and amino acids are sent to bone marrow, while the remainder of the cell forms biliverdin and bilirubin. E. Bilirubin is secreted in bile. D. Bilirubin is converted to urobilins and stercobilins in the large intestine. C. Urobilins and stercobilins are eliminated in digestive and urinary waste. T or F
question
B
answer
PLASMA thromboplastin is a factor in the ________ pathway. A) extrinsic B) intrinsic C) common D) retraction E) fibrinolytic
question
B
answer
PF-3 (platelet factor 3) is a factor in the ________ pathway. A) extrinsic B) intrinsic C) common D) retraction E) fibrinolytic
question
A
answer
Tissue factor (Factor III) is a factor in the ________ pathway. A) extrinsic B) intrinsic C) common D) retraction E) fibrinolytic
question
C
answer
Thombrin is produces in the ________ pathway (activated by Factor X activating prothombrin). A) extrinsic B) intrinsic C) common D) retraction E) fibrinolytic
question
A
answer
The major effect of vitamin K deficiency in the body is that it leads to __________. A)a breakdown of the common pathway, inactivating the clotting system B)the body becoming insensitive to situations that would necessitate the clotting mechanism C)an overactive clotting system, which might necessitate thinning of the blood D) All of the listed responses are correct.
question
E
answer
Activated Factor x activates a complex called _________ activator which converts the proenzyme ____________ into the enzyme thombrin. A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) factor VIII. D) thrombin. E) prothrombin
question
D
answer
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalyzed by the enzyme A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) factor VIII. D) thrombin. E) prothrombinase.
question
A
answer
Plasminogen is converted to its active form by an enzyme called A) tissue plasminogen activator. B) papain. C) fibrinolysin. D) prothrombin. E) polymerase.
question
C
answer
As repairs are processed, the clot gradually disolves in a process called A) Leukospoiesis B) Hemopoiesis C) Fibrinolysis D) Fibrinogenisis
question
B
answer
A plasma protein essential for blood coagulation is A) albumin alpha. B) fibrinogen. C) immunoglobulin A. D) metalloprotein D. E) lipoprotein C.
question
B
answer
Which enzyme digests fibrin strands in a blood clot after healing at the injury site has occurred? A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) factor VIII. D) thrombin. E) prothrombinase.
question
D
answer
One function of platelets is to assist in the A) destruction of bacteria. B) removal of worn out red blood cells. C) immune response during an infection. D) forming a temporary path in the walls of damaged blood vessels E) transport of blood gases such as oxygen.
question
A
answer
What cell uses defensins to kill pathogens? A) neutrophils B) eosinophils C) basophils D) lymphocytes E) monocytes
question
B
answer
What is the precursor of all blood cells in the human body? A)myeloblast B)hemocytoblast C)megakaryocyte D)None of the listed responses is correct.
question
D
answer
Hemocytoblasts are differentiated by A) erythropoietin. B) bilirubin. C) thrombopoietin. D) colony-stimulating factors. E) plasmin.
question
B
answer
Platelets live _______ days A) 15-17 B) 9-12 C) 20-25 D) 50-65
question
B
answer
Which of the following is not needed in thrombopoiesis? A) thrombopoietin B) a hole to patch C) interleukin 6 D) Multi- CSF
question
C
answer
Factor I is __________ A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) fibrinogen D) thrombin. E) prothrombinase.
question
D
answer
Factor II is __________ A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme. B) plasmin. C) fibrinogen D) prothrombin. E) prothrombinase.
question
D
answer
Pernicious anemia caused by a lack of intrinsic factor is specifically treated by A) oral doses of iron. B) injections of iron. C) oral doses of vitamin B12. D) injections of vitamin B12. E) blood transfusion.
question
D
answer
Adosterone and antidiuretic hormone are key hormones in making A) clotting factors. B) formed elements. C) leukocytes. D) plasma. E) antibodies.
question
Except for __________, the following statements about blood are true. a.The viscosity is three to five times greater than water. b The pH is slightly acidic. c. It contains about 55% plasma. D. It contains dissolved gases.
answer
B
question
The formed elements of blood consist of _________. A. platelets B. red blood cells C. white blood cells D. All of these are formed elements of blood.
answer
D
question
Plasma makes up approximately what percentage of whole blood?
answer
55%
question
Except for the amount of __________, plasma and interstitial fluid differ little in composition. A. water B. protein C. glucose D. sodium ion
answer
B
question
The most abundant solute in plasma is __________.
answer
protein
question
What is the role of transferrin in the cycle shown above?
answer
It transports iron ions in the plasma.
question
Which of the labels in the figure indicate a cell normally found in the circulating blood?
answer
reticulocyte
question
Red blood cells (RBCs) are removed from the circulation after about __________.
answer
120 days
question
Red blood cells carry __________ to the lungs and __________ to the tissues.
answer
carbon dioxide; oxygen
question
The most abundant protein in blood is __________.
answer
hemoglobin
question
Reticulocyte is a stage in the development of __________.
answer
red blood cells
question
The formed elements are largely produced within the __________.
answer
red bone marrow
question
__________ stimulates production of red blood cells.
answer
erythropoietin
question
What evidence in this figure indicates that this is not a first pregnancy?
answer
Presence of maternal anti-Rh antibodies Antibodies against Rh antigen are only generated after a first pregnancy.
question
People with type "O" blood are considered "universal donors" for transfusions because __________.
answer
their blood lacks A and B antigens
question
A person with a type A positive blood type can safely receive blood from all of these donors except __________.
answer
B positive
question
Which of these is not a surface antigen found on red blood cells? A. Rh B. A C. B D. O
answer
D
question
Which of these is characteristic of monocyte? A. Reduces inflammation B. Provides defense against specific antigens C. Releases cytotoxic enzymes D. Engulfs pathogens
answer
D
question
Which of these is characteristic of eosinophil? A. Release histamine B. Releases cytotoxic enzymes C. Provides defense against specific antigens D. Reduces inflammation
answer
B, D
question
Which of the formed element stem cells is developmentally the most different from the others?
answer
Lymphoblast Lymphoid stem cells differentiate separately from the myeloid stem cell, which gives rise to all the other blood cells.
question
The white blood cell type that most rapidly increases in number after a bacterial infection is the __________.
answer
neutrophils
question
Which of these statements about basophils is not true? A. They are abundant. B. They promote inflammation. C. They release histamine. D. They contain cytoplasmic granules.
answer
A
question
Granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) stimulates production of __________. A. lymphocytes B. neutrophils C. monocytes D. platelets
answer
B
question
The agranular leukocyte (agranulocyte) that is capable of phagocytosis is the __________. A. eosinophil B. lymphocyte C. monocyte D. neutrophil
answer
C
question
Granulocytes are produced in __________. A. white bone marrow B. the liver and spleen C. the lymph nodes D. red bone marrow
answer
D
question
The largest white blood cell in circulation is the __________. A. eosinophil B. lymphocyte C. neutrophil D. monocyte
answer
D
question
If a patient has thrombocytopenia, the best therapy is infusion of __________.
answer
purified platelets
question
An important function of thrombocytes is to __________. A. transport blood gases B. transport nutrients C. transport clotting factors D. transport thrombopoietin
answer
C
question
Megakaryocytes are the source of __________.
answer
platelets
question
Which of the pathways shown above will occur within a damaged vessel?
answer
Both the intrinsic and the common pathways
question
Most of the plasma proteins required in the coagulation process are produced by __________.
answer
the liver
question
During fibrinolysis __________.
answer
clots slowly dissolve
question
The common pathway in coagulation ends with __________.
answer
conversion of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin
question
The enzyme that dissolves fibrin is named __________.
answer
plasmin
question
The complex process that leads to the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen is called __________.
answer
coagulation
question
Which of these phases is not part of hemostasis? A. erythropoiesis phase B. vascular phase C. coagulation phase D. platelet phase
answer
A
question
Serum can't coagulate because the __________ has been removed.
answer
fibrinogen
question
Which blood type is called the universal donor?
answer
Type O
question
An individual whose blood type is AB negative can .
answer
receive any blood type except that with an Rh antigen
question
Which of the following is characteristic of all leukocytes? A. they are nucleated B. they have cytoplasmic granules C. they are phagocytic D. they are the most numerous elements formed in blood
answer
A
question
Tom's blood type is AB positive. What does this mean? A. antibodies to A and B are present in the plasma B. he can only receive blood from a donor who is AB positive C. there are no antibodies to A to B or to Rh antigens in the plasma D. his blood lacks the Rh factor
answer
C
question
Platelets .
answer
stick to damaged areas of blood vessels and help seal the break
question
Blood is classified as a(n) __________ tissue.
answer
Connective
question
Which of the following cells are NOT found in the blood? A. Lymphocytes B. Thrombocytes (platelets) C. Leukocytes D. Chondrocytes E. Erythrocytes
answer
D
question
Which type of cell functions to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body? Neutrophils Megakaryocytes Macrophages Basophils Erythrocytes
answer
Erythrocytes
question
Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood, is mainly composed of _________________. Protein Electrolytes (Na+, Cl-, K+, etc.) Lipids Hormones Water
answer
Plasma is 92% water.
question
Which of the following are functions of blood? Transport of nutrients, gases, ions, and wastes Coagulation Control of the chemical composition of interstitial fluid Immunity
answer
All are correct
question
Visible cytoplasmic granules are NOT present in .
answer
monocytes and lymphocytes
question
Visible cytoplasmic granules are present in .
answer
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
question
When viewing a blood smear under a microscope, the cells with the visible nuclei are ___________. platelets erythrocytes leukocytes none of the above
answer
leukocytes
question
Which white blood cells are first to arrive at the site of a wound?
answer
neutrophils
question
What white blood cells are most abundant in lymphoid tissue?
answer
lymphocytes
question
_________________ is the substance of the red blood cell (erythrocyte) that binds to oxygen and carbon dioxide.
answer
Hemoglobin
question
Mature red blood cells that are in circulation are multinucleate. True or False
answer
false. Mature red blood cells are anucelate. During the maturation process, red blood cells lose their nucleus.
question
Platelets, which are involved with blood clotting, are fragments of which cells?
answer
Megakaryocytes
question
Which of the following cells are classified as lymphocytes?
answer
T cells, B cells
question
When neither anti-A sera nor anti-B sera clump on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is Type .
answer
Type O
question
Which type of blood is considered to be the universal recipient?
answer
Type AB
question
Antibodies are proteins that can randomly bind to antigens. true or false
answer
false. Antibodies are protein molecules secreted by plasma B cells. Antibodies exhibit specificity and will bond only to certain antigens.
question
A patient with type A blood will naturally produce antibodies for the A antigen. true or false
answer
False A patient with type A blood will express type A antigen on the surface of the red blood cells. A person with type A blood will produce antibodies to type B antigen.
question
A person with which blood type is considered to be a universal donor?
answer
Type O- people with type O- blood can receive only type O- blood
question
Which of the following scenarios may induce erythroblastosis fetalis?
answer
Rh-negative mother; Rh-positive fetus
question
Administering _____________ can prevent an Rh-negative mother from producing anti-Rh antibodies (anti-D) following exposure to the Rh antigen.
answer
RhoGam
question
A ________________ measures the percentage of total blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells.
answer
Hematocrit test
question
A woman has a hematocrit of 25%. What does this indicate?
answer
Anemia normal hematocrit for a woman is between 37% and 47%
question
A low hematocrit would impair which bodily function?
answer
Oxygen transport
question
During coagulation, insoluble protein threads called ___________ trap platelets to help form a clot.
answer
Fibrin
question
What is heparin?
answer
An anticoagulant
question
A patient with a slower-than-normal coagulation time might be at risk for which of the following?
answer
Hemorrhage
question
A hematocrit primarily measures the volume of .
answer
red blood cells
question
What prevents blood from clotting?
answer
heparin
question
CO stands for ? and is the?
answer
Cardiac output, and is the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in 1 minute. CO=SV*HR
question
SV stands for? and is the ?
answer
Stroke volume, and is the amount of blood pumpled out of ventricles in 1 beat.
question
If jims heart rate is 75bpm, and his stroke volume is 70/ml beat what is jims CO?
answer
70ml * 75 bpm = 5250 CO
question
What does EDV stand for?
answer
End diastolic volume
question
What does ESV stand for?
answer
End systolic volume
question
If before Jim's heart attack, values were EDV=130 ml ESV= 50- ml what is his SV?
answer
80=130-50
question
cardiac pacemaker:
answer
SA node
question
Bundle of his:
answer
av conducting fibers
question
p wave:
answer
Atrial depolarization
question
lubb sound:
answer
av valves close, semilunar valves open
question
dubb:
answer
semilunar valves close
question
atrial reflex:
answer
bainbridge reflex
question
baroreceptors:
answer
monitor blood pressure
question
sympathetic neurons:
answer
increases heartrate
question
fills atria:
answer
venous return
question
filling time:
answer
ventricular diastole
question
cardiac output:
answer
SV * HR
question
cardiac control:
answer
medulla oblingata
question
how does atonomic innervations affect heart rate?
answer
If SNS is up so is heart rate, if PNS is up, decrease in HR
question
how does bainbridge atrial reflex affect HR?
answer
increase in venous return, stretches heart, and reflexive increase in HR.
question
how does hormones affect heart rate?
answer
epinephrine and norepi, and thyroid hormones can cause increases in HR
question
how does venous return affect heart rate?
answer
if venous return is increased, Hr is increased.
question
if Bill was diagnosed with a tumor of adrenal medulla, which resulted in excessive amounts of norepi being released into blood stream. how does this affect heart rate and CO? which stroke volume parameters would this alter? how would this affect cardiac output?
answer
heart rate? ups because epi and norepi affect SA node. CO? ups it. cardiac output? ups it Stroke volume parameters? ESV
question
same as above. how does this affect contractility?
answer
ups it, more forcefully
question
the only vessels whose walls are thin enough to exchange with the surrounding cells are:
answer
capillaries
question
which of the following would reflect the typical hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end of the capillary?
answer
35MMHG
question
the colloid osmotic pressure in the capillary is caused by:
answer
proteins in the blood
question
what pressure draws fluid into the capillary?
answer
colloid osmotic pressure
question
typically reabsorption of fluid into the capillary takes place at the arterial end or venous end of the capillary?
answer
venous
question
plug in the following values and determine if NFP is into or out of the capillaries. CHP= 35 MM hg BCOP. 1. 25 mm 2. Filtration 3. reabsorbition
answer
filtration
question
if a patient suffers from hypertension, which parameter of net filtration pressure would be most affected.
answer
CHP
question
assume patient A has high BP and their CHP=60MMhG. If BCOP is normal, what is happening?
answer
Filtration occours, fluid may accumulate in the tissues causing edema.
question
peripheral resistance depends on all of the following except? 1. BV diameter 2. Blood viscosity 3. blood vessel length 4. blood colloid osmotic pressure
answer
4. BCOP
question
which helps move blood around the systemic system?
answer
Arterial pressure greater than venous pressure
question
elevated capillary hydrostatic pressure
answer
forces more fluid across endothelium into the tissues.
question
where are sensors for arterial baroreceptors located?
answer
carotid artery and aortic arch
question
if blood pressure is increased at arterial baroreceptors, what would happen with activity level of parasympathetic nervous system and SNS?
answer
increased PNS and decreased SNS activity
question
which of the following would cause vasodilation of arterioloes?
answer
decreased activity of the SNS
question
a decrease in BP at arterial baroreceptors would result in?
answer
vasoconstriction of arterioles, and an increase in cardiac output.
question
stenosis is a permanant narrowing of an artery. As with artheriosclerosis, resulting in a reduction of blood flow to the kidneys. Which would occur with stenosis of a renal artery?
answer
renin secretion will increase.
question
when mucsle cells contract they release substances that cause nearby precapillary spinchters to relax. This is an example of ?
answer
autoregulation
question
would an inhibitor of angiotenin 2 cause an increase in BP?
answer
NO
question
which brain region contains the cardiovascular centers?
answer
medulla
question
pulmonary trunk carries ? blood ? the lungs
answer
deoxygenated, to
question
which organ produces renin and erythropoietin to help maintain normal BP and hematocrit?
answer
kidneys
question
aldosterone would ? BV
answer
increase
question
ADH wojuld ? Bv
answer
increase
question
ADH:
answer
retains water
question
ALDOSTERONE:
answer
hormone that results in retention of sodium
question
ERYTHROPOIETIN
answer
hormone that stimulates RBC production
question
NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE:
answer
hormone is released from the heart that elliminates sodium and water from the body( gets rid of)
question
NOREPINEPHRINE:
answer
hormone released from adrenal gland that stimulates SNS
question
RENIN:
answer
homone released from kidneys that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1.
question
Aldosterone would ? BV
answer
increase
question
ADH would ? BV
answer
increase
question
angiotenin2 would ? BV
answer
increase
question
NATRIUETIC PEPTIDES WOULD ? BV
answer
decrease
question
the "hole" between the right and left atrium of fetus?
answer
FORAMEN OVALE
question
ARTERY=
answer
AWAY FROM HEART
question
veins=
answer
return from heart
question
capillaries are:
answer
small thin walled vessels
question
arteries go to
answer
arterioles
question
veinules go to
answer
veins
question
location of the heart;
answer
mediasteinum, in the thorasic cavity. bulk of mass lies left of midline.
question
apex
answer
bottom of heart
question
base
answer
top of heart
question
pericardium:
answer
protects heart like a canvas covering. 2 parts, fibrous pericardium outer layer, and serous pericardium inner thin layer. like a double bag.
question
visceral pericardium
answer
attaches to surface of the heart
question
pericardial cavity
answer
filled with serous fluid
question
Heart walls?
answer
1. epi (upon) cardium outermost layer 2 myo (myo= muscle) pumping layer of heart 3 endo (within) thin layer of CT covered by endothelium
question
Cardiocytes
answer
single, centrally located nucleus. many mitochonndria, branching interconnections between cells, intercalleted disks, striated.
question
right atrium
answer
recieves blood from the systemic and coronary circulation.
question
chordae tendinae
answer
like a tiedown for tricuspid valve. connective tissue cords attached to cusps of valve
question
trabeculae carnae are
answer
muscular ridges on walls
question
pulmonary circuit
answer
deoxygenated blood flows from right venticle into: left pulmonary artery, branches repeatedly within lungs. Is exchanged for 02 at capillaries. Oxygenated blood is then returned to left atrium via two left pulmonary veins, two right pulmonary veins.
question
left atrium
answer
recieves oxygenated blood from 4 pulmonary veins. The left atriventricluar valve or BICUSPID valve guards entrance into left ventricle. also called MITRAL valve
question
tell about the left ventricle:
answer
*thick muscular walls *can create sufficient pressure to push blood through large systemic circut
question
tell about right ventricle:
answer
right ventricle has less muscle than left, pumps muscle to lungs only.
question
recite blood flow thru heart:
answer
*right atrium *right ventricle *up into right pulmonary valve *pulmonary circuit *into left atrium down thru bicuspid valve *into left ventricle *into aortic valve *aorta and systemic circuit
question
coronary circulartion: right and left coronary artery
answer
right coronary artery follows the coronary sulcus around the heart and gives off two branches. Posterior and right marginal branch. LEFT coronary artery branches into the anterior and circumflex artery. ARTERIAL anastamoses is the "backup" plan for another route for blood.
question
coronary blood circulation:
answer
main veins drain DEOXYGENATED blood into the coronary sinus on the posterior surface of the heart. Drains into right atrium.
question
major tributaries that drian into the coronary sinus:
answer
*great cardiac vein *posterior cardiac vein *middle cardiac vein *small cardiac vein * anterior cardiac vein
question
what two kinds of cells are involved in a normal heartbeat?
answer
1. contractile cells 2. specialized muscle cells (act as pacemaker)
question
99% of muscle cells in heart are?
answer
contractile cells. Slow calcium channels highly sensitive to changes in Ca2+. Too little calcium released is a systolic dysfunction and too slow of calcium removal is a diastolic dysfuntion.
question
conduction system:
answer
contains the SA node. (pacemaker) Ventricular conducting cells consist of: 1. av bundle 2. left and right bundle branches=bundle of his 3.purkinjie fibers
question
normal sinus rhythm:
answer
normal p,q,r,s,t waves, normal intervals
question
sinus bradycardia:
answer
brady=slow
question
sinus tachycardia:
answer
tachy=fast
question
a fibrillation:
answer
irregular baseline,irregular ventricular response. (sudden dropped q,r,s complex)
question
av block 2nd degree:
answer
intermittantly skipped ventricular beats. (q,r,s absent)
question
v-fibb
answer
rapid, wide irregular ventricular complexes. (squiggles, no real q,r,s )
question
systole:
answer
systolic contraction
question
Diastole:
answer
diastolic relaxation
question
what is a p wave due to ?
answer
atrial depolarization
question
EDV is?
answer
end diastolic volume. The end of atrial systole each ventricle is full and this is called EDV.
question
what is the QRS complex due to?
answer
ventricular depolarization
question
ventricular systole:
answer
av valves close.(lubb) ventricular pressure increases, forcing blood through semilunar valves (ventricular ejection) pressure drops, and semilunar valves close.
question
ventricular diastole:
answer
all valves are closed. semilunar valves close (dubb) myocardium relaxes, ventricular pressure drops, and av valves open and blood flows passivly. ventricles refill.
question
T waves represent?
answer
ventricular repolarization
question
auscultation is?
answer
listening to heart sounds via stethescope
question
EDV is?
answer
end diastolic volume, amount of blood left in each ventricle at end of ventricluar diastole.(before empty)
question
ESV is?
answer
end systolic volume. the amount of blood remaining in each ventricle at the end of the ventricular systole. (after empty)
question
stroke volume:
answer
the amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle during a single beat. EDV-ESV=SV
question
ejection fraction
answer
the percentage of blood ejected out of the heart/beat %=SV/EDV
question
most important factor in an exam of a single cardiac cycle?
answer
stroke volume
question
cardiac output is?
answer
the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in 1 minute/ CO=HRxSV
question
cardiac reflexes for autonomic control
answer
Baroreceptors control BP chemoreceptors monitor oxygen levels
question
cardiac centers
answer
cardioaccelatory center increases HR cardioinhibitory center decreases HR
question
Which of the following statements about blood is false? Blood is about 55 percent plasma. Blood contains buffers that control pH. Blood is more viscous than water. The normal pH of blood is 6.8 to 7.0. Cells in blood comprise the formed elements.
answer
The normal pH of blood is 6.8 to 7.0.
question
Each of the following is a characteristic of whole blood, except a: red color from hemoglobin. built-in system for clotting. temperature of approximately 38 degrees Celsius. pH of 7.4. viscosity about the same as water.
answer
viscosity about the same as water.
question
Which of the following is not one of the formed elements of blood? platelets antibodies RBCs lymphocytes basophils
answer
antibodies
question
Approximately 45 percent of blood volume is composed of the antibodies. plasma. clotting factors. formed elements. leukocytes.
answer
formed elements
question
The percent fraction of formed elements relative to whole blood is the packed volume. differential cell count. hematocrit. specific gravity. viscosity.
answer
hematocrit
question
The most abundant component of plasma is (are) nutrients. proteins. ions. gases. water.
answer
water
question
The chief difference between plasma and interstitial fluid involves the concentration of water. electrolytes. proteins. glucose. nitrogen wastes.
answer
proteins
question
The combination of plasma and formed elements is called lymph. packed blood. whole blood. extracellular fluid. serum.
answer
whole blood
question
After blood is fractionated, the percentage of each type of white blood cell can be determined. it can be transfused immediately into the recipient. specimens can be sent to the labs for identification of bacteria, viruses, etc. its components are separated for the purpose of analysis. antibody and antigen can be added together to look for a reaction.
answer
its components are separated for the purpose of analysis.
question
You have spent 24 hours traveling from the U.S to New Zealand, on quite a few airplanes with many stops. Because of the stress, changes in time zones, and short blocks of time between planes, you find yourself tired with a headache when you arrive. You are severely dehydrated. A hematocrit value on your blood would be ________ than normal because ________. lower; the bone marrow is making fewer red blood cells due to the latitude of the airplanes lower; more red blood are being made by the bone marrow higher; more plasma proteins are made by the liver higher; you have less blood plasma volume
answer
higher; you have less blood plasma volume
question
A plasma protein essential for blood coagulation is metalloprotein D. albumin alpha. lipoprotein C. immunoglobulin A. fibrinogen.
answer
fibrinogen.
question
Which organ secretes most of the plasma proteins? liver heart brain kidney pancreas
answer
liver
question
Plasma proteins essential in body defense are the metalloproteins. fibrinogens. lipoproteins. immunoglobulins. albumins.
answer
immunoglobulins
question
The most abundant plasma protein is albumin. transferrin. hemoglobin. antibodies. fibrinogen
answer
albumin
question
Which of the following statements is true about hemoglobin? All that is needed to bind oxygen is a molecule of heme. Each hemoglobin molecule can carry four oxygen atoms. Each hemoglobin molecule is made up of one alpha and one beta chain of polypeptide. Hemoglobin can only bind oxygen.
answer
Each hemoglobin molecule can carry four oxygen atoms.
question
Mrs. Higgins needs to have major surgery. Two weeks before the surgery, her doctor prescribes EPO. Which of the following statements best explains his reason for doing this? By prescribing EPO, the doctor will decrease her hematocrit so that her blood is less likely to clot during surgery. By prescribing EPO, the doctor will be able to increase oxygen levels because EPO causes hemoglobin to bind oxygen more efficiently. By prescribing EPO, the doctor can stimulate Mrs. Higgins's body to produce an overabundance of RBCs, which can be harvested and saved for her surgery. After she takes EPO, Mrs. Higgins's risk of infection will go down because of increased production of WBCs.
answer
By prescribing EPO, the doctor can stimulate Mrs. Higgins's body to produce an overabundance of RBCs, which can be harvested and saved for her surgery.
question
Which of these proteins functions to store or transport iron? ferritin hemoglobin ferritin, hemosiderin, transferrin transferrin hemosiderin
answer
ferritin, hemosiderin, transferrin
question
The developmental stage at which erythrocytes enter the circulation is as proerythrocytes. hemocytoblasts. reticulocytes. band forms. myeloid cells.
answer
reticulocytes.
question
The level of erythropoietin in the blood would rise due to all of the following except as a consequence of hemorrhage. anemia. periods of fasting. high altitude. when blood flow to the kidneys is disrupted.
answer
periods of fasting.
question
Most of the iron that is removed from degraded hemoglobin is stored in yellow bone marrow. excreted by the intestines. recycled to the red bone marrow. excreted by the kidneys. excreted by the liver.
answer
recycled to the red bone marrow.
question
Erythropoiesis is stimulated when carbon dioxide levels in the blood decrease. coagulation begins. blood flow to the kidney declines. blood pressure increases. oxygen levels in the blood increase.
answer
blood flow to the kidney declines.
question
In which of the following situations would you expect the blood level of bilirubin to be elevated? low hematocrit during coagulation iron-deficient diet low blood volume an alcoholic with a damaged liver
answer
an alcoholic with a damaged liver
question
In adults, erythropoiesis exclusively takes place in yellow bone marrow. red bone marrow. the liver. lymphoid tissue. the spleen.
answer
red bone marrow.
question
________ are immature erythrocytes that are present in the circulation. Normoblasts Myeloblasts Band cells Erythroblasts Reticulocytes
answer
Reticulocytes
question
Excess iron is stored in the liver and spleen as hemoglobin. transferrin. ferritin. hemosiderin. hemosiderin and ferritin.
answer
hemosiderin and ferritin.
question
Mary is tested for the amount of hemoglobin in her blood. The test results indicate that her hemoglobin level is 16 g/dL of blood. This value indicates that she has fewer red blood cells than normal. her hematocrit is probably lower than normal. she is suffering from anemia. her hemoglobin level is normal. she may be suffering from a form of leukemia.
answer
her hemoglobin level is normal.



