Biology Chapter 12.3: Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer Cells – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
what does the cell cycle appear to be driven by?
answer
specific chemical signals present in the cytoplasm
question
what are the sequential events of the cell cycle directed by?
answer
A Cell cycle control system
question
what is the cell cycle control system regulated by?
answer
Both internal and external controls
question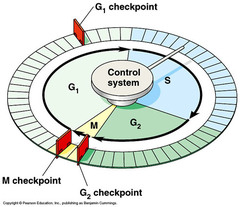
what do checkpoints in the cell cycle do?

answer
these checkpoints are where the cell cycle stops until a go-ahead signal is received
question
what happens if a cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint?
answer
it will usually complete the S, G2, and M phases and divide
question
what happens if the cell does NOT receive the go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint?
answer
it will exit the cycle, switching into the G0 phase.
question
what is the G0 phase?

answer
a nondividing state, where the cell goes when it doesn't receive the go-ahead signal
question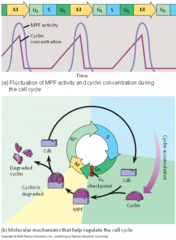
which two types of regulatory proteins are involved in cell cycle control?

answer
cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
question
what does the CDKs activity fluctuate?
answer
because it is controlled by cyclins. cyclins, concentrations vary with the cell cycle
question
What is MPF?
answer
(maturation-promoting factor) -A cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers a cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into the M phase
question
what is an example of an internal signal?

answer
kinetochores not attached to spindle microtubules send a molecular signal that delays anaphase
question
what are some external signals?
answer
growth factor proteins
question
What are released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide?
answer
Growth Factor Proteins
question
what does the PDGF (platelet- derived growth factor) do?
answer
stimulates the division of human fibroblast cells in culture
question
what is a clear example of external signals?
answer
density-dependent inhibition
question
what is density-dependent inhibition?
answer
in which crowded cells stop dividing
question
what do most animal cells exhibit?
answer
anchorage dependence
question
what is anchorage dependence?
answer
in which they must be attached to a substratum in order to divide
question
do cancer cells exhibit density-dependent inhibition or anchorage dependence, like a healthy cell?
answer
no, they're rebels!!
question
do cancer cells respond normally to the body's control mechanisms?
answer
no
question
do cancer cells eed growth factors to grow and divide?
answer
no
question
what do cancers create, to grow and divide?
answer
growth factors
question
what type of cells have an abnormal cell cycle control system?
answer
cancer cells
question
what process converts a normal cell into a cancerous cell?
answer
transformation
question
what do they call the lump, at the original site?
answer
a benign tumor
question
what are benign tumors?
answer
-tumors that do not grow in an unlimited, aggressive manner -doesn't invade surrounding tissues -nor metastasize
question
what do malignant tumors do?
answer
invade surrounding tissues and metastasize
question
what is metastasize?
answer
exporting cancer cells to other parts of the body
question
if a parent cell has 10 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will be in each daughter cell?
answer
10 chromosomes
question
in which stage are chromosomes replicated?
answer
S of interphase
question
what is the purpose of mitosis?
answer
produce new offspring



