Basics Anesthesia Machine – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Wood's Metal
answer
A safety device that melts under excessive heat (;200 degrees F) to allow the gas to escape preventing an explosion
question
Joule Thompson Effect
answer
"Joule is cool" Cooling effect once compressed gas is allowed to escape in open space
question
Adiabatic Heat of Compression
answer
Compression of cylinder contents into a small space generates heats and may cause combustion
question
PSIG numbers
answer
Ó2 - 2200 N2O - 745 Air - 1900
question
USA Colors
answer
Ó2 - Green N2O - Blue Air - Yellow
question
Capacity (L)
answer
Ó2 - 660 N20 - 1590 Air - 625
question
PISS
answer
Ó2 - 2-5 N2O - 3-5 Air - 1-5
question
What is Critical Temperature
answer
The critical value at which a gas is pressured and forms a liquid, low temperature Above critical temperature, gas will remain in gaseous state
question
Critical Temperature of Ó2 and N2O
answer
Oxygen: -119 degrees C N2O: 39.5 degrees C, hence why it's liquid in the tank
question
Celsius and Fahrenheit conversion
answer
Multiply Celsius temp by 9/5 Add 32 degrees Example: convert 37* C to Fahrenheit. 37 * 9/5 = 333/5 = 66.6 66.6 + 32 = 98.6* F
question
Supply failure alarm system
answer
4. Activated when Ó2 falls below 28 psi Alarms sounds before 25 psi, the point at which N2O flow will cease
question
Second stage pressure regulator
answer
5. Gas pressure is decreased to a constant pressure of 16 psi as flow from wall varies at times between 40-50psi After passing 2nd stage pressure regulator, sits in "stand by" at flow control valve
question
Flowmeter safety mechanisms
answer
-Tubes are hand calibrated and no two tubes are alike -Gas specific and are not interchangeable between machines and gases
question
Sequence of flowmeter safety mechanism
answer
Sequence of flowmeter tubes is very important to decrease chance of hypoxic mixture. -Gas flow is from left to right -Ó2 is always to the Right or Downstream of all other gases and closest to the manifold outlet -Any leak in flowmeters will vent other gases out before Ó2. -Decreases the chance that Ó2 will be diluted or lost
question
Flowmeter: Interlink Mechanism /Proportioning System
answer
-Flow valves linked mechanically or pneumatically so Ó2 cannot be set below 25% -Ensures adequate % of Ó2 delivery and prevents hypoxic mixture -Ó2 flow control spindle is connected to the N2O spindle, so that if Ó2 goes down, N2O goes down also, and if N2O goes up Ó2 level will go up also if Ó2 % drops below room air percent
question
Interlink mechanism
answer
-Ó2 spindle is Connected to n2o spindle If you incr. N2O flow then Ó2 flow will incr. If you incr. Ó2 flow; N2O will not incr. If you decr. N2O flow; Ó2 flow will not decr. FYI: -The N2O spindle has 14 teeth -The Ó2 spindle has 29 teeth -So......If you rotate the N2o knob 2.07 times, the Ó2 will rotate once
question
Vaporizers
answer
-Volatile anesthetics are liquids at room temperature and atmospheric pressure -Vaporization is the conversion of liquid to vapor - takes place in a closed container referred to as a vaporizer -The energy necessary for molecules to escape from the liquid to enter the gas phase is supplied as heat -Heat of Vaporization = the number of calories required at a specific temperature to convert 1 G of liquid to vapor
question
Vaporizers are:
answer
-Agent specific, precisely calibrated to compensate to changes in temperature and variations of gas flow -Constructed of metals with high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to flow from the vaporizer in to the anesthetic in the liquid phase, supplying the energy for the heat of vaporization
question
Vaporizer flow pattern
answer
-Ó2 (Ó2 + N2O) enter vaporizer and pass through a filter A relief valve exists which will open if gas flow exceeds that which is required for delivery of gas conc. on dial -Temp. compensating bypass valve exists -Changes in temp are. constant (room & cooling due to vaporization) -Bypass valve will open and allow gas to bypass vaporizer chamber
question
Never tilt the vaporizers beyond
answer
45 degrees If it is tilted, the vaporizer must be drained and dried or gas delivery will be uncertain
question
The vaporizer interlock ensures that
answer
-Only one vaporizer is turned on -Gas enters only the one which is on -Trace vapor output is minimized when the vaporizer is off -Vaporizers are locked into the gas circuit, thus ensuring they are seated correctly.
question
If wrong agent in vaporizer
answer
Most modern vaporizers have agent specific fill devices which virtually eliminate this from happening but,if it does happen, an unknown concentration of gas will be delivered to the patient.
question
Vapor output with wrong vapor in vaporizer
answer
HLH: Higher Vp agent in Lower vp vaporizer chamber = higher concentration delivered. LHL: If lower vp agent is in higher vp vaporizer chamber = lower concentration will be delivered. *If this occurs, must empty, flush with 100% oxygen gas and dry
question
What type of vaporizer is used for Desflurane
answer
TEC 6 vaporizer
question
TEC 6 Vaporizers
answer
-Made specifically for Desflurane -Vapor pressure of Des is 3-4 x's that of other inhaled anesthetics -Boils at approx. 22.8 degrees C -Electrically heated -To approx. 39 degrees C -If not heated the large amounts of desflurane required (d/t MAC value 4-9 x's other IA's) would cause excessive cooling of the vaporizer making conventional temperature compensating mechanism ineffective
question
Breathing system
answer
-The function of any breathing system is to deliver oxygen and anesthetic gases, and eliminate carbon dioxide *CÓ2 washout is accomplished either with adequate fresh gas flow (FGF) or by soda lime absorption (or other neutralizing chemicals.) -The components of the circle system help us avoid the problems of pollution in the O.R. environment, anesthetic agent wastage ; loss of patient heat and humidity caused by the high fresh gas flows required by the Mapleson circuits.
question
2 ways CÓ2 can be washed out
answer
Fresh gas flow or Chemical neutralization of CÓ2
question
APL valve: aka "pop-off valve"
answer
-Limits amount of pressure inside the patient's lungs during manual ventilation -If pressure reaches the setting of the APL knob, the valve opens and allows excess gas to escape to the scavenging system -Turning knob to right (closing) increases the pressure -Turning to left (opening) decreases the pressure
question
Manual ventilation: (i.e. spontaneous, or hand(bag)/mask)
answer
Amount of oxygen flowing to patient is controlled by APL valve
question
APL valve closed when mask ventilating a patient
answer
Pt may receive back pressure related to too much flow built up inside ambu bag. Build up of PEEP. Ambu bag will be over inflated
question
APL valve too open
answer
If too open no pressure will build up within ambu bag. ambu bag will remain deflated and pt will not receive oxygen.
question
CÓ2 absorbents
answer
2 most common types: Soda lime (most common) Baralyme Also Amsorb exsists
question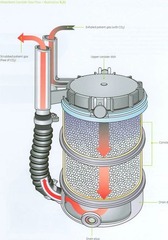
CÓ2 absorbent flow (image)

answer
Turns purple as it becomes exhausted.
question
Mesh size is
answer
A compromise between absorptive capacity and resistance to flow. Do not want mesh size to be too large, so that patient can blow against it. Not too much resistance, not too little. Must be 4-8.
question
Indicator dye
answer
Ethyl violet *note: even exhausted absorbent will turn white if not used and allowed to cool, but will quickly return to purple once heated.
question
Final products of CÓ2 neutralization
answer
Carbonates + Water + Heat
question
Amsorb
answer
More costly Does not form compound A or carbon monoxide
question
Toxic Products
answer
Sevoflurane interacts with strong bases in soda lime or baralyme to form degradation products that are toxic to kidneys in animals in high concentrations Compound A
question
Compound A chemical makeup
answer
Fluoromethyl-2,2,-difuro-1-(trifluromethyl) vinyl ether
question
Factors that increase Compound A
answer
-Total gas flow rates below 1 L/min -Use of baralyme rather than soda lime -High absorbent temperatures (if feel very hot absorbent canister, change it) -High concentration of sevoflurane -Drying of the carbon dioxide absorbent -Fresh soda lime (is very dry initially because it hasn't been dampened yet from use) -Machine on all night -Length of anesthetic
question
Carbon Monoxide formation
answer
-Desflurane, isoflurane ; enflurane with absorbents produces carbon monoxide. *Higher levels with desflurane, then enflurane, then isoflurane* -High concentrations with absorbers that have not been used for 24 hours or ;
question
Factors increasing CO
answer
Use of baralyme rather than soda lime Higher temperatures in absorber Dry absorbent*** High anesthetic concentrations Increase length of time
question
Unidirectional valves are
answer
Inspiration and expiration. On inspiration, inspiratory valve should flutter and on expiration, expiratory valve should flutter
question
Machine selector valve
answer
allows the selection of manual or mechanical ventilation. Isolates Apl valve from rest of system *When pt placed on ventilator mode, APL valve (as a safety mechanism) needs to be left open.
question
Tidal Volume
answer
volume of gas entering or leaving the patient during the inspiratory or expiratory phase time
question
Minute Volume
answer
sum of the tidal volumes in one minute
question
Ventilatory frequency
answer
number of respiratory cycles per minute
question
Inspiratory flow time
answer
the period between the beginning and end of inspiratory flow
question
Inspiratory pause time
answer
Period from the end of inspiratory flow to the start of excitatory flow
question
Inspiratory phase time
answer
period of time between the start of inspiratory flow and the beginning of expiratory flow, or it is the sum of the inspiratory flow time and the inspiratory pause time.
question
Excitatory flow time
answer
time between the beginning and end of expiration
question
Excitatory pause time
answer
Interval from the end of excitatory flow to the start of inspiratory flow
question
Excitatory phase time
answer
Time between the start of expiratory flow and the start of inspiratory flow or it is the sum of the expiratory flow time and the expiratory pause time
question
Inspiratory and expiratory phase time ratio
answer
I:E ratio is the ratio of inspiratory phase time to expiratory phase time. Normal is 1:2
question
Inspiratory flow rate:
answer
volume of gas per unit time that passes from the patient connection of the breathing system to the patient
question
Excitatory flow rate
answer
volume of gas per unit time returned from the patient during the expiratory phase
question
Resistance
answer
pressure difference per unit flow across the airway; it usually increases as flow increases
question
Compliance
answer
ratio of a change in volume to a change in pressure
question
Anesthesia ventilator power source
answer
Compressed gas, electricity or both -Modern "piston ventilators" do not require driving gas, all mechanical and electronic -Contemporary bellows require both
question
Bellows

answer
-the bellows is housed in a chamber and the inside of the bellows is connected to the breathing system. -the bellows separates breathing system gases from driving gas Inside the bellows there is both fresh gas and inspiratory gas
question
Minute ventilation calculated by
answer
MV = TV x RR
question
Two sets of gases
answer
Driving Gas - outside the bellows Patient Gas - inside the bellows
question
Control panel
answer
VT, RR, MV, I:E ratio
question
VT setting
answer
10-15 ml/kg (depending on ETCÓ and PIP)
question
I:E ratio
answer
Uses 1 for the inhalation time and an appropriate number expressing the relative length for exhalation time. Usually start with 1:2
question
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends limiting room concentration of:
answer
N2O : 25 ppm Halogenated agents: 2 ppm Halogenated agents with N2O : 0.5 ppm
question
Scavenger system transfer tubing is
answer
19 or 30 mm, sometimes yellow color-coded
question
Components of the scavenger system
answer
Gas collection assembly Transfer tubing Scavenging interface Gas disposal tubing Gas disposal assembly
question
Scavenging System - active
answer
-Connects to the hospital suction system -Positive ; negative pressure relief valves protects the patient from the negative pressure of the vacuum system and positive pressure of an obstruction in the disposal system -3 liter reservoir bag is present which hold excess gas until it can be removed -Vacuum control valve is adjusted to 10-15 L of waste gas per minute
question
Scavenging system - passive
answer
-Interfaces with the hospital ventilation duct -Relies on the build-up of gases in the bag to passively empty into the hospital ventilation system (passive not very common)
question
Parts of the machine that receive gas at cylinder pressure - high pressure system
answer
Hanger yoke Hanger yoke check valve Cylinder pressure regulator Cylinder pressure gauge *all drop pressure to 45 psi
question
Intermediate pressure system
answer
Receives gases at relatively low and constant pressures (16-55psi/pipeline pressures) -Pipeline inlets and pressure gauges -Ventilator power outlet accessory -Ó2 flush valve -Supply failure alarm system -Second stage pressure regulator -Flowmeter valves *note After pressure relief valve on hanger yolk dropped to 45psi, then intermediate pressure system drops to 16-55psi
question
Low pressure system
answer
Components distal to the flowmeter needle -Flowmeter tubes -Vaporizers -Temperature compensating bypass valve -Common gas outlet *note: Gas from flowmeter to patient
question
Alarms that must remain on
answer
breathing circuit pressure, oxygen concentration, exhaled volume or carbon dioxide (or both).
question
PISS
answer
-Pin Index and Safety System -Used for the hanger yoke system -Prevents misconception of a cylinder to the wrong yoke
question
The Hanger Yoke System is
answer
Where the backup cylinders are in the machine, normally in the back
question
The Hanger Yoke System
answer
-clamping device resists leaks ; contains a filter. -must have a check valve to prevent transfilling ; a cylinder pressure gauge. -There must be cylinder pressure regulators, to reduce the cylinder pressure (2200psi) to 40-45psi. -The machine must use pipeline gas as long as pipeline pressure is greater than 50 psi.
question
Flowmeters
answer
-Single control for each gas -Uniquely shaped oxygen flow control knob -Valve stops (or other mechanism) so that excessive rotation will not damage the flowmeter. -Oxygen must enter the common manifiold downstream of other gases -An oxygen flush is present, capable of 35-75 L/min flow which does not proceed through any vaporizers.
question
Vaporizers safety mechanisms
answer
-Concentration-calibrated -An interlock must be present Avoids 2 gases being. turned on simultaneously -Liquid level indicated, to prevent overfilling -No discharge of liquid anesthetic occurs from the vaporizer even at maximum fresh gas flow
question
Common gas outlet
answer
Only one common gas outlet at 22 mm outer diameter, 15 mm inner diameter, which is designed to prevent accidental disconnection
question
DISS
answer
Diameter Indexing Safety System: Safety mechanism for wall connections
question
Check valve
answer
drops the pressure coming into the machine from the backup cylinder to 40-45 psi and from the wall to 50 psi.
question
Oxygen supply from a central supply source
answer
-Enters machine through a pipeline (wall supply) -Enters at a PSI (pressure per square inch) of 50-55 -Inlets are indexed for specific gas DISS (Diameter Index Safety System) - non-interchangeable connections
question
Check valves are located: upstream or downstream?
answer
downstream (closer to the machine) from the pipeline inlet to prevent reverse flow of gases -thereby avoiding flow of gas from machine to wall supply
question
Cylinder pressure
answer
Cylinder pressure -measured by a bourdon pressure gauge -Ó2 = 2000-2200 psi (multiply by 0.3 to convert psi to Liters) -N2O = 750 psi A cylinder pressure regulator converts cylinder pressure to a constant pressure of ~45 psi downstream of the regulator -This is intentionally slightly less than the pipeline pressure because the machine will use the gas from the source with the higher pressure. This will also help prevent the silent depletion of cylinder contents if a cylinder is inadvertently left open after machine checks
question
Time to Ó2 cylinder exhaustion
answer
-Time to exhaustion is calculated by dividing the remaining Ó2 volume in the cylinder by the rate of Ó2 consumption -Remaining volume in liters (L) in an E cylinder is calculated by dividing the cylinder pressure by 2200 psig then multiplying by 660 L -Example: Cylinder gauge reads 1,000 psig 1000 psig/2200 psig x 660 L 0.45 x 660 = 300 L remaining in the tank *note: If pt is being mechanically ventilated, the machine uses some Ó from the tank to drive the bellows. MV = TV X RR. 2200psi = amount in a full tank.
question
Ó2 consumption during mechanical ventilation
answer
Ó2 flowmeter rate + (minute ventilation) *Example*: -FGF is 0.5 LPM Ó2 ; 1.0 LPM of N2O (total fresh gas flow = 1.5LPM) -Ventilator setting: TV: 0.7 L ; RR: 10 bpm ( 7 LPM) (mv = TVxRR) -0.5 + 7 = 7.5 LPM ( Ó2 Consumption) *Expected time to exhaustion 300 L / 7.5 LPM ~40 minutes remaining (ignoring gas sampled by the gas analyzer and circuit leaks) -Time to exhaustion during non-mechanical ventilation???? LPM/(Liters remaining in tank) e.x. 7.5LPM/300L
question
N2O cylinders
answer
-N20 will read 745 psig until all the liquid in the cylinder has vaporized to gas -It can be assumed that 75% of N2O cylinder gas has been exhausted when a decrease in N20 pressure is observed (Gauge reads ; 745 psig) ***The volume of N2O cylinder cannot be determined based on the psig***



