Atomic Physics – Physics 30 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion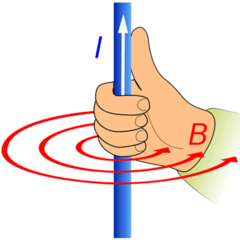
First Hand Rule

answer
thumb - direction of charge flow fingers - curl in direction of magnetic field
question
Second Hand Rule
answer
thumb - points towards magnetic north pole fingers - coil in direction of current
question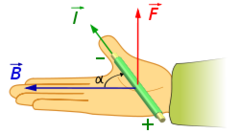
Third Hand Rule

answer
thumb - direction of charge flow extended fingers - point towards SOUTH magnetic pole palm - direction of force
question
Left Hand Rules
answer
Used for electron current
question
Right Hand Rules
answer
Used for conventional current
question
Dalton's Billiard Ball Model
answer
- all matter made of atoms - atoms are smallest particle of matter - atoms are indivisible - atoms of different elements have different properties; can combine in predictable whole number ratios
question
Thomson atomic model experiment
answer
cathode ray tube experiment Proved the existence of sub-atomic particles in an atom. JJ Thompson took a cathode and an anode and placed them into a vacuum tube along with a pin-wheel and a a special screen that glowed green when hit. When Thompson passed electricity through the cathode and anode a ray was emitted on the screen. this ray had mass and was negatively charged.
question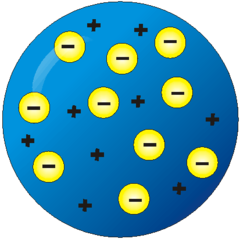
Thomson's Plum Pudding model

answer
free floating negative electrons inside a larger positively charged mass drawback: attraction between unlike charges should cause atom to collapse
question
ruthfords atomic model experiment
answer
"gold foil" experiment This was Ernst Rutherford's experiment that led to the discovery of the nucleus as the small, dense, positively charged center of the atom and the development of the nuclear theory of the atom.
question
Bohr atomic model
answer
Atoms described as electrons orbiting the nucleus at specific energy levels. Eph = ?Ee- = hf = hc/wavelength drawback: could only explain hydrogen emission spectrum, could not explain why moving e- didn't emit EMR
question
Rutherford's Planetary Model
answer
Rutherford said that electrons move around a small nucleus just like planets orbit the sun drawback: attraction between unlike charges should cause atom to collapse
question
relationship between frequency wavelength and energy
answer
The greater the energy, the larger the frequency and the shorter (smaller) the wavelength. Given the relationship between wavelength and frequency — the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength — it follows that short wavelengths are more energetic than long wavelengths.
question
how does frequency, wavelength and energy form the electromagnetic (light) spectrum
answer
right side has bigger wavelengths but less enery the left side has smaller wavelengths and more energy and it has a higher frequency
question
how does the atom absorbs specific light energies
answer
ground state-the lowest energy state of an atom or other particle. excited state-higher in energy than the ground state, moves up in rings
question
de Broglie's hypothesis
answer
if waves can behave like particles, then particles can behave like waves
question
electron diffraction experiment
answer
performed by Germer + Davisson and GP Thomson, provided evidence that particles could exhibit wavelike properties
question
de Broglie atomic theory
answer
- electrons are circular standing waves around nucleus - electrons exist at locations of constructive interference and orbitals where the circumference is equal to whole number multiples of de Broglie wavelengths - electrons acting as waves don't emit EMR
question
Schrodinger's Quantum Mechanical Model
answer
- electron cloud - region with high probability of finding an electron - limit to # of e- in each orbital
question
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
answer
it is impossible to know exactly both the momentum and the position of a particle at the same time
question
Dirac
answer
predicted existence of anti-matter
question
nucleons
answer
term that describes protons and neutrons
question
isotopes
answer
atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
question
strong nuclear force
answer
the powerful attractive force that binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus idenpendent of charge
question
nuclear mass defect
answer
the mass of every atom is measurably less than the total mass of its individual particles ?m = m (nucleons) - m (nucleus)
question
mass-energy equivalence
answer
calculates energy lost in mass defect (converted to Ek of neutrons and nuclei or E of gamma photons)
question
nuclear binding energy
answer
- the energy required to decompose an atomic nucleus into its component protons and neutrons - energy released when protons and neutrons come together to form atom
question
radioactivity
answer
The process in which some substances spontaneously emit radiation (in form of EMR waves, charged particles, or uncharged particles)
question
Becquerel (Bq)
answer
Measures the rate at which a sample of radioactive material decays (1Bq = 1 emission (or decay) per second)
question
Geiger counter
answer
instrument that measures radiation output
question
factors that determine radiation strength
answer
- type - amount - activity (amount of radiation produced over time)
question
increase safety around radiation
answer
- less exposure time - more distance between people and source - more shielding
question
biological effects of radiation
answer
- break chemical bonds - cell damage + mutation
question
alpha particle properties
answer
- penetrating ability: paper - energy level: low - ionization ability: high - hazard level: low
question
beta particle properties
answer
- penetrating ability: cardboard - energy level: low - ionization ability: moderate - hazard level: low
question
gamma particle properties
answer
- penetrating ability: lead - energy level: high - ionization ability: low - hazard level: high
question
unstable nuclides
answer
- have too few neutrons in relation to protons - tend to disintegrate - all atomic #s greater than 82 refer to these
question
conservation laws that apply to all nuclear processes
answer
- conservation of charge, nucleons, momentum, and mass-energy
question
top numbers in nuclear equations obey...
answer
law of conservation of nucleons
question
bottom numbers in nuclear equations obey...
answer
law of conservation of charge
question
alpha decay
answer
alpha particles emitted in this decay
question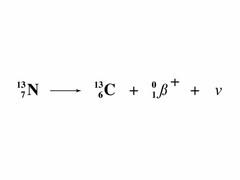
beta positive decay
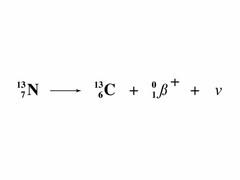
answer
positrons emitted in this decay Note: massless and chargeless NEUTRINOs produced
question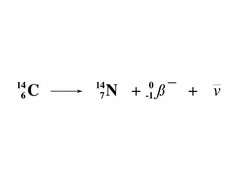
beta negative decay
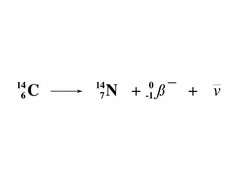
answer
negative electrons emitted in this decay Note: massless and chargeless ANTI-NEUTRINO produced
question
gamma decay
answer
emission of high E photon in this decay no transmutation occurs Note: gamma photon is massless and chargeless
question
when radiation separated using electric or magnetic fields...
answer
alpha particle - less curvature than beta beta particle - greatest curvature gamma particle - no curvature
question
factors that affect radioactivity
answer
- mass of sample (more sample, more ____ ) - half-life these are factors affecting ___
question
half-life
answer
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay (refer to diagrams in booklets)
question
half-life decay equation
answer
N = N0(1/2)^n N = amount of radioactive nuclei remaining N0 = original amount of sample n = number of half-lives
question
number of half-lives equation
answer
n = t/t(1/2) t = time of decay = age t(1/2) = half-life
question
decay series
answer
a sequence of successive radioactive decays that proceeds until a stable nuclide is reached
question
radioactive dating
answer
measurement of the amount of radioactive material (usually carbon 14) that an object contains C-14 half-life = 5730 years - cannot be used for objects older than 60,000 years old U-238 half-life = 4.5 billion years
question
all elements beyond this are artificial and unstable
answer
uranium
question
artificial transmutation
answer
creating new elements (usually in particle accelerator)
question
nuclear fission
answer
The process by which a large nucleus is split into smaller nuclei through a collision with a slow-moving neutron
question
controlled vs uncontrolled fission reactions
answer
nuclear weapons vs nuclear power plants (demonstrates ___ )
question
nuclear power plant moderator
answer
material (usually heavy water containing deuterium) that slows down high E neutrons emitted from fission reactions to sustain chain reaction
question
nuclear power plant control rod
answer
between fuel rods, absorbs neutrons, prevents overheating
question
advantages of nuclear power
answer
- extremely high energy density - easy to trigger
question
disadvantages of nuclear power
answer
- radioactive waste - gamma shielding required - non-renewable
question
nuclear fusion
answer
The process by which two or more small nuclei fuse to make a bigger nucleus powers the stars and hydrogen bombs
question
nuclear fusion releases energy because...
answer
binding energy per nucleon greater than that of original nuclei
question
as binding energy per nucleon increases...
answer
as the stability of the nucleus increases... (refer to diagrams in booklet)
question
- factors that allow the sun to facilitate fusion reactions
answer
- high temp., high atom speed, overcome electrostatic repulsive forces, strong nuclear force binds atoms together
question
- factors that allow fusion reactors on earth to work
answer
precise and strong magnetic fields overcome coulomb's force
question
bubble chamber
answer
Ek of passing charged particles causes superheated liquid to boil, leaving tracks in this device
question
cloud chambers
answer
moving charges cause gas condensation, leaving tracks in this device
question
analyzing particle tracks
answer
- radii (lighter curves more than heavier) - charge - positive and negative curve in opposite directions (3rd hand rule) - neutral particles don't leave tracks - pair production (electron and positron produced by high E photon) refer to diagrams
question
alpha particle track
answer
this particle track is: - broad - (+) charge
question
proton particle track
answer
this particle track: - curves more than alpha, less than beta - (+) charge
question
beta particle track
answer
this particle track: - curves the most - (+) or (-) charge
question
as particles spiral in tracks...
answer
as particles in detection chambers lose energy..
question
all equations from particle accelerators apply to...
answer
all equations from mass spectrometers apply to...
question
energy of cosmic rays in the range of...
answer
10^2 - 10^14 MeV energy range for ___ rays
question
cyclotron
answer
protons speed up across gap max speed at exit Eki = Ekf + Ep Fc = Fm
question
standard model
answer
the current theoretical model that describes the fundamental particles and forces in nature
question
leptons
answer
- don't interact with strong nuclear force -relatively small - mass, but no internal structure
question
hadrons
answer
- don't interact with strong nuclear force -relatively large
question
mesons
answer
- middle mass
question
baryons
answer
- large mass
question
fermions
answer
- half integer spin
question
bosons
answer
- whole integer spin - move between quarks and leptons to produce fundamental forces
question
quarks
answer
- discovered by Taylor - high E e- directed at protons, scattering patterns = unequal distribution of charge - 3 of each can make up a proton or neutron - fractional charges - cannot be isolated
question
up quark
answer
+2/3 charge 1.5-4 MeV/c^2
question
down quark
answer
-1/3 charge 4-8 MeV/c^2
question
protons are made of...
answer
2 up, 1 down quarks
question
neutrons are made of...
answer
1 up, 2 down quarks
question
1. strong nuclear (within nucleus) force carrier
answer
gluon
question
2. electromagnetic (infinite) force carrier
answer
photon
question
3. weak nuclear (between quarks) force carrier
answer
W and Z bosons
question
4. gravity (infinite) force carrier
answer
graviton
question
strengths of the standard model
answer
- experiments support predictions - electron scattering verifies quark's existence - organizes subatomic particles - incorporates special relativity - predicted W and Z bosons
question
weaknesses of the standard model
answer
- doesn't explain different size and mass of particles - doesn't account for gravity - doesn't work with general relativity - doesn't reveal necessity of 2nd and 3rd gen. particles - matter and anti-matter discrepancy



