Flashcards on Art History Vocabulary
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Neolithic

answer
relating to or denoting the later part of the Stone Age, when ground or polished stone weapons and implements prevailed.
question
Paleolithic

answer
relating to or denoting the early phase of the Stone Age, lasting about 2.5 million years, when primitive stone implements were used.
question
Megalithic

answer
relating to or denoting prehistoric monuments made of or containing megaliths
question
Representational
answer
Any art that attempts to depict an aspect of the external, natural world in a visually understandable way.
question
Abstract
answer
Art that does not attempt to describe the appearance of visible forms but rather to transform them into stylized patterns or to alter them in conformity to ideals.
question
Sculpture in the round

answer
Three-dimensional sculpture that is carved free of any background or block.
question
Relief sculpture

answer
A sculpted image or design whose flat background surface is carved away to a certain depth, setting off the figure(s).
question
Circa
answer
(often preceding a date) approximately.
question
Dolmen

answer
A prehistoric structure made up of two or more large (often upright) stones supporting a large, flat, horizontal slab or slabs.
question
Passage tomb or passage grave

answer
A prehistoric tomb under a cairn, reached by a long, narrow, slab-lined access passage or passageways.
question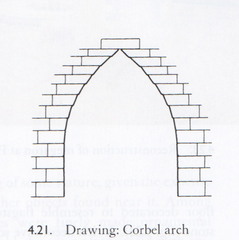
Corbel arch

answer
Arch or vault formed by courses of stones, each of which projects beyond the lower course until the space is enclosed; usually finished with a capstone.
question
Posts

answer
Two uprights
question
Lintels

answer
A horizontal element
question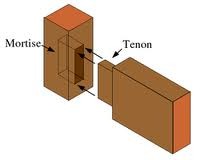
Mortise and tenon joint

answer
pieces that fit like a lego
question
Stele

answer
An upright stone slab decorated with inscriptions or reliefs.
question
Hierarchic Scale
answer
The use of differences in size to indicate relative importance.
question
Ziggurat

answer
A tall stepped pyramidal structure of earthen materials, often supporting a shrine.
question
Cuneiform
answer
An early form of writing with wedge-shaped marks impressed into wet clay with a stylus; used primarily by ancient Mesopotamians
question
Inlay
answer
A decorative process in which pieces of one material are set into the surface of an object fashioned from a different material.
question
Votive

answer
An image created as a devotional offering to a god or other deity.
question
Register
answer
A device used in systems of spatial definition.
question
Cylinder Seal

answer
A small cylindrical stone decorated with incised patterns.
question
Mastaba

answer
A flat-topped, one-story building with slanted walls over an ancient Egyptian undeground tomb.
question
Necropolis

answer
A large cemetery or burial area, literally "city of the dead"
question
Pylon

answer
A massive gateway formed by a pair of tapering walls of oblong shape.
question
Hypostyle Hall

answer
A large interior room characterized by many closely spaced columns that support its roof.
question
Filigree

answer
Delicate decoration with fine wires
question
Granulation
answer
A technique for decorating gold in which tiny balls of the precious metal are fused to the main surface in a pattern
question
Repousse

answer
A technique of pushing or hammering metal from the back to create a protruding image.
question
Niello

answer
A metal technique in which a black sulfur alloy is rubbed into fine lines engraved into a metal. When heated, the alloy becomes fused with the surrounding metal and provides contrasting detail.
question
Corbel Arch

answer
Arch or vault formed by courses of stones, each of which projects usually finished with a capstone.
question
Dressed Stone

answer
Highly finished, precisely cut blocks of stone laid in even courses, creating a uniform face with fine joints. Often used as a facing on the visible exterior of a building, especially as a veneer for the facade.
question
Black Figure

answer
A technique of ancient Greek pottery in which black figures are painted on a red clay ground.
question
Red Figure

answer
A technique of ancient Greek ceramic painting in the sixth and fifth centuries BCE. Characterized by red-clay-colored figures reserved on s black background.
question
Caryatid

answer
A sculpture of a draped female figure acting as a column supporting an entablature.
question
Contrapposto

answer
An Italian term meaning "set against," used to describe the Classical convention of representing human figures with opposing alternations of tension an relaxation on. either side of a central axis to imbue figures with a sense of the potential for movement.
question
Peristyle Colonnade
answer
A surrounding colonnade in Greek architecture. A peristyle building is surrounded on the exterior by a colonnade.
question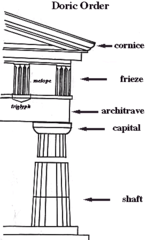
Doric Order

answer
The column shaft of the Doric Order can be fluted or smooth-surfaced and has no base. The Doric capital consists of an undecorated echinus and abacus. The Doric entablature has a plain architrave, a frieze with metopes and triglyphs, and a simple cornice.
question
Ionic Order

answer
The columns have a base, a fluted shaft, and capital decorated with volutes. The entablature consists of n architrave of three panels and moldings, a frieze usually containing sculpted relief ornament, and a cornice with dentils.
question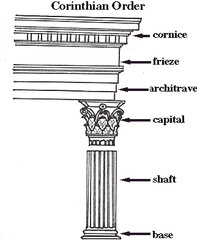
Corinthian Order

answer
Includes a base, a fluted column shaft with a capital elaborately decorated with acanthus leaf carvings. Its entablature consists of an architrave decorated with moldings, a frieze often containing sculptured reliefs, and a cornice with dentils.
question
Pediment
answer
A triangular gable found over major architectural elements such as Classical Greek porticoes, windows, or doors.
question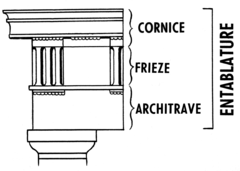
Entablature

answer
The horizontal elements above the columns and capitals.
question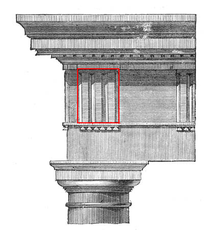
Triglyph

answer
Rectangular blocks between the metopes of a Doric frieze.
question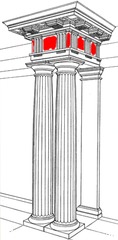
Metope

answer
The carved, painted, or plain rectangular spaces between the triglyphs of a Doric frieze.
question
Shaft
answer
The main vertical section of a column and the base, usually circular in cross section.
question
Capital

answer
The sculpted block that tops a column.
question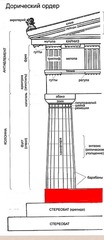
Stylobate

answer
In Classical architecture, the stone platform on which a temple stands
question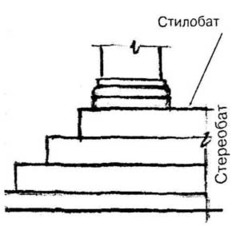
Stereobate

answer
The series of steep steps that form a platform for Greek temples.
question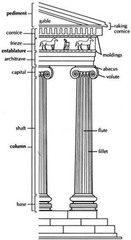
Fluting

answer
Shallow concave grooves running vertically on the shaft of a column, pilaster, or other surfaces.
question
Aqueduct
answer
A trough to carry flowing water supported, if necessary, by arches
question
Engaged Columns

answer
Columns attached to the wall.
question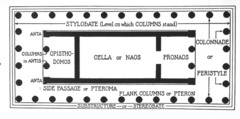
Cella/Naos

answer
The principal interior room in a Greek or Roman temple within which the cult statue was usually housed.
question
Cameo

answer
A low-relief carving on a semiprecious stone or gemstone.
question
Coffer

answer
A recessed decorative panel that is used to reduce the weight of and to decorate ceilings or vaults.
question
Modeling
answer
In painting, the process of creating the illusion of three-dimensionality by the use of highlights and shading.
question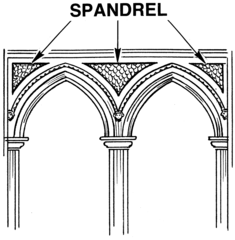
Spandrel

answer
The area of wall adjoining the exterior curve of an arch between its springing and the keystone, or the area between two arches, as in an arcade
question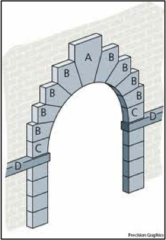
Keystone

answer
The topmost voussoir at the center of an arch, and the last block to be placed. The pressure of this block holds the arch together. Often of a larger size than the other voussoirs and/or decorated.
question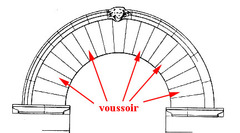
Voussoirs

answer
The oblong, wedge-shaped stone blocks used to build an arch.
question
Springing
answer
The start of the arch.
question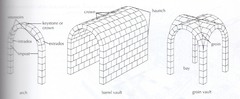
Impost

answer
A block imposed between the top of a pier or above the capital of a column in order to provide extra support at the spring of the arch.
question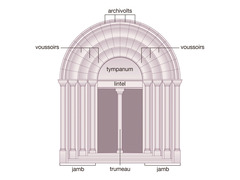
Jamb

answer
In architecture, the vertical element found on both sides of a door or an opening in a wall, often supporting an arch or lintel
question
Basilica

answer
A type of building used throughout Roman Empire for civic public functions.
question
Nave
answer
Big aisle in the middle of basilica
question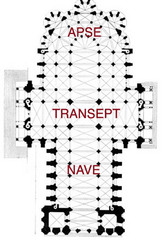
Apse

answer
A large semicircular or polygonal niche protruding from the end wall of a building.
question
Colonnade

answer
A row of columns, supporting a straight lintel or a series of arches.
question
Clerestory

answer
Ceiling that goes higher than side aisles, usually with open space that allows light to come into building.
question
Catacomb
answer
An underground cemetery consisting of tunnels of different levels, having niches for burials, urns, and sarcophagi, and often incorporating rooms.
question
Loculus

answer
A recess in an ancient catacomb or tomb, where a body or cinerary urn was placed.
question
Cubiculum

answer
A small private room for burials in the catacombs.
question
Narrative Image
answer
A picture the recounts an event drawn from a story, either factual or fictional. In a continuous narrative, multiple scenes from the same story appear within a single compositional frame.
question
Iconic Image
answer
A picture that expresses or embodies an intangible concept or idea
question
Mosaic

answer
Images formed by small colored stone or glass pieces affixed to a hard, stable surface.
question
Spolia

answer
A repurposed building stone for new construction, or decorative sculpture reused in new monuments, is the result of an ancient and widespread practice whereby stone that has been quarried, cut, and used in a built structure, is carried away to be used elsewhere.
question
Marble revetment/veneer
answer
In architecture, the exterior facing of a building, often in decorative arts, a thin exterior layer of finer material laid over less valuable material.
question
Diptych
answer
Two panels of equal size, usually decorated with paintings or reliefs and hinged together.
question
Iconoclasm
answer
The banning and/or destruction of icons and religious images.
question
Encaustic
answer
A painting medium using pigment suspended in hot wax.
question
Sanctuary/Choir
answer
The section of a Christian church reserved for the clergy, monks, or nuns, either between the transept crossing and the apse or extending into the nave-separated from the rest of the church by screens or walls and fitted with stalls.
question
Reliquary
answer
A container, often made of a precious material, used as a repository for sacred relics.



