AP Gov: Unit 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
single-issue groups

answer
political campaigning or political support based on one essential policy area or idea
question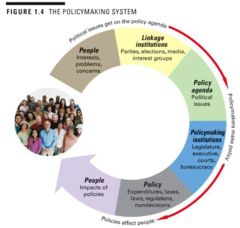
policymaking system

answer
the act of creating new laws or setting standards for a government or business
question
linkage institutions

answer
a structure within society that connects people to the government: elections, political parties, interest groups, media
question
policy agenda

answer
a set of issues and policies laid out by political groups as well as topics under discussion by a governmental executive, or a cabinet in government that tries to influence current and near-future political news and debate
question
policymaking institutions

answer
develop rules that conflicts within society are to abide by (laws, policies): legislative, executive, courts, bureaucracy
question
public policy

answer
a choice that government makes in response to a political issue; a policy is a course of action taken with regard to some problem
question
popular sovereignty
answer
the principle that the government's authority is created and sustained by the consent of its people, through their elected representatives, who are the source of all political power
question
direct democracy

answer
a form of democracy where the people decide on policy initiatives directly
question
indirect democracy

answer
citizens elect representatives to make laws on their behalf
question
majority rule

answer
the making of binding decisions by a vote of more than one-half of all people who participate in an election
question
minority rights

answer
normal individual rights that are applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic, or sexual minorities; and also the collective rights given to minority groups
question
pluralist theory

answer
power is distributed among many groups; for example, groups of like-minded people, unions, professional associations, and business lobbyists
question
elite & class theory

answer
small minority; consisting of members of the economic elite and policy-planning networks, holds the most power (independent of a state's democratic elections process)
question
hyperpluralism

answer
government attempts to represent or meet the needs of too many different groups, and they inevitably end up favoring one group over another, which disrupts democracy
question
policy gridlock

answer
difficulty of passing laws in a legislature because the votes for and against a proposed law are evenly divided, there is no majority
question
individualism

answer
moral, political or social outlook that stresses human independence and the importance of individual self-reliance and liberty
question
unitary government
answer
system of political organization in which most or all of the governing power resides in a centralized government
question
confederation
answer
group of nations or states, or a government encompassing several states or political divisions, in which the component states retain considerable independence
question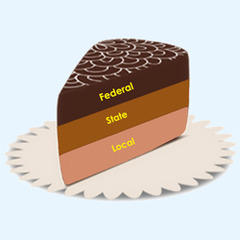
federalism (federal system of government)

answer
power is shared between the federal government and state governments
question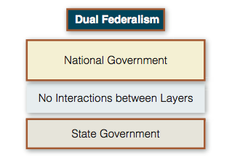
dual federalism

answer
the concept that the national government and the state governments have sovereign power in their respective spheres of authority
question
cooperative federalism

answer
concept that the state governments, local governments, and the federal government share responsibility in the governance of the people
question
fiscal federalism

answer
idea that, acting under some federal constraints, states should set their own economic policies rather than follow directives from the central government
question
New Federalism

answer
the transfer of certain powers from the United States federal government back to the states
question
supremacy clause

answer
establishes the United States Constitution, federal statutes, and treaties as "the supreme law of the land"
question
McCulloch v. Maryland

answer
Maryland was trying to tax the national bank and Supreme Court ruled that federal law was stronger than the state law (necessary and proper clause)
question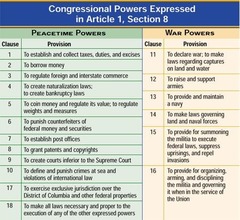
enumerated powers

answer
Congress may exercise the powers that the Constitution grants it, subject to the individual rights listed in the Bill of Rights
question
implied powers

answer
powers not explicitly named in the Constitution but assumed to exist due to their being necessary to implement the expressed powers that are named in Article I
question
elastic clause

answer
a statement in the U.S. Constitution (Article I, Section 8) granting Congress the power to pass all laws necessary and proper for carrying out the enumerated list of powers
question
Gibbons v. Ogden

answer
1824 case in which the Supreme Court ruled that states could not regulate commerce on interstate waterways
question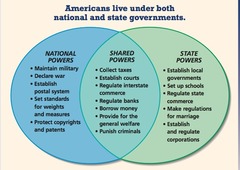
concurrent powers

answer
powers that are shared by both the State and the federal government; powers may be exercised simultaneously within the same territory and in relation to the same body of citizens: regulating elections, taxing, borrowing money, and establishing courts
question
inherent powers

answer
the President derives these powers from the loosely-worded statements in the Constitution that "the executive Power shall be vested in a President" and the president should "take care that the laws be faithfully executed"
question
reserved powers

answer
powers which under the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution are reserved to the states or the people; these are sometimes said to be "states' rights"
question
categorical grants

answer
grants, issued by the United States Congress, which may be spent only for narrowly defined purposes; main source of federal aid to state and local government, can be used only for specific purposes and for helping education or categories of state and local spending (strict provisions on the way it is to be spent)
question
block grants

answer
a large sum of money granted by the national government to a regional government with only general provisions as to the way it is to be spent
question
formula grants

answer
grants-in-aid in which a formula is used to determine the amount of federal funds a state or local government will receive
question
project grants

answer
grant programs in which states submit proposals for projects to the federal government and the national government chooses which to fund on a competitive basis
question
mandates

answer
the authority granted by an electorate to act as its representative
question
Define government and identify the functions that governments perform. What is the role of politics in government?

answer
-the system of people, laws, and officials that define and control the country that you live in -to establish justice, to ensure domestic tranquility, to provide for the common defense, to promote the general welfare, and to secure the blessings of liberty -politics decides how the government's power should be used
question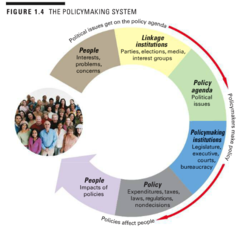
What are the principal components of the policymaking system? Explain how a political issue travels through the policymaking system by using an example.

answer
1. recognizing the problem 2. agenda setting 3. formulating the policy 4. adopting the policy 5. implementing the policy 6. evaluating the policy -ex: muckrakers and concerned citizens brought up unethical practices in the food and medicine industries pressing the government to take action; result: legislation such as the Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 --> led to creation of Food and Drug Administration
question
What is the definition of democracy? What are the basic principles of traditional democratic theory?

answer
-system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives -equality in voting, effective participation, enlightened understanding, citizen control of the agenda, inclusion, majority rule, minority rights, representation
question
Compare, contrast, and critically evaluate the three theories of American democracy: pluralist theory, elite & class theory, and hyperpluralism.

answer
-pluralist: interest group activity brings representation to all (provides key link between people and government, groups compete, no one group is likely to become dominant, groups play by "rules of the game," groups weak in one resource can use another) -elite: a few groups, primarily the wealthy, have most of the power (groups unequal in power, most power held by largest corporations, corporate elites prevail when it comes to big decisions) -hyperpluralism: too many groups are getting too much of what they want, resulting in government policy that is often contradictory and lacking in direction (groups become too powerful in political process as government tries to aid every interest, trying to please each group results in confusing policy)
question
In what specific ways did the philosophy of John Locke influence the origins of the American national government & the Declaration of Independence?

answer
-three branches of government, separation of powers -protect individual rights, government serves the people -government protect others' liberties: property
question
What philosophical views did the delegates to the Constitutional Convention share? How did they influence the nature of the Constitution?

answer
-wanted to create new government instead of fixing the old one -new government would have all the powers of the Confederation Congress, plus additional powers over the states -voted on the Virginia plan and signaled their approval for it, then began to modify it -division of the legislature from the executive and judiciary was a natural and uncontested point -division of the legislature into an upper and lower house wasn't questioned either -executive function had to be independent of the legislature -president should choose judges and the Senate confirm them -mechanism to invalidate bad laws by congress: executive veto -vice president: to provide the president a successor if he was unable to complete his term -Three-Fifths Compromise -the house would elect the president if no candidate had an electoral college majority
question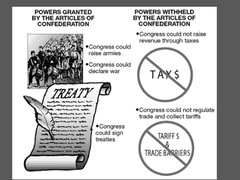
How did the colonial experience shape the policy agenda at the Constitutional Convention? What issues comprised the agenda and how were they resolved?

answer
-needed to address problems of weak central government that existed under Articles of Confederation (which was written so loosely due to British government having too much power during the colonial era) -coastal states and states along the Mississippi wanted to continue trade with foreign nations but other states were skeptical -Constitution established federal government with more specific powers, including those related to relations with foreign governments (President acquired authority to conduct foreign relations) -government that relied upon a series of checks and balances by dividing federal authority between the Legislative, the Judicial, and the Executive branches of government (to resolve foreign trade and debt issues)
question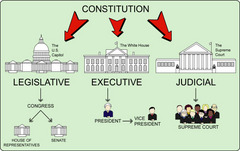
What is the Madisonian model of government? How is it reflected in the structure of American government? What issues or problems does it raise?

answer
-a structure of government in which the powers of the government are separated into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial - proposed this governmental scheme so that one branch would not accumulate enough power to influence the others (or, in the worst case, become dominant) -some believe it's an inefficient form of government because it takes so long for change to occur and responses to pressing concerns are not immediate enough
question
What are the advantages and disadvantages of federalism for democracy? Give examples to illustrate your answer.

answer
-advantages: fosters state loyalties, practices pragmatism, creates laboratories of democracy (during 1990s, Wisconsin governor Tommy Thompson experimented with welfare policy, those experiments influenced federal welfare reform), leads to political stability, encourages pluralism, ensures separation of powers and prevents tyranny -disadvantages: prevents creation of a national policy, leads to a lack of accountability, citizen ignorance
question
How and why has federalism contributed to the growth of the national government?

answer
-the United States moved from a system of dual federalism to one of cooperative federalism in which the national and state governments share responsibility for public policies -the strength of the national government has grown over that of the states because most problems and policies today require the authority and resources of the national government



