Anesthetic Machine and Equipment – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion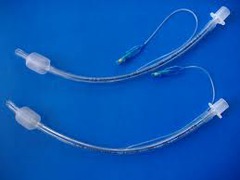
Endotracheal tubes are used for

answer
Used to deliver anesthetic gas from the breathing circuit to the patient's lungs.
question
Composition of ET tubes
answer
Polyvinyl chloride Red rubber (sucks because it absorbs disinfectants) Silicone rubber
question
Types of ET tubes
answer
Murphy - has eye, beveled patient end Magill - Beveled patient end, no eye Cole - Distal end is smaller then the proximal end
question
Internal diameter in mm of ET tubes
answer
Dogs - Size 5 to 14 mm Cats - Size 3 to 4.5 mm
question
Stylet and ET tubes
answer
Is kept within lumen of tube/ plastic coated wire, provides rigidity.
question
Laryngoscope
answer
Holds tongue and epiglottis. Beneficial when visualization of larynx is hard
question
Anesthesia Machine
answer
Designed to deliver a volatile gaseous anesthetic using a carrier gas (o2) to and from a patient by means of a circuit of corrugated tubing. Liquid anesthetic gas must be vaporized mixed with O2 and given to patient
question
Color codes of gas tanks
answer
Green - O2 oxygen Blue - N20 Nitrous Oxide
question
"E" Gas tanks
answer
Small attached to machines. Contains 660 L of O2, PSI of full tank is 1900 to 2200
question
"H" gas tanks
answer
Contains 6900 L of O2, PSI of full tank 1900 to 2200
question
Nirtrous Oxide gas tanks
answer
Is both liquid and gas in tank, PSI is constant 750 until tank is empty.
question
Formula for "E" size O2 tank
answer
Multiply PSI by 0.3 = liters remaining in tank
question
Formula for "H" size O2 tank
answer
Multiply PSI by 3.0 = liters remaining in tank
question
Yoke
answer
Facilitates tank attachment.
question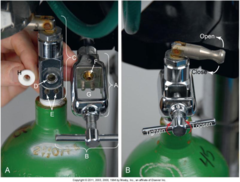
Pin index system

answer
Cannot attach wrong tank
question
Tank Pressure Gauge

answer
Indicates pressure of gas remaining in tank. Change tank when pressure drops to 100 to 200 PSI
question
Pressure reducing Valve
answer
Pressure regulator. Reduces pressure of gas as it leaves tank and enters machine. Safe pressure for machine. Reduces to 50 to 75 PSI
question
Flowmeter

answer
Sets the gas flow rate (O2). PSI is further reduced to 15 PSI.
question
Vaporizer
answer
Converts liquid anesthetic to a vapor state. Adds it to the carrier gas. If no carrier gas if flowing, no anesthetic is delivered. Isoflurane and Sevoflurane
question
Indicator window
answer
Allows visualization of amount of anesthetic in vaporizer.
question
Precision Vaporizers

answer
Delivers an exact concentration of anesthetic as selected. In % concentrations.
question
Types of filler systems
answer
1. Keyed filler Systems 2. Funnel Filler systems
question
Non- precision vaporizers
answer
Ohio No. 8 - glass jar and wick Dial settings unrelated to concentration of gas delivered.
question
VOC
answer
Vaporizer out of circuit. Not within breathing circuit. precision
question
VIC
answer
Vaporizer in circuit. withing breathing circuit. non precision
question
Factors that influence vaporizer form
answer
Temperature /carrier gas flow rate/ back pressure and respiratory rate/depth
question
Breathing Circuit
answer
System that carries anesthetic and oxygen from vaporizer via the fresh gas inlet to patient and conveys expired gases away from patient.
question
Re-breathing system
answer
Circle system. Semiclosed or closed.
question
Fresh gas inlet

answer
Where the carrier gas and anesthetic gas enter the breathing circuit.
question
Inspiratory breathing tube
answer
Conducts gases from the inspiratory one way valve to the patient attachement. Y tubes. . Small animal - 22 mm
question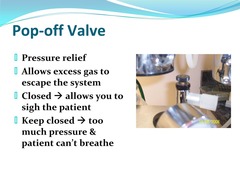
Pop off Valve

answer
Safety feature of a circle system. Allows excess gas to exit the anesthetic circuit and enter the scavenging system. Prevents build up of excessive pressure within circuit.
question
Pop off valve is normally open except when
answer
bagging or breathing for the patient
question
Reservoir Bag

answer
Verifies ET tube potency. Allows for monitoring of respiration. Minimum size of bag is 6 times the patients tidal volume. Keep 3/4 full during anesthesia
question
Canister for CO2 absorbent

answer
Removes C02 from expired gases. Uses soda lime or barium hydroxide lime as absorbent. Absorbent must be fresh and functional to prevent re-breathing of CO2
question
CO2 Absorbent
answer
Color indicators shows when it has been exhausted. Changes from white to purple. Change when 1/3 to 1/2 absorbent color changes. Approx. 6-8 hours of use
question
Oxygen Flush Valve

answer
Allows O2 to bypass the flowmeter and vaporizer and enter the machine delivering directly to the breathing circuit. Flow is 35 to 75 L a minute. Can be used to dilute anesthetic in system/ fill a bag.
question
When do we no use the oxygen flush valve
answer
With non- rebreathing system/ disconnect from patient before using
question
Pressure Manometer

answer
Measures the pressure of the gases within the breathing system. Also indicating pressure withing lungs. Expressed in cm of H20/ mm of mercury. Pressures over 15 cm of H20 (11 mm of HG) indicate buildup of air within the machine.
question
When bagging a healthy animal...
answer
Don't go over 15 cm H20/ higher pressures needed for open chest and GDV
question
Negative pressure relief valve
answer
Designed to open and admit room air to the circuit if a negative pressure is detected in the circuit. May be due to: too active scavenge, O2 flow rate too low, tank runs out of O2.
question
Scavenger System
answer
Keeps excess gas waste from the operating room environment. Can be active or passive
question
Non- rebreathing circuit
answer
Non circle system. Semi-open system. Little or no expired gases are recirculated to the patient. High gas flows help to dilute CO2
question
Examples of non-rebreathing circuit and whom you would use it for
answer
Use of patients weighing 15 pounds or less. Bain, Modified Jackson, Ayres T piece, Norman Mask elbow. Use smaller diameter tubes to carry gases to patient
question
Carrier Gas flow rates
answer
Usually oxygen alone, but may be a mix. Based on patients weight, type of system being used, phase of anesthetic procedure.
question
Classification of Breathing Systems
answer
open - Non rebreathing, non circle, Ex is induction chamber Semi open- Non rebreathing, non circle, Bain and modified jackson Semi Closed- Partial rebreathing, circle system. Closed- Total rebreathing, circle system
question
Gas flow for rebreathing circuit
answer
Partial rebreathing semi closed. For patients greater then 15 pounds. Induction: 50-100 ml/kg/min. Maintenance: 20-40 ml/kg/min. and Recovery is the same as maintenance
question
Gas flow for non-rebreathing
answer
For patients less then 15 pounds. Induction: 2-3 x the maintenance flowrate Maintenance: Bain- 150 to 200 ml/kg/min for other systems: 400 to 600 ml/kg/min Recovery: Same as maintenance
question
Care and use of CO2 canister
answer
Fill canister 1/3 full, tap out dust, another 1/3, tap out dust/ last 1/3 and tap. Leave about 1/2 inch at top for air circulation.
question
Gas flow for total rebreathing circuit
answer
Total rebreathing/ closed. Maintenance is 5 to 10 ml/kg/min. Do not use nitrous oxide in a closed system
question
Gas flow for open systems
answer
Chamber 5L/ min. Mask 300 ml/kg/min or 30 x tidal volume 1-3 L/ min for animals less then 10 kg 3-5 L/min for animals more then 10 kg



