Androgen Drugs – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What drugs have androgenic actions?
answer
Testosterone Methyltestosterone Oxymetholone
question
Testosterone is converted to what?
answer
DHT which is the active form
question
how is testosterone transported in the blood?
answer
SHBG -- protein bound
question
What places make testosterone
answer
MOST 95% in leydig cells of testes rest is in the adrenal glands (Zona reticularis) and some in the ovary
question
Testosterone is made from what ?
answer
Progesterone and DHEA
question
how is testosterone replacement admin?
answer
I.M. NOT by oral b/c of significant first pass effect
question
What are testosterones used for replacement?
answer
Testosterone Proprionate (short acting) Testosterone enanthate Testosterone cypionate (long acting)
question
how is methyltestosterone admin?
answer
oral or buccal admin
question
What is methyltestosterone used for?
answer
Hypogonadism -- replacement therapy Delayed puberty Breast cancer --- antagonist vs. estrogen
question
how is oxymetholone admin?
answer
Oral
question
What was oxymetholone used for?
answer
anemia --- but been replaced by EPO androgen replacement therapy
question
What are the uses of androgens?
answer
Replacement therapy Stimulates Erythropoiesis ---- more RBCs Short stature --- it will increase the length of long bone but can increase closure of plate Athletic performance b/c of anabolic functions
question
Side effects of Androgens
answer
Women ---Virilization (hirsutism, enlarged clitoris, deepened voice) and menstrual irregularity + liver probs Men == Impotence, decreased spermatogenesis, gynecomastia, liver probs (jaundice, increases liver enzymes, risk for cancer) + psychotic episodes Children == early epiphyseal closure & if during utero abnormal sex development and also abnormal sex maturation
question
What are the antiandrogens?
answer
Ketaconazole Spironolactone Finasteride Cyproterone acetate Flutamide
question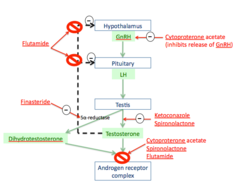
MOA of Ketoconazole

answer
antifungal agent that is involved in blocking gonadal and adrenal steroid synthesis blocks p450 enzymes involved in adrogen synthesis lecture says competitive antagonist of cholesterol esterase the rate limiting step in androgen synth
question
What antiandrogen drug also interferes with synthesis of other steroids?
answer
Ketoconazole
question
What antiandrogen inhibits p450?
answer
Ketoconazole
question
Use of Ketoconazole
answer
Used for advanced prostate cancer that is RESISTANT to first line antiandrogen drugs
question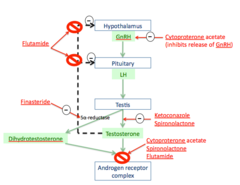
MOA of spironolactone

answer
K+ sparing Diurectic that is an aldosterone antagonist also INHIBITS androgen binding to Androgen receptor lecture says competitive antagonist of cholesterol esterase the rate limiting step in androgen synth
question
What is Spironolactone used for besides diuretic?
answer
to TX hirsutism
question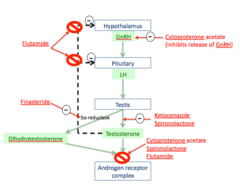
MOA of Finasteride

answer
Blocks 5a-reductase
question
What enzyme converts Testosterone to DHT?
answer
5alpha-reductase
question
What tissues depend on DHT and not testosterone for stimulation?
answer
Prostate cells and hair follicles
question
What is Finasteride used for?
answer
BPH !!! and for hair loss in men [lower doses] (male pattern baldness) as well as early stages of prostate cancer
question
What does finasteride NOT cause that other antiandrogens do?
answer
impotence, infertility, and loss of libido
question
What antiandrogen drug does NOT cause impotence, infertility, or loss of libido?
answer
Finasteride
question
Why does finasteride not cause infertility/loss of libido?
answer
Because it does NOT interfere with the actions of testosterone
question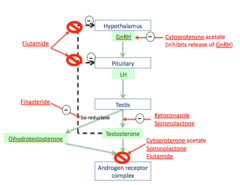
MOA of Cyproterone acetate

answer
competitive antagonist of DHT-androgen receptor binding has progesterone like activity ---> suppresses GnRH secretion
question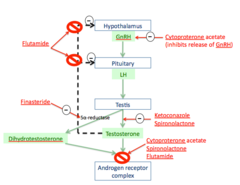
MOA of Flutamide

answer
Pure competitive antiandrogen to androgen receptors and it BLOCKS negative feedback loops for testosterone --> temporary increase in GnRH and actions of testosterone
question
Use of Flutamide
answer
used for advanced prostate cancer
question
What drug is best for BPH?
answer
Finasteride
question
Adverse effects of Flutamide
answer
gynecomastia hot flushes impotence
question
Use of Antiandrogens
answer
Prostatic hyperplasia & cancer Acne Male Pattern baldness Virilization syndromes Precocious puberty Inhibition of sex drive -- [sex offenders?]
question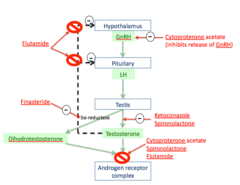
MOA of leuprolide

answer
GnRH agonist and agonist of LH receptor used for advanced prostate cancer
question
What drugs are used for prostate cancer?
answer
Flutamide Leuprolide & other hi-potency GnRH analogs -- Histrelin, Narfarelin (nasal) -- chronic admin will cause downregulation of GnRH receptors so less LH/FSH made and thus less testo DES -- nonsteroidal estrogen that antagonizes physiologic effects of testo GnRH anatagonists --- abarelix and degarelix
question
What drug did they think was a male contraceptive?
answer
Gossypol
question
adverse effects of Leuprolide
answer
HA Light headedness Nausea Hypogonadism with continuous treatment
question
How do GnRH AGONISTs treat prostate cancer?
answer
initially causes agonistic action at the GnRH receptor (give flutamide to block these effects), but within several weeks, testosterone production falls to low levels. Chronic administration --> decreased gonadotropins and end-product hormones
question
What drugs block androgen receptor?
answer
Flutamide Spironolactone Cyproterone (DHT)
question
What are the clinical uses of testosterone
answer
Androgen replacement for hypogonadism Stimulate RBC production in anemias promote Weight gain in pts. with wasting syndromes (like AIDS)
question
Why are testosterones abused by athletes?
answer
because of the anabolic effects that it also has.... increas muscle size and strength and it can increase RBC
question
What is testosterone propionate used for?
answer
hypogonadism delayed puberty receptor positive breast cancer
question
What is testosterone enanthate used for?
answer
hypogonadism delayed puberty metastatic breast cancer -- mets to bone
question
What is testosterone cypionate used for?
answer
treatment of hypogonadism -- long acting
question
What is fluoxymesterone used for?
answer
treatment of hypogonadism in men and breast cancer in women
question
What is oxandrolone used for?
answer
increased ratio of anabolic-to-androgenic activity -- abuse potential -- can cause cholestatic jaundice and liver toxicity



