Abnormal Psychology Unit 1 Exam – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Anal Stage
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the second psychosexual stage, which occurs in the second year of life when the anus is considered the principal erogenous zone
question
Asylums
answer
-- refuges established in western Europe in the fifteenth century to confine and provide for the mentally ill -- forerunners of the mental hospital
question
Behavior Therapy
answer
a branch of psychotherapy conceived narrowly as the application of classical & operant conditioning to the alteration of clinical problems but more broadly as applied experimental psychology in a clinical context
question
Behaviorism
answer
-- John B. Watson -- a school of thought that considers the effects of stimuli in the environment on observable behavior only (i.e., not on consciousness or mental functioning)
question
Cathartic Method
answer
-- introduced by Breuer & developed by Freud in the late nineteenth century -- a therapeutic procedure to relieve emotional suffering whereby a patient recalls & relives an earlier emotional catastrophe & reexperiences the tension & unhappiness
question
Classical Conditioning
answer
-- Ivan Pavlov -- a simple methodology in which a neutral stimulus is paired with a stimulus that has meaning -- after many associations, the neutral stimulus takes on the same meaning -- has the most relevance to the development of phobias
question
Clinical Psychologist
answer
an individual who has earned a Ph.D. degree in psychology or a Psy.D. & whose training has included an internship in a mental hospital or clinic
question
Collective Unconscious
answer
Jung's concept that every human being carries within the wisdom, ideas, & strivings of those who have come before
question
Conditioned Response (CR)
answer
an automatic response established by training to an ordinarily neutral stimulus
question
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
answer
a previously neutral stimulus that, after repeated association with an unconditioned stimulus, elicits the response produced by the unconditioned stimulus itself
question
Counseling Psychologist
answer
a doctoral-level mental health professional whose training is similar to that of a clinical psychologist, though usually with less emphasis on research & serious psychopathology
question
Defense Mechanism
answer
-- ways of coping with anxiety ^repression: the action or process of suppressing a thought or desire in oneself so that it remains unconscious ^displacement: the unconscious transfer of an intense emotion from its original object to another one ^sublimation: socially unacceptable impulses or idealizations are unconsciously transformed into socially acceptable actions
question
Demonology
answer
suggests that evil beings reside within individuals with mental illness & control their minds & bodies
question
Ego
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the predominantly conscious part of the personality, responsible for decision making & for dealing with reality
question
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
answer
-- a treatment that produces a convulsion by passing electric current through the brain -- despite public concerns about this treatment, it can be useful in alleviating profound depression
question
Exorcism
answer
procedure to drive out the evil spirits
question
Extinction
answer
-- the elimination of a classically conditioned response by the omission of the unconditioned stimulus -- in operant conditioning, the elimination of the conditioned response by the omission of reinforcement
question
Fixation
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the arrest of psychosexual development at a particular stage through too much or too little gratification at that stage
question
Genital Stage

answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the final psychosexual stage, reached in adulthood, in which heterosexual interests predominate
question
Harmful Dysfunction
answer
proposed definition of psychological disorder that contains both a value judgment (harmful) & a purtatively objective scientific component (dysfunction)
question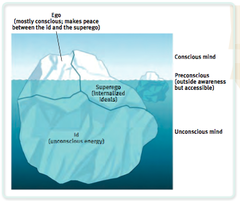
Id

answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the part of the personality present at birth, comprising all the energy of the psyche & expressed as biological urges that strive continually for gratification
question
Latency Period
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the years between ages 6 & 12, during which id impulses play a minor role in motivation
question
Law of Effect
answer
-- Edward Thorndike -- a principle of learning that holds that behavior is acquired by virtue of its consequences
question
Libido
answer
-- Freudian term for the life-integrating instinct or force of the id -- sometimes equated with sexual drive
question
Marriage & Family Therapist
answer
-- a mental health professional who specializes in treating couples & families & in how these relationships impact mental health -- training can be at the master's or Ph.D. level, & some M.S.W. programs offer training in marriage & family therapy
question
Modeling
answer
-- Albert Bandura -- learning by observing & imitating the behavior of others or teaching by demonstrating & providing opportunities for imitation
question
Moral Treatment
answer
-- a therapeutic regime, introduced by Philippe Pinel during the French Revolution, whereby mentally ill patients were released from their restraints & were treated with compassion & dignity rather than with contempt & denigration -- Dorothea Dix
question
Negative Reinforcement
answer
strengthens responses, but it does so by removing an aversive event or stimulus
question
Operant Conditioning
answer
-- B.F. Skinner -- learning occurs in operant conditioning when an individual's behavior is reinforced in some manner
question
Oral Stage

answer
-- in psychoanalytic theory, the first psychosexual stage, which extends into the second year -- during this stage the mouth is the principle erogenous zone
question
Phallic Stage
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the third psychosexual stage, extending from ages 3 to 5 or 6, durring which maximum gratification is obtained from genital stimulation
question
Pleasure Principle
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the demanding manner by which the id operates, seeking immediate gratification of its needs
question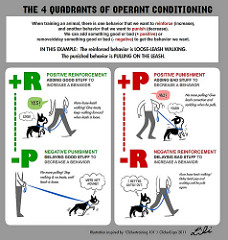
Positive Reinforcement

answer
the strengthening of a tenancy to exhibit a desired behavior by rewarding responses in that situation with a desired reward
question
Psyche
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the totality of the id, ego, & superego including both conscious & unconscious components
question
Psychiatric Nurse
answer
-- a nurse, typically with a bachelor's degree who receives specialized training in mental illness -- a nurse practitioner may prescribe psychiatric medication
question
Psychiatrist
answer
a physician (M.D.) who has taken specialized postdoctoral training, called residency, in the diagnosis, treatment, & prevention of psychological disorders
question
Psychoactive Medications
answer
prescribed chemical compounds -- for example, Prozac -- having a psychological effect that alters mood or thought process
question
Psychoanalysis
answer
-- primarily the therapy procedures pioneered by Freud, entailing free association, dream analysis, & working through the transference neurosis -- more recently the term has come to encompass the numerous variations on basic Freudian therapy
question
Psychoanalytic Theory

answer
-- Sigmund Freud -- abnormal behavior emerges as a result of unresolved conflicts in the unconscious -- criticized extensively for its lack of empirical support but greatly influenced thinking about psychopathology
question
Psychological Disorder
answer
-- the DSM defines a psychological disorder as clinically significant behavioral or psychological symptom patterns -- the definition includes a number of key features including distress, disability or impaired functioning, violation of social norms, & dysfunction
question
Psychopathology
answer
-- abnormal behavior ^personal distress ^disability ^violation of social norms ^dysfunction -- that causes distress or life interference in the individual or in others around him/her -- the field concerned with the nature & development of psychological disorders
question
Psychotherapy
answer
a primarily verbal means of helping troubled individuals change their thoughts, feelings, & behavior to reduce distress & to achieve greater life satisfaction
question
Reality Principle
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the manner in which the ego delays gratification & otherwise deals with the environment in a planned, rational fashion
question
Social Worker
answer
a mental health professional who hold a master of social work (M.S.W.) degree
question
Stigma
answer
the pernicious beliefs & attitudes held by a society, ascrubed to groups considered deviant in some manner, such as people with mental illnesses
question
Superego
answer
in psychoanalytic theory, the part of the personality that acts as the conscience & reflects society's moral standards as learned from parents & teachers
question
Systematic Desensitization
answer
-- Joseph Wolpe -- a major behavioral therapy procedure that has a fearful person, while deeply relaxed, imagine a series of progressively more fearsome situations, such that fear is dispelled as a response incompatible with relaxation -- useful for treating psychological problems in which anxiety is the principal difficulty
question
Transference
answer
the venting of the analysand's emotions, either positive or negative, by treating the psychoanalyst as the symbolic representation of someone important in the past
question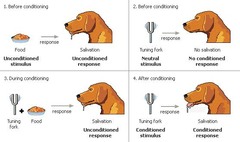
Unconditioned Response (UCR)

answer
behavior that occurs naturally due to a given stimulus
question
Unconditioned Stimulus (ECS)
answer
a stimulus that elicits an unconditioned response
question
Unconscious
answer
-- a state of unawareness without sensation or thought -- in psychoanalytic theory, the part of the personality, in particular the id impulses or energy, of which the ego is unaware
question
Alfred Adler
answer
-- early adherent of Freud, split -- founder of individual psychology ^people inextricably tied to their society because fulfillment found doing things for the social good -- importance of working towards goals like Jung -- prebehaviorist
question
Aaron Beck
answer
-- original cognitive theory of depression -- depressed people show biased processing of information -- depression caused and maintained by the way depressed individuals interpret events in their environment -- negative triad
question
Josef Breuer
answer
-- introduced cathartic method ^relieve emotional suffering by recalling & reliving an earlier emotional catastrophe -- treated Anna O. -- older colleague of Freud
question
Dorothea Dix
answer
-- crusaded against bad conditions and advocated for the humane treatment of individuals with mental illness -- major role in establishing mental hospitals in the U.S.
question
Jean Martin Charcot
answer
-- hysteria caused by nervous system, biological, but also psychological -- legitimized hypnotism
question
Albert Ellis
answer
-- internal sentences that people repeat to themselves cause problems -- rational-emotive behavior therapy ^irrational beliefs are identified and challenged
question
Sigmund Freud
answer
-- pioneered psychoanalytic theory -- characterization of defense mechanisms -- developed Breuer's cathartic method -- psychoanalysis
question
Francis Galton
answer
-- proponent of the biological viewpoint -- one of the earliest genetic researchers -- twin studies, concludeing that many behavioral characteristics were hereditary -- eugenics
question
Hippocrates
answer
-- father of modern medicine; separated from magic, religion, superstision -- proposed that abnormal behavior was the result of some brain pathology like other physical aliments -- earliest to assign brain dysfunction with thought/action dysfunction
question
Carl Jung

answer
-- broke with Freud -- established analytical psychology -- collective unconscious consisting of archetypes -- cataloged extroversion/introversion
question
Franz Anton Mesmer
answer
-- hysteria caused by distribution of universal magnetic fluid, biological -- early practitioner of modern-day hypnotism -- became to be regarded as a quack
question
Paracelsus
answer
-- attributed odd behavior to misalignment of moon & stars -- "lunacy"
question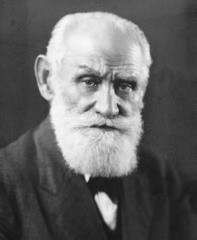
Ivan Pavlov
answer
discovered classical conditioning
question
Philippe Pinel
answer
-- moral treatment -- crusaded against bad conditions and advocated for the humane treatment of individuals with mental illness
question
Benjamin Rush
answer
-- father of American psychiatry -- drew great amounts of blood to relieve disorders -- believed people curable with fear so convinced patients they were close to death
question
B.F. Skinner

answer
-- originated the study of operant conditioning -- renamed Thorndike's "law of effect" "principle of reinforcement"
question
Edward Thorndike

answer
formed law of effect leading eventually to operant conditioning
question
John B. Watson

answer
-- first major figure establishing behaviorism -- "Little Albert" experiment
question
Joseph Wolpe
answer
developed systematic desensitization
question
Paradigm
answer
a basic set of assumptions that guides theorizing and research within a field
question
Rational-Emotive Therapy
answer
-- Albert Ellis -- irrational beliefs are identified and challenged
question
Agonist
answer
a drug that stimulates receptors normally specific to a particular neurotransmitter
question
Allele
answer
any of the various forms of a particular gene
question
Amygdala
answer
-- critical to the induction and experience of fear -- a sub-cortical structure of the temporal lobe involved in attention to emotionally salient stimuli & memory of emotionally relevant events
question
Antagonist
answer
-- a drug that dampens the effect of a neurotransmitter on its receptors -- for example, many dopamine antagonists block dopamine receptors
question
Anterior Cingulate
answer
-- in the sub-cortical region of the brain, the anterior portion of the cingulate gyrus, stretching about the corpus callosum -- plays a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate -- involved in certain higher-level functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, impulse control, and emotion
question
Attachment Theory
answer
-- John Bowlby -- the type or style of an infant's attachment to his or her caregivers can set the stage for psychological health or problems later in development
question
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
answer
-- the division of the nervous system that regulates involuntary functions -- innervates endocrine glands, smooth muscle, & heart muscle -- initiates the physiological changes that are part of the expression of emotion
question
Behavior Genetics
answer
-- attempts to identify the extent to which psychopathology can be attributed to the transmission of genes -- the study of individual differences in behavior that are attributable to differences in genetic makeup
question
Behavior Medicine
answer
an interdisciplinary field concerned with integrating knowledge from medicine & behavioral science to understand health & illness & to prevent as well as treat psychological disorders & other illnesses in which a person's psyche plays a role
question
Behavioral Activation (BA) Therapy
answer
clinical approach to depression that seeks to increase participation in positively reinforcing activities
question
Brain Stem
answer
-- the part of the brain connecting the spinal cord with the cerebrum -- contains pons & medulla oblongata -- functions as a neural relay station
question
Cardiovascular Disease
answer
medical problems involving the heart & the blood circulation system such as hypertension or coronary heart disease
question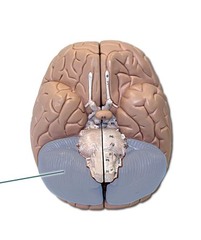
Cerebellum

answer
an area of the hindbrain concerned with balance, posture, & motor coordination
question
Cognition
answer
-- the process of knowing -- the thinking, judging, reasoning & planning activities of the human mind -- behavior is now often explained as depending on these processes
question
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)
answer
-- behavior therapy that incorporates theory & research on cognitive processes such as thoughts, perceptions, judgments, self-statements, & tacit assumptions -- a blend of both cognitive & behavioral paradigms
question
Cognitive Behavioral Paradigm
answer
-- stems from behaviorism and cognitive theory -- general view that people can best be understood by studying how they perceive & structure their experiences & how this influences behavior
question
Cognitive Restructuring
answer
any behavior therapy procedure that attempts to alter the manner in which a client thinks about life so that he or she changes overt behavior & emotions
question
Copy Number Variation (CNV)
answer
-- refers to a variation in gene structure involving copy number changes in a defined chromosome region -- could be in the form of deletion or duplication
question
Corpus Collosum
answer
the large band of nerve fibers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres
question
Cortisol
answer
-- a "stress hormone" secreted by the adrenal cortices -- helps the body prepare to face threats
question
Diathesis
answer
predisposition toward a disease or abnormality
question
Diathesis-Stress
answer
biological vulnerabilities predispose the development of psychopathology, and an environmental stressor causes the psychopathology to be expressed
question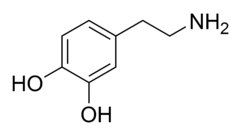
Dopamine

answer
-- central nervous system neurotransmitter -- a catecholamine that is also a precursor of norepinephrine -- apparently figures into schizophrenia & Parkinson's disease
question
Emotion
answer
the expression, experience, & physiology that guide responses to problems & challenges in the environment
question
Epigenetics
answer
the study of changes in gene expression that are caused by something other than changes in the DNA (gene) sequence or structure, such as DNA methylation
question
Exposure
answer
real-life (in-vivo) or imaginal confrontation of of a feared object or situation, especially as a component of systematic desensitization
question
Frontal Lobe
answer
-- the anterior portion of each cerebral hemisphere, in front of the central sulcus -- active in reasoning & other higher mental processes
question
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
answer
inhibitory neurotransmitter that may be involved in the anxiety disorders
question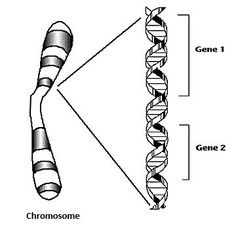
Gene

answer
the smallest portion of DNA within a chromosome that functions as a piece of functional hereditary information
question
Gene Expression
answer
the switching on & off of the reading (transcription & translation) of genes into their products (usually proteins) & thus their associated phenotypes
question
Gene-Environment Interaction
answer
the influence of genetics on an individual's sensitivity or reaction to an environmental event
question
Genetic Paradigm
answer
how our genes interact with our environment to determine behavior
question
Genotype
answer
-- an individual's unobservable, genetic constitution, that is, the totality of genes present in the cells of an individual -- often applied to the genes contributing to a single trait
question
Gray Matter
answer
the neural tissue -- made up largely of nerve cell bodies -- that constitutes the cortex covering the cerebral hemisphere, the nuclei in lower brain areas, columns of the spinal cord, & the ganglia of the automatic nervous system
question
Health Psychology
answer
a branch of psychology dealing with the role of psychological factors in health & illness
question
Heritability
answer
the extent to which variability in a particular behavior/disorder within a population can be attributed to genetic factors
question
Hippocampus
answer
in the subcortical region of the brain, the long, tubelike structure that stretches from the septal area into the temporal lobe; thought to be the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system
question
HPA-axis
answer
-- the neuroendocrine connections among hypothalamus, pituitary gland, & adrenal cortex -- central to the body's response to stress
question
Hypothalamus
answer
in the subcortical region of the brain, the structure that regulates many visceral processes, including metabolism, temperature, perspiration, blood pressure, sleeping, & appetite
question
In-Vivo
answer
as applied in psychology, taking place in a real-life situation
question
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
answer
-- a short-term, here-&-now focused psychological treatment initially developed for depression & influenced by the psychodynamic emphasis on relationships -- aims to guide a patient in solving problems in their interpersonal relationship -- studied as a treatment for postpartum depression and depression during pregnancy at the University of Iowa by Dr. O'Hara
question
Molecular Genetics
answer
studies that seek to determine the components of a trait that are heritable by identifying relevant genes & their functions
question
Neuron

answer
a single nerve cell
question
Neuroscience Paradigm
answer
mental disorders are a result of irregular brain processes
question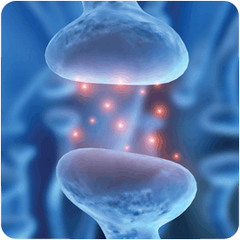
Neurotransmitters

answer
chemical substances important in transferring a nerve impulse from one neuron to another, for example, serotonin & norepinephrine
question
Nonshared Environment
answer
factors distinct among family members, such as relationship with friends or specific experiences unique to that person
question
Norepinephrine
answer
-- a catecholamine neurotransmitter, disturbances of which have been related to mania, depression, & particularly to anxiety disorders -- it is also a sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitter, a hormone released in addition to epinephrine & similar in action, & a strong vasoconstrictor
question
Object-Relations Theory
answer
variant of psychoanalytic theory that focuses on the way children internalize (introject) images of the people who are important to them (parents), such that these internalized images (object representations) become part of the ego & influence how the person reacts to the world
question
Occipital Lobe
answer
-- the posterior portion of each cerebral hemisphere, situated behind the parietal lobe & above the temporal lobes -- responsible for reception & analysis of visual information & for some visual memory
question
Parasympathetic Nervous System
answer
-- the division of the automatic nervous system that is involved with maintenance -- controls many of the internal organs & is active primarily when the organism is not aroused
question
Parietal Lobe
answer
-- the middle division of each cerebral hemisphere, situated behind the central sulcus -- the receiving center for sensations of the skin & of bodily positions
question
Phenotype
answer
-- the totality of psychical characteristics & behavioral traits of an individual or a particular trait exhibited by an individual -- the product of interactions between genetics & the environment over the course of development
question
Polygenic
answer
as applied to psychopathology or any other trait, cause by multiple genes contributing their effects, typically during multiple stages of development
question
Polymorphism
answer
any specific difference in DNA sequence that exists within a population
question
Prefrontal Cortex
answer
the region of the frontal lobe that helps maintain an image of threats & rewards faced, as well as maintain focus & plan relevant to those threats & rewards
question
Pruning
answer
in neural development, the selective loss of of synaptic connections, especially in the fine-tuning of brain regions devoted to sensory processing
question
Reuptake
answer
cellular process by which released neurotransmitters are taken back into the presynaptic cell, terminating their present postsynaptic effect but making them available for subsequent modulation of nerve impulse transmission
question
Schema
answer
a mental structure for organizing information about the world
question
Septal Area
answer
-- in the subcortical region of the brain, the area anterior to the thalamus -- pleasure zone in animals -- role in reward and reinforcement
question
Serotonin
answer
a neurotransmitter of the central nervous system whose disturbances apparently figure in depression
question
Serotonin Transporter Gene
answer
a particular gene critical to the gene-environment interactions that apparently contribute to the development of depression
question
Shared Environment
answer
factors that family members have in common, such as income level, child-rearing practices, & parental marital status & quality
question
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
answer
-- a variation in gene sequence -- specifically, differences between people in a single nucleotide (A, T, G, or C) in the DNA sequence of an particular gene
question
Sympathetic Nervous System
answer
the division of the automatic nervous system that act on bodily systems -- for example, contracting blood vessels reducing activity of the intestines & increasing the heartbeat -- to prepare the organism for exertion, emotional stress, or extreme cold
question
Synapse

answer
small gap between two neurons where the nerve signal passes electrically or chemically from the axon of the first to the dendrites, cell body, or axon of the second
question
Temporal Lobe
answer
-- a large region of each cerebral hemisphere situated below the lateral sulcus & in front of the occipital lobe -- contains primarily auditory & general association areas
question
Thalamus
answer
-- a major brain relay station consisting of two egg-shaped lobes -- receives impulses from all sensory areas except the olfactory & transmits them to the cerebrum for higher processing
question
Time-Out
answer
an operant conditioning procedure in which, after bad behavior, the person is temporarily removed from a setting where reinforcers can be obtained & placed in a less desirable setting, for example, in a boring room
question
Transcription

answer
-- in genetics, the first step in gene expression -- a section of DNA sequence is transcribed to RNA -- a sequence of DNA synthesizes a copy of RNA
question
Ventricles
answer
cavities deep within the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, that connect to the spinal cord
question
White Matter
answer
neural tissue, particularly of the brain & spinal cord, consisting of tracts or bundles of myelinated (sheathed) nevere fibers
question
Mary Ainsworth
answer
attachment styles
question
John Bowlby
answer
attachment theory
question
Thomas Kuhn
answer
subjective factors as well as our human limitations enter into the conduct of scientific inquiry
question
Alternate-Form Reliability
answer
the relationship between scores achieved by people when they complete two versions of a test that are judged to be equivalent
question
Behavioral Assessment
answer
a sampling of ongoing cognitions, feelings, & overt behavior in their situational complex
question
BOLD
answer
-- blood oxygen level dependent -- the signal detected by functional MRI studies of the brain -- measures blood flow & thus neural activity in particular regions
question
Categorical Classification
answer
a person either has or does not have a particular disorder
question
Clinical Interview
answer
-- general term for conversation between a clinition & a patient that is aimed at determining diagnosis, history, causes of problems, & possible treatment options -- can lead to low reliability of diagnoses -- several structured interviews have been developed in the past twenty years to increase interviewer reliability -- building rapport with the individual is important in obtaining information
question
Comorbidity
answer
the co-occurrence of two disorders, as when a person has depression & social phobia
question
Concurrent Validity
answer
the extent to which previously undiscovered features are found among patients with the same diagnosis
question
Construct Validity
answer
reflects the extent to which the variable that is measured by a test (i.e., depression) is related to other variables that would be predicted theoretically
question
Content Validity
answer
the extent to which a measure adequately samples the domain of interest
question
Criterion Validity
answer
the extent to which a measure is associated in an expected way with some other measure
question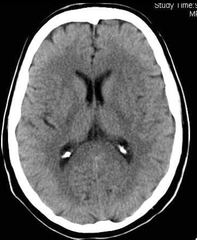
CT or CAT Scan

answer
computerized axial tomopgraphy, a method of diagnosing in which x-rays are taken from different angles & then analyzed by computer to produce a representation of the part of the body in cross section
question
Diagnosis
answer
the determination that the set of symptoms or problems of a patient indicates a particular disorder
question
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5)
answer
-- the system that describes the symptoms that make up categories of psychopathology -- by the American Psychiatric Association May of 2013
question
Dimensional Diagnostic System
answer
an approach to assessment in which a person is placed on a continuum
question
Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA)
answer
form of self-observation involving collection of data in real time (like diaries) regarding thoughts, moods, & stressors
question
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
answer
a recording of the electrical activity of the heart, made with an electrocardiograph
question
Electrodermal Responding
answer
a recording of the minute electrical activity of the sweat glands on the skin, allowing inference of an emotional state
question
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
answer
a graphic recording of electrical activity of the brain, usually of the cerebral cortex, but sometimes of lower areas
question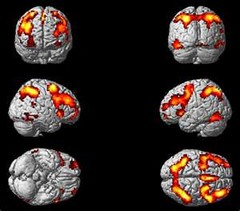
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)

answer
modification of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that allows researchers to take pictures of the brain so quickly that metabolic changes can be measured, resulting in a picture of the brain at work rather than of its structure alone
question
Intelligence Test
answer
-- Alfred Binet -- a standerdized means of assessing a person's current mental ability, for example, the Stanford-Binet test or the Wechsler Adult Intelegence Scale -- consist of tasks assessing language, abstract thinking, visuo-spatial skills, attention and concentration, nonverbal reasoning, and speed of processing -- together, scores on these subtests make up an individual's intelligence quotient (IQ)
question
Internal Consistency Reliability
answer
the degree to which different items of an assessment are related to one another
question
Interrater Reliability
answer
the relationship between the judgments that at least two raters make independently about a phenomenon
question
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
answer
-- a technique for measuring the structure (or, in the case of functional magnetic resonance imaging, the activity) of the living brain -- the person is placed inside a large circular magnet that causes hydrogen atoms to move -- the return of the atoms to their original positions when the current to the magnet is turned off is translated by a computer into pictures of brain tissue
question
Metabolite
answer
-- a chemical breakdown product of an endogenous molecule, such as a neurotransmitter, or of an exogenous drug -- used to gauge current or recent level of its precursor
question
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
answer
-- most well-known personality inventory -- a lengthy personality inventory that identifies individuals with sates such as anxiety, depression, masculinity-femininity, & paranoia, through their true-false replies to groups of statements
question
Neurologist
answer
a physician who specializes in medical diseases that affect the nervous system, such as muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, or Alzheimer's disease
question
Neuropsychological Tests
answer
-- uses testing in order to localize areas of the brain that are not functioning properly -- usually include those that assess attention, verbal and visual memory, and perception -- older adults complete neuropsychological assessments to measure whether their cognitive abilities are declining
question
Neuropsychologist
answer
a psychologist who studies how brain dysfunction affects cognition, emotion, & behavior
question
Personality Inventory
answer
self-report measures that assess a variety of adaptive and maladaptive personality traits
question
PET Scan
answer
computer-generated picture of the living brain, created by analysis of emissions from radioactive isotopes injected into the bloodstream
question
Predictive Validity
answer
the extent to which predictions can be made about the future behavior of patients with the same diagnosis
question
Projective Hypothesis
answer
the notion that standard but highly unstructured stimuli, as found in Rorschach assessment's series of inkblots, are necessary to bypass defenses in order to reveal unconscious motives & conflicts
question
Projective Test
answer
-- a psychological assesment device, such as Rorschach assessment's series of inkblots, employing a standard but vague stimuli -- unstructured format allows an individual's unconscious motives, attitudes, & fears to emerge -- questionable reliability & validity of -- often take an inordinate amount of time to score and interpret -- use declining
question
Psychological Tests
answer
-- standardiszed proceedures designed to measure performance on a particular task or to assess personality -- the performance of an individual is compared to normative values in order to assess his or her relative standing on psychological variables
question
Psychophysiology
answer
-- the discipline concerned with the bodily changes that accompany psychological events -- combines biological approaches with the study of behavior -- usually used in research rather than in clinical settings because of the high cost of the purchase and maintenance of the equipment
question
Reactivity
answer
the phenomenon wherein behavior changes because it is being observed
question
Reliability
answer
consistency of measurement
question
Research Domain Criteria (RDoC)
answer
a long-term project by the National Institute of Mental Health to develop new ways of classifying psychological disorders based on dimensions of observable behavior & neurobiological measures
question
Rorschach Inkblot Test

answer
-- Hermann Rorschach -- a projective test in which the examinee us instructed to interpret a series of 10 inkblots reproduced on cards
question
Self-Monitoring
answer
in behavior assessment, a procedure whereby the individual observes & reports certain aspects of her or her own behavior, thoughts, or emotions
question
Standardization
answer
the process of constructing a normed assessment procedure that meets the various psychometric criteria for reliability & validity
question
Stress
answer
-- state of an organism subjected to a stressor -- can take the form of increased alertness & motor activity & in the long term can cause breakdown of an organ or development of a psychological disorder
question
Structured Interview
answer
-- the interview questions assess symptoms that make up DSM diagnoses and are asked in a standard manner -- questions and decision rules are specified in advance so that the interviewer uses his or her judgment only in rare instances
question
Test-Retest Reliability
answer
when the same individuals take a test on two different occasions
question
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
answer
a projective test consisting of black-&-white pictures, each depicting a potentially emotion-laden situation, about each of which the examinee is instructed to make up a story
question
Validity

answer
-- ensures that the test measures what it is supposed to measure -- pertains to the meaningfulness of the category
question
American Psychiatric Association
answer
-- main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States -- the largest psychiatric organization in the world -- publishes DSM
question
Alfred Binet
answer
intelligence testing
question
Hermann Rorschach
answer
projective Rorschach Inkblot Test
question
ABAB Design
answer
-- also reversal design -- experimental studies that can be conducted on single subjects -- behavior is measured during a baseline period (A), during a period when a treatment is introduced (B), during the reinstatement of the conditions that prevailed in the baseline period (A), and finally during a reintroduction of the treatment (B) -- commonly used in operant research to isolate cause-effect relationships
question
Adoptees Method
answer
research method that studies children who were adopted & reared completely apart from their parents, thereby eliminating the influenced of being raised by disordered parents
question
Analogue Experiment
answer
investigate variables that are related but not identical to psychopathology for ethical and convenience reasons
question
Association Study
answer
a type of molecular genetics study where researchers examine the relationship between a specific allele of a gene & a trait or behavior in the population
question
Case Study
answer
-- the collection of historical or biographical information on a single individual, often including experiences in therapy -- less rigorous than the correlational or the experimental design -- but has played an important role in the description of psychopathology -- especially useful for presenting information on rare instances of abnormal behavior
question
Clinical Significance
answer
the degree to which effect size is large enough to be meaningful in predicting or treating a clinical disorder
question
Concordance
answer
as applied to behavioral genetics, the similarity in psychiatric diagnosis or in other traits within a pair of twins
question
Control Group
answer
those for whom the active condition of the independent variable is not administered, thus forming a baseline against which the effects of the active condition of the independent variable can be evaluated
question
Correlation
answer
the tendency of two variables, such as height & weight, to covary
question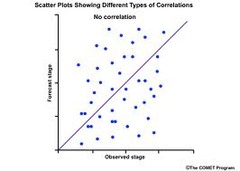
Correlation Coefficient

answer
-- a statistic ranging in value from -1.00 to +1.00 that measures the degree to which two variables are related -- the sign indicates whether the relationship is positive or negative -- the magnitude indicates the strength of the relationship
question
Correlational Method
answer
the research strategy used to establish whether two or more variables are related without manipulating the independent variable
question
Cross-Fostering
answer
research method that studies offspring who were adopted & reared completely apart from their biological parents, where the adoptive parent has a particular disorder but the biological parent does not, thereby introducing the influence of being raised by disordered parents
question
Cross-Sectional Design
answer
studies in which different age groups are compared at the same time
question
Cultural Competence
answer
the capacity of the therapist to understand the patient's cultural framework and its implications for therapeutic work
question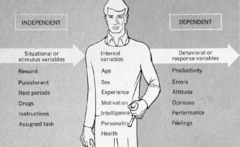
Dependent Variable

answer
in a psychological experiment, the behavior that is measured & is expected to change with manipulation of the independent variable
question
Directionality Problem
answer
a difficulty that arises in the correlatioal method of research when it is known that two variables are related but it is unclear which is causing the other
question
Dissemination
answer
the process of facilitating adoption of efficacious treatments in the community, most typically by offering clinicians guidelines about the best available treatments along with training on how to conduct those treatments
question
Dizygotic (DZ) Twins
answer
-- birth partners who developed from separate fertilized eggs & who are only 50% alike genetically, just as siblings born from different pregnancies involving the same father -- also called fraternal twins
question
Double-Blind Procedure
answer
-- a method for reducing biasing effects of the expectations of research participant & examiner -- neither is allowed to know whether the independent variable of the experiment is being applied to the participant
question
Effectiveness
answer
how well the therapeutic treatment works in the real world in the hands of broader samples of nonacademic, less supervised therapists
question
Efficacy
answer
how well a therapeutic treatment works under rarified academic conditions
question
Empirically Supported Treatment
answer
approaches whose efficacy has been demonstrated & documented through research that meets the APA's standards for research on psychotherapy
question
Epidemiology
answer
-- the study of the frequency and distribution of a disorder in a population -- important in identifying mental disorders that affect a large percentage of the population, preventative & educational efforts
question
Experiment
answer
-- we can infer causality only here -- randomly assign participants to different conditions -- manipulate independant variable and observe its effect on dependent variable -- ethical problems creating psychopathology where none existed before for testing
question
Experimental Effect
answer
a statistically significant difference between two groups experiencing different manipulations of the independent variable
question
External Validity
answer
the extent to which the results of a study can be considered generalizable
question
Family Method
answer
a research strategy in behavior genetics in which the frequency of a trait of of abnormal behavior is determined in relatives who have varying percentages of shared genetic background
question
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
answer
-- studies of variations in the entire human genome to identify associations between variations in genes & particular behaviors, traits, or disorders -- large sample sizes are needed for these types of studies
question
High Risk Method
answer
a research technique involving intensive examination of people, such as the offspring of people with schizophrenia, who have a high probability of later developing a disorder
question
Hypothesis
answer
specific explanation or prediction about what should occur or be found if a theory is true or valid
question
Incidence
answer
in epidemiological studies of a particular disorder, the rate at which new cases occur in a given place at a given time
question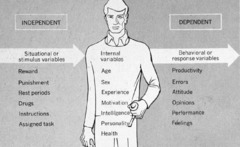
Independent Variable

answer
in a psychological experiment, the factor, experience, or treatment that is under the control of the experimenter & that is expected to have an effect on participants as assessed by changes in the dependent variable
question
Index Cases
answer
the person who in a genetic investigation bears the diagnosis or trait in which the investigator is interested
question
Internal Validity
answer
the extent which results can be confidently attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable
question
Longitudinal Design
answer
investigation that collects information on the same individuals repeatedly over time, perhaps over many years, in an effort to determine how phenomena change
question
Meta-Analysis
answer
provides a method to integrate studies that test a similar research question by standardizing the results
question
Monozygotic (MZ) Twins
answer
genetically identical twins who have developed from a single fertilized egg
question
Placebo
answer
in inactive therapy or chemical agent, or any attribute or component of such therapy or chemical, that affects a person's behavior for reasons related to his or her expectation of change
question
Placebo Effect
answer
-- the action of a drug of psychological treatment that is not attributable to any specific operations of the agent -- for example a tranquilizer can reduce anxiety both because of its special biochemical action & because the recipient expects relief
question
Prevalence
answer
in epidemiological studies of a disorder, the percentage of a population that has the disorder at a given time
question
Probands
answer
the sample of people who in a genetic investigation bears the diagnosis or trait in which the investigator is interested
question
Random Assignment
answer
-- a method of assigning people to groups by chance -- the procedure helps to ensure that groups are comparable before the experimental manipulation begins
question
Randomized Control Trials (RCTs)
answer
-- studies in which clients are randomly assigned to receive either active treatment or a comparison (a placebo condition involving no treatment or an active-treatment control group that receives another treatment) -- experimental treatment studies, where the independent variable is the treatment type & the dependent variable is client outcome
question
Reversal Designs
answer
-- also ABAB design -- experimental studies that can be conducted on single subjects -- behavior is measured during a baseline period (A), during a period when a treatment is introduced (B), during the reinstatement of the conditions that prevailed in the baseline period (A), and finally during a reintroduction of the treatment (B) -- commonly used in operant research to isolate cause-effect relationships
question
Risk Factor
answer
a condition or variable that increases the likelihood of developing a disorder
question
Single-Case Experimental Design
answer
-- a design for an experiment conducted with a single subject -- typically, behavior is measured within a baseline condition, then during an experimental or treatment condition, & finally within the baseline condition again
question
Statistical Significance
answer
-- refers to the likelihood that results from a research study are due to chance -- if there is less than a 5 percent possibility that results were obtained due to chance -- depend on sample size, the more research subjects in a study, the smaller the correlation needs to be to achieve statistical significance
question
Theory
answer
a formally stated & coherent set of propositions that explain & logically order a range of phenomena, generating testable predictions or hypotheses
question
Third Variable Problem
answer
the difficulty in the correlational method of research whereby the relationship between two variables may be attributed to a third factor
question
Treatment Outcome Research
answer
studies designed to assess whether medical or psychological approaches are efficacious in relieving symptoms of a disorder
question
Twin Method
answer
research strategy in behavior genetics in which concordance rates of monozygotic & dizygotic twins are compared
question
Antidepressant
answer
-- any drug that alleviates depression -- also widely used to treat anxiety disorders
question
Attribution
answer
-- the explanation a person has for why an event or behavior has occurred ^stable/unstable ^global/specific
question
Attributional Style
answer
-- stable/unstable & global/specific -- people who believe negative life events are due to stable & global causes are likely to become hopeless
question
Behavioral Couples Therapy
answer
-- clinical approach to depression in which a couple works to improve communication & satisfaction -- more likely to relieve relationship distress than individual cognitive therapy
question
Bipolar I Disorder
answer
-- individuals have experienced a full-fledged manic episode in their lifetimes -- does not require the experience of a major depressive episode, but most experience at least one
question
Bipolar II Disorder
answer
-- individuals have experienced episodes of elevated mood that are less intense than mania ^hypomanic episodes -- does require the experience of a major depressive episode
question
Cognitive Biases
answer
-- tendencies to perceive events in a negative manner -- for example, by attending to or remembering negative information more than positive information -- hypothesized to be driven by underlying negative schemas
question
Cushing's Syndrome
answer
an endocrine disorder usually affecting young women, produced by oversecretion of cortisone & marked by mood swings, irritability, agitation, & physical disfigurement
question
Cyclothymic Disorder
answer
a form of biopolar disorder characterized by frequent periods of depressed mood and hypomania, with intermittent periods of normal mood of up to two months duration
question
Deep Brain Stimulation
answer
a neurological treatment in which electrodes are implanted into specific brain regions
question
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
answer
a DSM-5 disorder defined by severe temper outbursts & observably irritable mood between outbursts in you older than age 6
question
Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex
answer
a region of the prefrontal cortex involved in working memory, motor planning, organization, & regulation & implicated in many psychopathologies
question
Episodic Disorder
answer
the tendency of symptoms to improve, and then recur later, like MDD
question
Expressed Emotion (EE)
answer
hostility, criticism, & emotional overinvolvement directed from other people toward the patient, usually within a family
question
Flight of Ideas
answer
a symptom of mania that involves a rapid shift in conversation from one subject to another with on superficial associative connections
question
Hopelessness Theory
answer
-- highlights the role of attributional styles (the manner in which an individual formulates explanations for events that occur in his or her life) and how they can lead to hopelessness/depression -- stable & global factors
question
Hypomania
answer
less intense periods of elevated mood
question
Lithium
answer
a drug useful for treating both mania & depression in bipolar disorder
question
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
answer
-- experience of at least two weeks of depressed mood and/or loss of interest or pleasure -- must experience at least several of the following ^poor appetite or overeating ^sleeping too much or too little ^psychomotor agitation or retardation ^loss of energy ^feelings of worthlessness ^difficulty concentrating ^thoughts of death or suicide
question
Mania
answer
intense emotional state that is accompanied by flight of ideas, feelings of grandiosity, and rapid speech
question
Melancholic
answer
subtype of major depressive disorder in which the individual is unable to feel better even momentarily when something good happens, regularly feels worse in the morning & awakens early, & suffers a deepening of other symptoms of depression
question
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
answer
-- recent adaptation of cognitive therapy/restructuring that focuses on relapse prevention after successful treatment for recurrent episodes of major depression -- aims to "decenter" the person's perspective in order to break the cycle between sadness & thinking patterns
question
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors
answer
a group of antidepresant drugs that prevent the enzyme monoamine oxidase from deactivating catecholamines & indolamines
question
Mood Disorders
answer
disorders, such as depressive disorders or mania, in which there as disabling disturbances in emotion
question
Negative Triad
answer
-- Aaron Beck -- depression -- negative views of ^the self ^the world ^the future
question
Neuroticism
answer
-- the tendency to react to events with greater-than-average negative affect -- a strong predictor of onset of anxiety disorders & depression
question
Nonsuicidal Self-Injury (NSSI)
answer
behaviors that are meant to cause immediate bodily harm but are not intended to cause death
question
Persistent Depressive Disorder
answer
-- also dysthymia -- a DSM-5 disorder defined by depressive symptoms that last at least two years
question
Peripartum Onset
answer
onset during pregnancy or within 4 weeks postpartum, characterizing a subtype of episodes of major depressive disorder or mania
question
Psychoeducational Approaches
answer
especially with bipolar disorder & schizophrenia, the component of treatment that helps people learn about symptoms, expected time course, triggers for symptoms, & treatment strategies
question
Psychomotor Agitation
answer
a symptom characterized by pacing, restlessness, & inability to sit still
question
Psychomotor Retardation
answer
a symptom commonly observed in major depressive disorder in which the person moves his or her limbs & body slowly
question
Rapid Cycling
answer
term applied to bipolar disorders if the person has experienced at least four episodes within the past year
question
Reward System
answer
-- system of brain structures involved in the motivation to peruse rewards -- believed to be involved in depression, mania, & substance use disorders
question
Rumination
answer
a person's tendency to dwell on negative thoughts may increase the risk of depression
question
Seasonal Affective Disorder
answer
-- a subtype of mood disorders in which episodes consistently occur at the same time of year -- in the most common form, MMD episodes consistently occur in the winter
question
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
answer
-- a specific form of serotonin reuptake inhibitors with less effect on dopamine & norepinephrine levels -- inhibit the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neuron, so that serotonin levels in the cleft are sustained for longer periods
question
Striatum
answer
a subcortical part of the forebrain and a critical component of the reward system
question
Suicide
answer
the intentional taking of one's own life
question
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
answer
a noninvasive technique in which pulsing magnets are used to intensify or diminish brain activity in a given region
question
Tricyclic Antidepressants
answer
-- a group of antidepressants with molecular structures characterized by three fused rings -- they interfere with the reuptake of norepinephrine & serotonin
question
Tryptophan
answer
-- amino acid that is the major precursor of serotonin -- experimental depletion has found that a lowered serotonin level causes temporary depressive symptoms in people with a personal or family history of depression
question
Positive Effect
answer
ability to constructively analyze a situation where the desired results are not achieved, but still obtain positive feedback which assists our future progression, suffers in depression
question
Postpartum Onset
answer
oneset anytime either during pregnancy or within the four weeks following delivery
question
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
answer
a DSM-5 disorder defined by mood & physical symptoms that consistently emerge in the week before menses & clear within a week after menses
question
Psychotic Features
answer
-- delusions or hallucinations characterizing a subtype of episodes of MDD or mania -- also used to refer to positive symptoms of schizophrenia
question
Second Messengers
answer
-- a method of cellular signalling where the signalling molecule does not enter the cell, but rather utilizes a cascade of events that transduces the signal into a cellular change -- secondary messengers are a component of signal transduction cascades
question
Somatic Arousal
answer
the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as butterflies in the stomach, rather than the cognitive part
question
Suicide Prevention Centers
answer
-- The National Suicide Prevention Lifeline -- crisis centers
question
DSM-5 Changes
answer
-- removal of the multiaxial system -- organizing diagnoses by causes ^diagnoses are still defined by symptoms -- enhanced sensitivity to the developmental nature of psychopathology -- new or combined diagnoses -- clearer criteria -- greater emphasis on ethnic & cultural considerations in diagnosis
question
Dysthymia
answer
a chronic depressive state similar to unipolar depression, but characterized by at least three depressive symptoms and a lack of suicidality
question
Interpersonal Therapy
answer
-- University of Iowa established for women with postpartum -- focuses on modifying problematic interpersonal interactions and relationships that contribute to an individual's depression
question
Behavioral Activation Therapy
answer
-- helps patients to increase their engagement with positively reinforcing activities -- research suggests is as effective without cognitive therapy in treating depression



