Abnormal Psychology in a Changing World – Chapter 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
psychological disorder

answer
Is a pattern of abnormal behavior that is associated with states of significant emotional distress, such as anxiety or depression, or with impaired behavior or ability to function, such as difficulty holding a job or even distinguishing reality from fantasy.
question
abnormal psychology
answer
The branch of psychology that deals with the description, causes, and treatment of abnormal behavior patterns.
question
medical model
answer
A biological perspective in which abnormal behavior is viewed as symptomatic of underlying illness.
question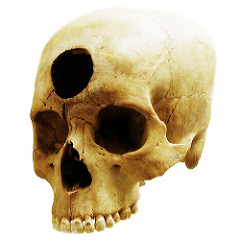
trephination

answer
A harsh, prehistoric practice of cutting a hole in a person's skull, possibly in an attempt to release demons.
question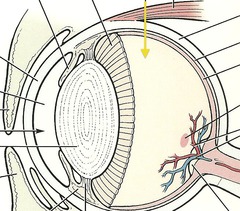
humors

answer
According to the ancient Hippocratic belief system, the vital bodily fluids (phlegm, black bile, blood, yellow bile).
question
deinstitutionalization

answer
a policy of shifting the burden of care from state hospitals to community-based treatment setting, which led to a wholesale exodus from state mental hospitals. The mental hospital population across the United States has plummeted from nearly 600,000 in the 1950s to about 40,000 today ("Rate of Patients," 2012). Some mental hospitals were closed entirely.
question
dementia praecox
answer
The term given by Kraepelin to the disorder now called schizophrenia.
question
general paresis
answer
A form of dementia resulting from neurosyphilis.
question
psychodynamic model

answer
The theoretical model of Freud and his followers, in which abnormal behavior is viewed as the product of clashing forces within the personality.
question
biopsychosocial model
answer
An integrative model for explaining abnormal behavior in terms of the interactions of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
question
scientific method
answer
A systematic method of conducting scientific research in which theories or assumptions are examined in light of evidence.
question
theory
answer
A formulation of the relationships underlying observed events.
question
hypothesis
answer
A prediction that is tested through experimentation.
question
informed consent
answer
The principle that research participants should receive enough information about an experiment beforehand to decide freely whether to participate.
question
confidentiality
answer
Protection of research participants by keeping records secure and not disclosing their identities.
question
naturalistic observation
answer
A research method in which behavior is observed and measured in its natural environment.
question
correlational method
answer
A scientific method of study that examines the relationships between factors or variables expressed in statistical terms.
question
correlation coefficient

answer
A statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables expressed along a continuum that ranges between -1.00 and +1.00.
question
longitudinal study
answer
A research study in which subjects are followed over time.
question
experimental method
answer
A scientific method that aims to discover cause-and-effect relationships by manipulating independent variables and observing the effects on the dependent variables.
question
independent variables
answer
Factors that are manipulated in experiments.
question
dependent variables
answer
Factors that are observed in order to determine the effects of manipulating an independent variable.
question
experimental group
answer
In an experiment, a group that receives the experimental treatment.
question
control group
answer
In an experiment, a group that does not receive the experimental treatment.
question
random assignment
answer
A method of assigning research subjects at random to experimental or control groups to balance the characteristics of people who comprise them.
question
selection factor
answer
A type of bias in which differences between experimental and control groups result from differences in the types of participants in the group, not from the influence of the independent variable.
question
blind
answer
A state of being unaware of whether one has received an experimental treatment or a placebo.
question
placebo
answer
An inert medication or bogus treatment that is intended to control for expectancy effects.
question
internal validity
answer
The degree to which manipulation of the independent variables can be causally related to changes in the dependent variables.
question
external validity
answer
The degree to which experimental results can be generalized to other settings and conditions.
question
construct validity
answer
The degree to which a test measures the hypothetical construct that it purports to measure.
question
epidemiological studies
answer
Research studies that track rates of occurrence of particular disorders among different population groups
question
survey method
answer
A research method in which large samples of people are questioned by means of a survey instrument.
question
incidence
answer
The number of new cases of a disorder that occurs within a specific period of time.
question
prevalence
answer
The overall number of cases of a disorder in a population within a specific period of time.
question
random sample
answer
A sample that is drawn in such a way that every member of a population has an equal chance of being included.
question
genotype
answer
The set of traits specified by an individual's genetic code.
question
phenotype
answer
An individual's actual or expressed traits.
question
proband
answer
The case first diagnosed with a given disorder
question
adoptee studies
answer
Studies that compare the traits and behavior patterns of adopted children to those of their biological parents and their adoptive parents.
question
case studies
answer
are intensive studies of individuals. Some case studies are based on historical material, involving subjects who have been dead for hundreds of years.
question
single-case experimental designs
answer
Case studies provide rich material, but are limited by difficulties in obtaining accurate and unbiased client histories, by possible therapist biases, and by the lack of control groups. Single-case experimental designs help researchers overcome some of these limitations.
question
reversal design
answer
An experimental design that consists of repeated measurement of a subject's behavior through a sequence of alternating baseline and treatment phases.
question
critical thinking
answer
Adoption of a questioning attitude and careful scrutiny of claims and arguments in light of evidence.



