Nuclear Chemistry Vocabulary Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Mass defect
answer
the difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its protons, neutrons, and electrons
question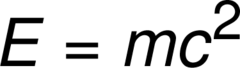
Nuclear binding energy
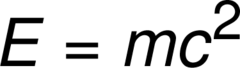
answer
the energy released when a nucleus is formed from nucleons
question
Nucleon
answer
a proton or neutron
question
Nuclide
answer
the general term for any isotope of any element; another term for an atom that is identified by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus
question
Alpha particle
answer
is two protons and two neutrons bound together and is emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay.
question
Beta particle
answer
an electron emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay
question
Daughter nuclides
answer
a nuclide produced by the decay of a parent nuclide
question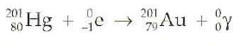
Electron capture
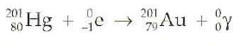
answer
the process in which an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom
question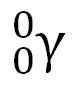
Gamma ray
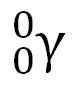
answer
a high-energy electromagnetic wave emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state
question
Nuclear radiation
answer
the particles or electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus during radioactive decay
question
Parent nuclide
answer
the heaviest nuclide of each decay series
question
Positron
answer
a particle that has the same mass as an electron but that has a positive charge, and is emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay
question
Radioactive decay
answer
the spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus into a slightly lighter and more stable nucleus, accompanied by emission of particles, electromagnetic radiation, or both
question
Radioactive Nuclide
answer
an unstable nucleus that undergoes radioactive decay
question
Transuranium element
answer
an element with more than 92 protons in its nucleus
question
Atomic nucleus
answer
Concentration of nearly all the mass, protons and neutrons
question
Nuclear Force
answer
the force that holds nucleons together, due to the presence of neutrons, more effective with smaller nuclei
question
Alpha Decay
answer
An unstable nucleus emits a helium nucleus (2 protons and 2 neutrons)
question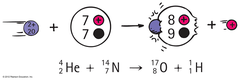
Artificial Transmutation

answer
Humans bombard nuclei with smaller particles in the lab resulting in the formation of a different nuclei. Particles gain speed in a particle accelerator.
question
Band of Stability
answer
A line on a graph that represents the ratio between neutrons and protons of stable nuclei. 1:1 for low atomic #'s 1.5:1 for high atomic #'s
question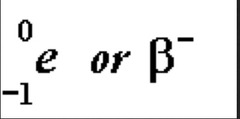
Beta Decay
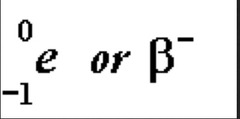
answer
A neutron in an unstable nucleus becomes a proton and a high speed electron (beta particle). The proton stays in the nucleus.
question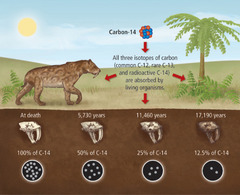
Carbon-14 (Radioactive) Dating

answer
The process in which the age of a carbon-containing sample is determined by measuring the amount of remaining C-14. The decay rate of C-14 is constant over time.
question
Chain Reaction
answer
A continuous series of fission reactions. A reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products which can be used to start another reaction
question
Control Rods
answer
They absorb and limit the number of free neutrons in order to control the number of nuclei that undergo nuclear fission.
question
Decay Series
answer
A series of successive decays that occur which eventually result in the production of a stable nucleus.
question
E=mc2
answer
An equation which explains that a small amount of matter can be turned into a large amount of energy.
question
Film Badges
answer
Tags or badges that rely on the exposure of film to measure the radiation a person experienced.
question
Gamma Decay
answer
High energy electromagnetic radiation that is emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited to ground state.
question
Geiger Counter
answer
An instrument that makes audible clicks when exposed to radiation. More clicks = higher levels of radiation.
question
Half-life
answer
t1/2 The time required for half of the atoms in a sample of an unstable isotope to decay.
question
Nuclear Fission
answer
The process in which a very large nucleus splits into more stable nuclei. This process releases large amounts of energy and additional neutrons.
question
Nuclear Fusion
answer
The process in which two or more smaller nuclei join together to make one larger nucleus. This is the source of energy in the sun. Releases the most energy.
question
Nuclear Meltdown
answer
This may occur if the cooling process in a nuclear reactor fails to remove the heat produced during the fission process.
question
Nuclear Power Plant
answer
An alternative source of energy is created when larger nuclei split and release heat energy which heats up water which turns to steam which spins a turbine which produces electricity. The largest concern with the process is the disposal of the radioactive waste that is generated.
question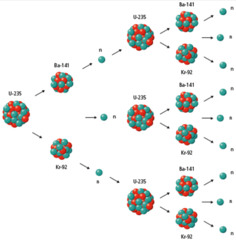
Nuclear Reaction

answer
A reaction in which an unstable nucleus changes to become more stable.
question
Radon in Homes
answer
A cancer-causing radioactive gas that is produced when uranium in the ground decays into radium which then decays further. This can be present in high concentrations in the basements of houses.
question
rem

answer
Roentgen Equivalent, Man A unit used to measure the potential biological damage radiation can do to living organisms
question
Roentgen
answer
A unit which is used to indicate the amount of radiation in the air.
question
Stable Nucleus
answer
A nucleus that has a neutron:proton ratio that is found on the "band of stability". A 1:1 ratio if it has a low atomic number and a 1.5:1 ratio if it has a high atomic number.
question
Transmutation
answer
A change in the identity of a nucleus as a result of a change in the number of protons in the nucleus.
question
Unstable Nucleus
answer
A nucleus that has a neutron:proton ratio that is NOT found on the "band of stability", a radioisotope.
question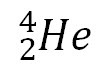
alpha emission
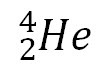
answer
When an alpha particle is given off (a product) in a nuclear reaction.
question
Nuclear bombardment
answer
A type of artificial transmutation where particle accelerators are used to hit nuclei with sub atomic particles such as neutrons or alpha particles.
question
electron
answer
A negative subatomic particle with effectively no mass.
question
proton
answer
A positive subatomic particle with a mass of 1 amu.
question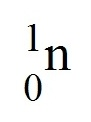
neutron
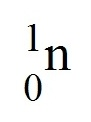
answer
A neutral subatomic particle with a mass of 1 amu.
question
scintillation counter
answer
A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation resulting in light pulses.
question
radioactive tracer
answer
A chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radioisotope so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products.
question
Nuclear waste
answer
The material that nuclear fuel becomes after it is used in a reactor. It looks exactly like the fuel that was loaded into the reactor -- assemblies of metal rods enclosing stacked-up ceramic pellets. A smaller percentage of radioactive material remains. Disposal of this material is the largest concern surrounding the use of nuclear power.
question
Critical Mass
answer
The amount of fissile material needed to sustain nuclear fission.
question
Nuclear Power Plant Fuel
answer
Only 0.7% of natural uranium is 'fissile', or capable of undergoing fission, the process by which energy is produced in a nuclear reactor. The form, or isotope, of uranium which is fissile is the uranium-235 (U-235) isotope.
question
Nuclear Power Plant Containment/Shielding
answer
A gas-tight shell or other enclosure around a nuclear reactor to confine fission products that otherwise might be released to the atmosphere in the event of an accident. Such enclosures are usually dome-shaped and made of steel-reinforced concrete.
question
Nuclear Power Plant Moderator
answer
A medium that reduces the speed of neutrons by reducing their temperature, usually water or graphite.
question
Nuclear Power Plant Coolant
answer
Water used to remove heat from the reactor, generates steam used to produce electricity. Loss of coolant to the reactor core is the most common cause of nuclear accidents.
question
Electromagnetic Radiation
answer
Includes X-rays and gamma rays
question
9 times
answer
Radioisotopes can be used to date objects as old as ___ __________ their half life (t?/?).
question
short
answer
Radioisotopes used for nuclear medicine (taken internally) should have a (short/long) half life.
question
both fission and fusion
answer
Mass is converted into energy during: fission fusion both fission and fusion



