Biochemistry Ex1 Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, DNA – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion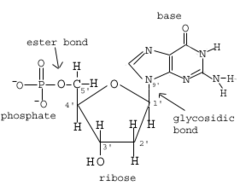
Nucleotides

answer
Building blocks of DNA and RNA. Composed of bases, sugars and phosphate groups
question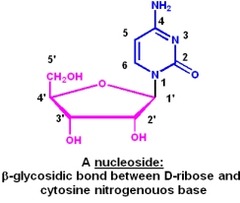
Nucleosides

answer
a base bonded to a sugar Ex. Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine, Thymidine (DNA), Uridine (RNA)
question
Bases Types in DNA/RNA
answer
make up nucleotides/nucleosides, two types: Pyrimidines (CUT) Purines (AG)
question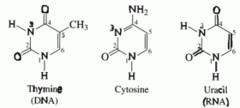
Pyrimidines

answer
Base type.Consists of: Cytosine (C) Uracil (U) in RNA Thymine (T) in DNA
question
Purines
answer
Base type consisting of Adenine (A) Guanine (G)
question
Sugars in Nucleotides
answer
Ribose and Deoxyribose Diffference is the lack or presence of oxygen on the #2 carbon always the D form of the sugar at 1 carbon and OH on is always up Beta on 1 carbon
question
DNA nucleotides
answer
consist of a base (A,T,C,G), deoxyribose and 1-3 phosphate groups
question
RNA nucleotides
answer
consist of a base (A,U,C,G), ribose, and 1-3 phosphate groups.
question
Triphosphates
answer
the building blocks of DNA and RNA.
question
ATP
answer
adenosine 5'-triphosphate nucleotide needed for RNA synthesis and also for storing metabolic energy in cells
question
Glycosidic Bonds
answer
bonds between the sugar and base in RNA/DNA. takes place on the 1 carbon of the sugar and 1 N of pyrimidine and 9N on purine
question
Nucleic acids
answer
linear polymers of nucleotides (polynucleotides) linked by phosphodiester bonds
question
Phosphodiester Bonds
answer
link nucleotides together Connect the 3' carbon of one nucleotide with the 5' carbon of another
question
DNA double helix
answer
held together by interchained hydrogen bonds involving A-T and G-C base pairs. Specific base pairing means that two DNA strands fo double helix have complementary sequences
question
Base Pairing and H Bonds in RNA
answer
A-T base pairs have 2 H-Bonds C-G Base pairs have 3 H-Bonds
question
Base Pairing in RNA
answer
some RNA molecules, particularly tRNA and rRNA, can have short double helical segments held together by A-U and G-C base pairing
question
Prevalence of total cell RNA's
answer
mRNA ~2% tRNA ~16% rRNA ~82%
question
Types of RNA
answer
messenger RNA (mRNA) ribosomal RNA (rRNA) transfer RNA (tRNA) small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and other
question
Transcription
answer
process of RNA synthesis from a DNA template Involves, RNA polymerase enzyme which constructs RNA
question
mRNA in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
answer
Prokaryotes: single mRNA can code for many polypeptides,no introns.can be translated into proteins even before transcription is completed because there is no nucleus to separate all the ingredients. Eukaryotes: single mRNA encodes only 1 polypeptide. More complex. Contain exons (coding segments) and introns (non-coding) segments that must be removed. Transcription occurs in the nucleaus and translation in the cytoplasm. mature mRNA's must transport.
question
Splicing
answer
removing introns to create mRNA that can leave nucleus and do fucntioons.
question
RNA polymerase
answer
synthesizes RNA from DNA coding by forming the phosphodiester linkages in RNA. New nucleotides always added to the 3' end, 5' end is started.
question
mRNA
answer
encode polypeptides, take place in transcription and translation. Encodes the protein code and transports from nucleus to cytoplasm.
question
Translation
answer
process of protein synthesis at ribosomes in cells. Involves mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA, amino acids, and other molecules.
question
Ribosomes
answer
composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins. function is to create proteins using mRNA and tRNA
question
rRNA structure
answer
complex secondary structure due to many short segments of A-U and G-C intrastrand hydrogen bonds
question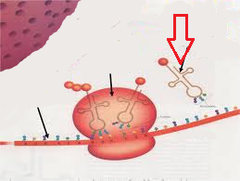
tRNA

answer
transfer amino acids to the growing polypeptide chains in ribosomes. Cloverleaf structure due to short hydrogen-bonded segments.
question
Acceptor stem
answer
3' end of of tRNA where amino acid is covalently linked
question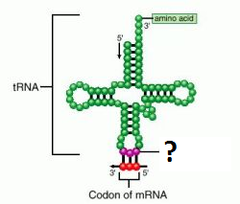
Anticodon

answer
Part on the anticodon loop of the tRNA structure that binds to the codon of the mRNA that specifies the amino acid
question
Nucleic Acid Primary Structure
answer
linear sequences of nucelotide bases along a DNA or RNA strand
question
Dideoxy or Chain Termination Method
answer
procedure to determine the primary structure/sequence of DNA. AKA DNA sequencing uses 2',3'-dideoxynucleotides to terminate growth of DNA chains 1) denature DNA and isolate one strand 2) add primer, DNA polymerase, dNTP's (deoxynucleoside triphosphate) and ddNTP's (dideoxynucleoside triphosphates) which are fluorescently labeled. 3)DNA polymerase extends the primer by sequentially adding nucleotides that base pair with the template 4)occasional incorporation of ddNTP terminates polymerization 5) you can now read by color and size because many DNA chains differ by one nucleotide.
question
2',3'-dideoxynucleotides
answer
aka ddNTP's lack a 3' OH group on top of a lacking 2' OH a 3'-5' phosphodiester bond cannot form therefore ending growth of DNA chain and produces a fragment
question
Nucleic Acid Secondary structure
answer
formation of double helix by specific base pairing, A-T (or A-U) and G-C.
question
B-DNA
answer
major form of DNA double helix of secondary structure. Right handed helix about 10 base pairs/turn. ~perpendicular Stacked .34 nm apart Repeat distance is 3.4 nm Has major/minor groove
question
Major Groove/Minor Groove
answer
bases of a base pair are not directly across helix axis from each other creating grooves in the double helix of B-DNA
question
Melting Temperature of DNA
answer
DNA with high G-C content (3 H-Bonds) has a higher temperature of which the strands separate/denature
question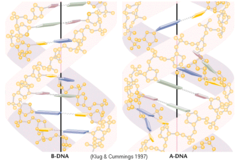
A-DNA

answer
formed by dehydrated DNA fibers. Similar to DNA/RNA hybrid double helices and double helical segments of RNA. Stacked at an angle to the axis due to water loss.
question
Z-DNA
answer
synthetic DNA formed by synthetic oligonucleotides with an alternating pyrimidine purine sequence ex. GCGCGCGCGC Left Handed helix
question
DNA Tertiary Structure
answer
Long-range, three-dimensional structure that includes supercoiling of circular DNA molecules in prokaryotes packaging of DNA into chromosomes in eukaryotes
question
Supercoils
answer
formed in circular DNA, or linear DNA with fixed ends, if the two strands of the double helix are underwound or overwound.
question
DNA Gyrase (Topoisomerase II)
answer
converts bacterial circular chromosomes to interwound supercoiled circles. Cuts DNA and a conformational change allows the DNA to pass through . Gyrase re-ligates the DNA and then releases it.
question
Higher Order Structure of Eukaryotic DNA
answer
Histones interact with DNA to produce nucleosomes, Coiling of Nucleosomes into Chromatin Fibers, Folding of Chromatin Fibers into DNA loops
question
Cruciform Structures
answer
Cruciform structure might be formed from a palindrome sequence. A inverted repeat sequence that just happens to correlate with another part of the same strand and it makes a cross.
question
Palindrome Sequence
answer
Reads the same left to right and right to left. Causes cruciform structures
question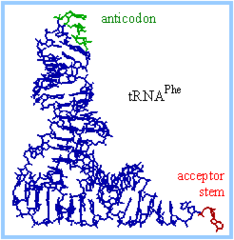
tRNA tertiary Structure

answer
cloverleaf secondary structures of tRNA are folded into L-Shaped tertiary structures. helps carry out their function of protein synthesis. Acceptor stem sticks out the ]one end. Anticodon binds to mRNA also sticks but at other end.
question
rRNA tertiary structure
answer
have many short segments of double helix which interact with numerous ribosomal proteins to form the precise 3-d structure of small and large ribosomal subunits which make up the funcitonal ribosome.
question
Recombinant DNA
answer
refers to laboratory techniques to manipulate DNA, includes topics such as cloning vectors, cDNA's, protein expression vectors, and PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
question
Cloning Vector
answer
DNA molecule into which foreign DNA is inserted for cloning -cloning-production of exact copy of DNA segment. Commonly used: plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC's), Yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC's) 1) cut with restriction endonucleases on foreigh and using chromosome 2) heat and allow to cool slowly such that foreign DNA can base pair. 3)DNA ligase seals the gaps in DNA
question
Restriction endonucleases
answer
useful in recombinant DNA because cut DNA at specific sequences 4-8 nucleotides. EcoRI cuts GAATTC
question
DNA ligase
answer
puts together two pieces of DNA
question
cDNA's
answer
DNA copies of mRNA molecules. First ADD oligonucleotide primers 1)Reverse transcriptase copies RNA into DNA used to synthesize first DNA strand 2)Ribonuclease treatment degrades mRNA strand 3)DNA polymerase synthesizes new strand
question
Reverse transcriptase
answer
copies RNA into DNA
question
Ribonuclease
answer
catalyzes the breaking down of RNA into smaller pieces
question
Protein Expression
answer
vectors used to synthesize proteins including human, in E. coli bacteria and others. cDNA molecule representing the gene of interest is inserted next to a promotor and a ribosome-binding site in the vector.
question
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
answer
an in vitro technique to greatly amplify the amount of a DNA segment. Involves multiple cycles of heating and cooling a reaction mixture that includes: 1) the DNA template, 2) oligonucleotide primers 3) deoxynucleotides 4) heat stable DNA polymerase
question
oligonucleotide primers
answer
a synthetic, single-stranded DNA used to initiate DNA replication from a specific target sequence
question
Blotting and Hybridization Methods
answer
allow specific DNA fragments (Southern Blotting), RNA molecules (Northern blotting), or proteins (Western Blotting) to be detected in a mixture of themselves and detected with probes (proteins-antibodies)
question
Human Gene Therapy
answer
functional versions of defective genes are introuced into human by virus-mediated gene delivery or other techniques to correct damage caused by gene mutations 1)expression cassette-cDNA and promotor 2)Cassette incorporated into virus which can infect (DNA virus vectors, Retrovirus RNA vectors)



