KHS AP English Literature Vocabulary Terms – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Allegory
answer
A story or poem in which characters, settings, and events stand for other people or events or for abstract ideas or qualities.
question
Alliteration
answer
Repetition of the same or similar consonant sounds at the beginning of words that are close together. Example: "The soul selects her own society."
question
Allusion
answer
A reference to a person, event, or work of art that is known from history, literature, religion, politics, sports, science, or another branch of culture.
question
Ambiguity
answer
Deliberately suggesting two or more different, and sometimes conflicting, meanings in a work
question
Anaphora
answer
Repetition of a word, phrase, or clause at the beginning of two or more sentences in a row. Ex: "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, ...it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair."
question
Anecdote
answer
A short and interesting story or an amusing event often proposed to support or demonstrate some point.
question
Antagonist
answer
Opponent or force that struggles against or blocks the hero, or protagonist, in a story.
question
Anticlimax
answer
The intentional use of fancy language to describe the trivial or commonplace, or a sudden transition from a significant thought to a trivial one in order to achieve a humorous or satiric effect.
question
Antihero

answer
Central character who lacks all the qualities traditionally associated with heroes. May lack courage, grace, intelligence, or moral scruples.
question
Antithesis

answer
The juxtaposition of sharply contrasting ideas in balanced words, phrases, grammatical structures, or ideas.
question
Aphorism

answer
A pithy/brief observation that contains a general truth, such as, "if it ain't broke, don't fix it." Or, "haste makes waste."
question
Apostrophe

answer
Calling out to an imaginary, dead, or absent person, or to a place or thing, or a personified abstract idea.
question
Archetype
answer
An idealized model of a person, object, or concept from which similar instances are derived, copied, patterned, or emulated.
question
Aside

answer
A comment made by a stage performer that is intended to be heard by the audience but supposedly not by other characters.
question
Assonance
answer
The repetition of similar vowel sounds followed by different consonant sounds especially in words that are together. Example: "Old age should burn and rave at close of day; Rage, rage, against the dying of the light."
question
Asyndeton
answer
Commas used without conjunction to separate a series of words, thus emphasizing the parts equally: instead of "Lions, tigers, and bears!" the writer uses, "Lions, tigers, bears!"
question
Ballad
answer
An emotional poem or form of verse, often a narrative, set to music.
question
Bildungsroman
answer
A special kind of novel that focuses on the psychological and moral growth of its main character from his or her childhood to maturity, or some portion thereof.
question
Blank verse
answer
Poetry written without rhymes, but which retains a set metrical pattern, usually iambic pentameter.
question
Cacophony
answer
Unpleasant sounds in the jarring juxtaposition of harsh letters or syllables which are grating to the ear, usually inadvertent, but sometimes deliberately used in poetry for effect.
question
Caesura
answer
A pause in a line of verse, indicated by speech patterns rather than due to specific metrical patterns.
question
Catharsis
answer
A sudden emotional breakdown or climax that consists of overwhelming feelings of great pity, sorrow, laughter, or any extreme change in emotion. In Greek theatre, a purging of emotion.
question
Chiasmus
answer
In poetry, a type of rhetorical balance in which the second part is syntactically balanced against the first, but with the parts reversed. Example: "Ask not what your country can do for you. Ask what you can do for your country."
question
Cliche

answer
A word or phrase, often a figure of speech, that has become lifeless because of overuse.
question
Colloquialism
answer
A word or phrase that is not formal or literary, typically one used in ordinary or familiar conversation. Slang.
question
Conceit
answer
A comparison of two unlikely, or vastly different things, that is drawn out within a piece of literature, and likened through the use of similes and metaphors.
question
Connotation
answer
An idea suggested by a word, apart from what it explicitly describes. The feeling that goes with a word.
question
Consonance
answer
The repetitive sounds produced by consonants within a sentence or phrase. This repetition often takes place in quick succession such as in pitter, patter.
question
Couplet

answer
Two consecutive rhyming lines of poetry.
question
Denotation
answer
The direct, specific, and literal meaning of a word.
question
Deus ex machina
answer
Any artificial device or coincidence used to bring about a convenient and simple solution to a plot.
question
Dialect
answer
A way of speaking that is characteristic of a certain social group or of the inhabitants of a certain geographical area.
question
Diction
answer
1: The choice of words, phrases, sentence structures, and figurative language in a literary work. 2: The manner or mode of verbal expression, particularly with regard to clarity and accuracy.
question
Dramatic irony
answer
An occasion in a play, film, or other work in which a character's words or actions convey a meaning unperceived by the character but understood by the audience.
question
Elegy
answer
A serious poem upon the death of a particular person, usually ending in consolation.
question
Enjambment
answer
The continuation of a sentence beyond the end of a line of poetry; when a phrase carries over a line-break without a major pause.
question
Epic
answer
A poem that celebrates, in a continuous narrative, the achievements of mighty heroes and heroines, often concerned with the founding of a nation or developing of a culture.
question
Epigraph
answer
A quotation or aphorism at the beginning of a literary work suggestive of the theme.
question
Epistrophe
answer
Device of repetition in which the same expression (a single word or phrase) is repeated at the end of two or more lines, clauses, or sentences. "Wherever they's a fight so hungry people can eat, I'll be there. Wherever they's a cop beatin' up a guy, I'll be there.... An' when our folk eat the stuff they raise an' live in the houses they build - why, I'll be there...."
question
Euphemism
answer
The substitution of a comfortable or inoffensive expression to replace one that might offend or suggest something unpleasant.
question
Euphony
answer
Harmony or beauty of sound which provides a pleasing effect to the ear, usually sought-for in poetry for effect.
question
Exposition
answer
In drama, the presentation of essential information regarding what has occurred prior to the beginning of the play.
question
Extended Metaphor
answer
A detailed and complex metaphor that extends over a long section of a work. May also be called a "conceit" or "epic metaphor."
question
Farce

answer
A type of comedy in which ridiculous and often stereotyped characters are involved in silly, far-fetched situations.
question
Flashback
answer
A retrospection where an earlier event is inserted into the normal chronology of the narrative.
question
Foil
answer
A character who functions to contrast against another character, usually the main character, in order to show more clearly their traits.
question
Foreshadowing
answer
The use of hints and clues to suggest what will happen later in a plot.
question
Formal Diction
answer
Language that is lofty, dignified, and impersonal.
question
Frame narrative
answer
A story within a story, within sometimes yet another story, as in, for example, Mary Shelley's Frankenstein or Heart of Darkness.
question
Free verse
answer
A kind of poetry that does not conform to a regular meter or rhyme scheme.
question
Genre
answer
A category of literary work which may refer to both the content of a given work — tragedy, comedy, pastoral — and to its form, such as poetry, novel, or drama. This term also refers to types of popular literature, as in science fiction or detective story.
question
Hamartia

answer
The error in judgment a character makes, because of their tragic flaw, which results in their downfall. Literally means "missing the mark" in Greek.
question
Hubris
answer
Excessive pride or ambition that leads to a character's downfall.
question
Hyperbole
answer
A figure of speech that uses an incredible exaggeration or overstatement, for effect. "If I told you once, I've told you a million times...."
question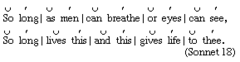
Iambic
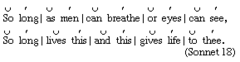
answer
A metrical pattern in poetry that consists of two syllables per foot in an unstressed - stressed pattern. "I am a pirate with a wooden leg."
question
Idiom
answer
A set expression or a phrase, comprising two or more words, that is not interpreted literally, but is understood to mean something quite different from what the individual words of the phrase would imply. Example: "I can't make heads or tails of this." "Let's hit the sack!" "That guy kicked the bucket."
question
Imagery
answer
The use of language to evoke the five senses. Types: visual, audial, tactile, olfactory, gustatory. The use of language to evoke a picture or a concrete sensation of a person, a thing, a place, or an experience.
question
Informal Diction
answer
Language that is more conversational and colloquial, more personal and similar to everyday speech.
question
In media res
answer
Latin for "into the middle of things." It usually describes a narrative that begins, not at the beginning of a story, but somewhere in the middle — usually at some crucial point in the action.
question
Interior monologue
answer
Writing that records the thinking that goes on inside a character's head; it is coherent as if character were talking.
question
Internal rhyme
answer
Rhymes that occur within a line of poetry, or in the middle of lines, that are near each other, instead of at the end of a line.
question
Irony
answer
A situation or statement characterized by a significant difference between what is expected or understood and what actually happens or is meant. The opposite or nearly the opposite of what you would expect.
question
Juxtaposition
answer
Poetic and rhetorical device in which normally unassociated ideas, words, or phrases are placed next to one another, creating an effect of surprise and wit.
question
Kenning
answer
A compound poetic phrase substituted for the usual name of a person or thing. Ex: "Whale Road" for ocean.
question
Litotes
answer
A form of understatement in which the positive form is emphasized through the negation of a negative form. Ex: It is not an ideal situation to be eaten by zombies.
question
Lyric
answer
A short poem in which the speaker expresses intense personal emotion rather than describing a narrative or dramatic situation.
question
Metaphor
answer
A figure of speech that makes a comparison between two unlike things WITHOUT the use of such specific words of comparison as like, as, than, or resembles.
question
Meter

answer
The repetition of sound patterns that creates a rhythm in poetry.
question
Metonymy
answer
A figure of speech in which a person, place, or thing, is referred to by something closely associated with it. "We requested from the crown support for our petition."
question
Mood

answer
The emotional tone or background that surrounds a scene.
question
Motif
answer
A recurring image, word, phrase, action, idea, object, or situation used throughout a work (or in several works by one author), unifying the work by tying the current situation to previous ones, or new ideas to the theme.
question
Ode
answer
A lyric poem that is somewhat serious in subject and tone, elevated in style, sometimes using an elaborate stanza structure.
question
Onomatopoeia
answer
The use of words whose sounds echo their sense. The words sounds like what it means. Buzz. Boom. Bang.
question
Oxymoron
answer
A figure of speech that combines opposite or contradictory terms in a brief phrase. Ex: "Jumbo shrimp."
question
Paradox
answer
A statement which contains seemingly contradictory elements or appears contrary to common sense, yet can be seen as true when viewed from another angle. Ex: "I must be cruel to be kind."
question
Parallelism
answer
The use of components in a sentence that are grammatically the same, or similar in their construction, sound, meaning or meter.
question
Parody
answer
A work that makes fun of another work by imitating some aspect of the writer's style.
question
Pastoral

answer
A poem, or other work, that describes the simple life of country folk who live a life of beauty, music, and love. Also an idyll.
question
Persona
answer
The narrator in a non-first person novel. The author's creation--the voice "through which the author speaks."
question
Personification
answer
A figure of speech in which an object or animal is given human qualities, feelings, thoughts, or attitudes.
question
Polysyndeton
answer
Sentence which uses a conjunction with NO commas to separate the items in a series. Ex: "X and Y and Z".
question
Protagonist
answer
The central character in a story, the one who initiates or drives the action.
question
Pun
answer
A "play on words" based on the multiple meanings of a single word or on words that sound alike but mean different things.
question
Quatrain
answer
A poem consisting of four lines, or four lines of a poem that can be considered as a unit.
question
Refrain
answer
A repeated stanza or line(s) in a poem or song.
question
Sarcasm
answer
Usually ironic language meant to hurt or mock someone or something and simultaneously amuse the audience. Ex: "Thrift, thrift, Horatio! The funeral bak'd meats did coldly furnish forth the marriage tables." (His mother married so soon after his father's death that they used the leftovers from the funeral at the wedding.)
question
Satire
answer
A work that uses mockery, humor, and wit to criticize and cause change in human nature and institutions.
question
Simile
answer
A figure of speech that makes an explicit comparison between two unlike things, using words such as like, as , than, or resembles.
question
Slant Rhyme

answer
A type of rhyme formed by words with similar but not identical sounds. Sometimes called Half rhyme, imperfect rhyme, near-rhyme or lazy rhyme. Example: chill and tulle or bridge and grudge.
question
Soliloquy

answer
A long speech made by a character in a play while no other characters are on stage, often expressing their inner thoughts and feelings.
question
Sonnet

answer
A short poem that has 14 fourteen lines and is written in iambic pentameter. Each line has 10 syllables. It has a specific rhyme scheme and a "volta" or a specific turn.
question
Stream of consciousness

answer
A style of writing that portrays the inner (often chaotic) workings of a character's mind.
question
Suspension of disbelief

answer
A willingness of a reader or viewer to ignore minor inconsistencies or unbelievable behavior so as to enjoy a work of fiction.
question
Symbol
answer
A person, place, thing, or event that has meaning in itself and that also stands for something more than itself.
question
Synecdoche
answer
A figure of speech in which a part represents the whole. Ex: "If you don't drive properly, you will lose your wheels."
question
Syntax
answer
The order of words when writing phrases, clauses, and sentences.
question
Tone
answer
The attitude a writer takes toward the subject of a work, the characters in it, or the audience, revealed through diction, figurative language, and organization.
question
Tragic flaw
answer
In a tragedy, the quality within the hero or heroine which leads to his or her downfall.
question
Verbal irony
answer
When a speaker says something that is the opposite, or nearly the opposite, of what they mean.
question
Voice

answer
The particular phrasings, tone, diction, and manner a writer uses that is distinctive to them.



