General psychology chapter 3 & 4 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Relatively meaningless bits of information that result when the brain proccesses electrical signals that come from the sense organs
answer
Sensation
question
Meaningful sensory experiences that
answer
Perception
question
When a sense organ changes or transforms physical signals into neural impulses sent to the brain for proccessing
answer
Transduction
question
decreased response to sense organs the more they are exposed to a stimulus
answer
adaptation
question
relatively meaningless bits of information that result when the brain processes electrical signals that come from the sense organs
answer
Sensation
question
A point above which a stimulus is perceived and below which it is not percieved
answer
Threshold
question
Least amount of something you can detect
answer
Absolute threshold
question
Stimulus you are not consciously aware of, but it can influence your mental processes, below absolute threshold, aware on some level
answer
Subliminal stimulus
question
So fast that you don't know if it works, exposure to a stimulus that may influence your thoughts and opinions in an advertisement
answer
Subliminal advertising
question
Smallest increase or decrease in a stimulus that you can detect Ex: vision test
answer
Just noticeable difference
question
The bigger a stimulus, the more it has to change to notice it Ex: height of buildings
answer
Weber's Law
question
Vision at the edge of a visual field
answer
Peripheral vision
question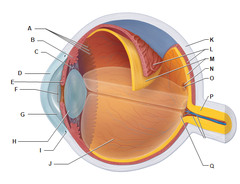
Outer membrane of the eye, focuses images that hit the eye

answer
Cornea
question
Lets light in, dark circle in the center of the iris, changes size based on the amount of light
answer
Pupil
question
Muscle that changes the pupil size, colored part of the eye
answer
Iris
question
Behind pupil and iris, makes small adjustments in focusing the image
answer
Lens
question
Back of the eye, size of a stamp, where visual receptors are located
answer
Retina
question
Sees in dim light, but not in color
answer
Rods
question
Sees color in bright light, "C cones, C for color"
answer
Cones
question
Cones and Rods
answer
What are the visual receptors on the retina?
question
Where the optic nerve leaves the eye. No rods, cones or vision here.
answer
Blind Spot
question
non painful nerve impulses compete with pain impulses that try to reach the brain
answer
Gate control theory
question
chemicals produced and released in response to injury or severe physical/physiological stress
answer
Endorphins
question
When perception is guided by previous knowledge, experiences, beliefs or expectations
answer
Top-down processing
question
Perception beginning with bits of information that combine to recognize patterns
answer
Bottom-up processing
question
Study of perception, how we take sensations and turn them into sensations
answer
Gestalt Psychology
question
Idea that we automatically divide what we look at into Figure (what we focus on) and Ground (background)
answer
Figure ground
question
If things have similar features, we group them together (color, shape and size)
answer
Similarity
question
Brain's tendency to fill in any missing gaps
answer
Closure
question
Idea that we group things together just because they are near eachother
answer
Proximity
question
When we organize stimuli, we see things in a continuous path, not in parts.
answer
Continuity
question
Idea that when things happen simultaneously in time and space, we think they go together.
answer
Conginuity
question
Choose what to pay attention too, and tune out the rest
answer
Selective attention
question
So much going on that you can't pay attention to everything
answer
Sensory overload
question
When we "know" a characteristic about something, we perceive it as staying the same even if the sensation changes
answer
Perceptual constancy
question
Seeing the world in 3-D
answer
Depth perception
question
Depends on the movement of both eyes Ex: Convergence and retinal despairity
answer
Binocular depth cues & examples
question
Idea that the eyes turn inward indicating how close or far away something is
answer
Convergance
question
Each eye sees something different, then the brain puts the images together
answer
Retinal despairity
question
Things seen with only one eye Ex: Lines, size, overlaps
answer
Monocular depth cues & examples
question
When you misperceive a stimulus, that is not really there Ex: thinking a leaf is a spider
answer
Illusion & example
question
When you perceive something, but there is no external stimulus, it can be any sense Ex: Feeling a spider crawling on you, but nothing is there
answer
Hallucination & Example
question
No, it varies on age, health, temp, air pressure etc...)
answer
Does the absolute threshold stay the same?
question
The bigger the stimulus, the more it has to change to be noticed
answer
What is the overall concept of just noticeable difference?
question
The eyes are constantly moving, each eye sees different things, the brain fills the gap
answer
Why don't we notice the blind spot?
question
In the brain
answer
Where do we actually "see"
question
Decrease in sensory response due to a stimulus being continuous, message stops getting sent to the brain Ex: No longer feeling the rings on your fingers
answer
Sensory adaption and example
question
When a message keeps getting sent to the brain, but the brain doesn't always acknowledge it Ex: the "new" factor
answer
Habituation and example
question
1. Results from more than one stimulus 2. Intensity depends of physical, emotional and physiological factors 3. Treatment involves the physical and emotional stress
answer
3 ways pain is different from other senses
question
The painful and non-painful neurons compete to reach the brain and pass the "gate" since a limited number of neurons can reach the brain
answer
gate control theory of pain
question
Increase in endorphin's means a decrease in pain
answer
How are endorphin's related to pain
question
illusion that a stimulus or object is moving, but really it is stationary
answer
Illusion of apparent motion
question
Named after the designer. Shows that perception of size can be distorted by changing depth
answer
What is the Ames Room?
question
Not knowing when something is wrong. Joint problems, fractures, infections and no sense of temperature.
answer
What are problems associated with being unable to feel pain?
question
Wide range of experiences from being acutely aware & alert to totally unresponsive
answer
Consciousness on continuum
question
Freud- mental place where unacceptable thoughts, feelings and beliefs are that are beyond awareness Medical- Results from trauma, anesthesia or disease; total lack of sensory awareness and the environment
answer
Difference between Freud's idea of consciousness and the medical term
question
Jobs, illness, drugs, caffeine etc..
answer
What affects Circadian rythym
question
Melatonin and light exposure
answer
What has been proven to help reset Circadian rhythm?
question
When someone has severe brain damage due to the cortex resulting in a long-term loss of cognitive function and awareness. Still able to breathe and maintain sleep cycle
answer
Persistent Vegetative state
question
Different levels of awareness of one's thoughts and feelings
answer
Consciousness
question
Awareness that differs from normal, waking consciousness
answer
Altered state of consciousness
question
Biological clock that's genetically programmed to regulate physiological responses within a 24 hour period, we are wired that way
answer
Circadian rhythym
question
A sleep disorder that can affect those who travel quickly across multiple time zones.
answer
Jet lag
question
Hormone to help sleep, created and released during exposure to dark
answer
Melatonin
question
Experience hallucinations and delusions from lack of sleep
answer
Sleep deprivation psychosis
question
Predictable changes in brain activity
answer
Stages of sleep
question
stages 1,2,3,4. No rapid eye movement
answer
Non-REM sleep
question
Movement during REM sleep
answer
REM behavior disorder
question
Spending an increased amount of time in REM sleep due to being deprived of it the night before
answer
REM rebound
question
As the brain becomes active during REM sleep, neurons are spontaneously firing
answer
Activation synthesis Theory
question
Difficulty sleeping
answer
Insomnia
question
Stop breathing during sleep, usually lasts 10 seconds-a couple minutes. Cause is snoring (tightening of the airway)
answer
Sleep Apnea
question
Chronic disorder marked by excessive sleepiness
answer
Narcolepsy
question
Bad dreams that happen in stage 4 sleep
answer
Night terrors
question
Bad REM dream, frightening, anxiety producing, great detail
answer
Nightmares
question
Altered state of consciousness characterized by narrowing attention and increased suggestability
answer
Hypnosis
question
Reduction in pain reported by people who undergo hypnosis
answer
Hypnotic anaglesia
question
Not remembering what happened while hypnotized
answer
Posthypnotic hypnosis
question
Stage 1- lasts a few minutes, going to sleep, heart slows down, muscles relax, breathing is irregular Stage 2- Body temp drops, start making deep spindles (brain wave activity) Stage 3- Deeper sleep, brain starts making new kinds of waves (delta waves) Stage 4- Making delta waves, goes into REM sleep
answer
Stages of sleep
question
90 minutes
answer
How long does stage 2,3,4 last?
question
Sleep that appears to be deep during REM sleep. Brain waves are similar to being awake
answer
What is paradoxical sleep?
question
To replenish memories, and the immune system.
answer
Why do we sleep?
question
Health, energy, focus, overeating, accidents, hallucinations
answer
Consequences of not sleeping.
question
Melatonin, Chamomile, reading, sleep meds
answer
Treatments for Insomnia
question
Humans are filled with aggressive impulses and they come out in our dreams
answer
Freud's explanation of dreams
question
Cured symptoms by creating hypnosis
answer
How is Anton Mesmer related to hypnotism?
question
Puts a person in altered state of consciousness where they are disconnected from reality, so they experience and respond to suggestions
answer
Altered state theory
question
Behaviors observed during hypnosis result from not being hypnotized, but ability to respond to pressures and suggestions
answer
Socio-cognitive theory
question
Helps recover memories, pain management, changes sensory experiences
answer
What does hypnosis do for the brain?
question
Dreaming about thoughts or experiences that happened during the day
answer
Extensive waking life
question
Texting-6 times Talking- 4 times
answer
How many more times does texting and talking increase you chances of an accident?



