Science Olympiad Name the Scientist – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Benjamin Franklin

answer
Benjamin Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States and in many ways was "the First American". A renowned polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, inventor, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his discoveries and theories regarding electricity. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among other inventions.
question
Galileo

answer
Galileo Galilei, often known mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian physicist, mathematician, engineer, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the scientific revolution during the Renaissance. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism. Galileo has been called the "father of modern observational astronomy", the "father of modern physics", the "father of science", and "the father of modern science". His contributions to observational astronomy include the telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, the discovery of the four largest satellites of Jupiter (named the Galilean moons in his honour), and the observation and analysis of sunspots. Galileo also worked in applied science and technology, inventing an improved military compass and other instruments.
question
Wilbur Wright

answer
The Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur, were two American brothers, inventors, and aviation pioneers who are credited with inventing and building the world's first successful airplane and making the first controlled, powered and sustained heavier-than-air human flight, on December 17, 1903. From 1905 to 1907, the brothers developed their flying machine into the first practical fixed-wing aircraft. Although not the first to build and fly experimental aircraft, the Wright brothers were the first to invent aircraft controls that made fixed-wing powered flight possible.
question
Thomas Edison
answer
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. Dubbed "The Wizard of Menlo Park", he was one of the first inventors to apply the principles of mass production and large-scale teamwork to the process of invention, and because of that, he is often credited with the creation of the first industrial research laboratory.
question
Alexander Graham Bell
answer
Alexander Graham Bell was an eminent Scottish-born scientist, inventor, engineer and innovator who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone
question
Edwin Powell Hubble

answer
Edwin Powell Hubble was an American astronomer who played a crucial role in establishing the field of extragalactic astronomy and is generally regarded as one of the most important observational cosmologists of the 20th century. Hubble is known for showing that the recessional velocity of a galaxy increases with its distance from the earth, implying the universe is expanding.
question
Carolus Linnaeus

answer
Carl Linnaeus, also known after his ennoblement as Carl von Linné, was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern biological naming scheme of binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology. Many of his writings were in Latin.
question
George Washington Carver

answer
George Washington Carver, was an American botanist and inventor. The exact day and year of his birth are unknown; he was born into slavery in Missouri, either in 1861, or January 1864. Carver's reputation is based on his research into and promotion of alternative crops to cotton, such as peanuts, soybeans, and sweet potatoes, which also aided nutrition for farm families. He wanted poor farmers to grow alternative crops both as a source of their own food and as a source of other products to improve their quality of life.
question
Sally Ride

answer
Sally Kristen Ride was an American physicist and astronaut. Born in Los Angeles, Ride joined NASA in 1978 and, at the age of 32, became the first American woman in space. After flying twice on the space shuttle Challenger, she left NASA in 1987. She worked for two years at Stanford University's Center for International Security and Arms Control, then the University of California, San Diego as a professor of physics, primarily researching non-linear optics and Thomson scattering. Ride remains the youngest American astronaut to travel to space.
question
Sir Henry Cavendish

answer
Henry Cavendish was a British natural philosopher, scientist, and an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. Cavendish is noted for his discovery of hydrogen or what he called "inflammable air". He described the density of inflammable air, which formed water on combustion, in a 1766 paper "On Factitious Airs". Antoine Lavoisier later reproduced Cavendish's experiment and gave the element its name.
question
Robert Fulton

answer
Robert Fulton was a colonial American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the first commercially successful steamboat. In 1800, he was commissioned by Napoleon Bonaparte to design the "Nautilus", which was the first practical submarine in history. He is also credited with inventing some of the world's earliest naval torpedoes for use by the British Royal Navy.
question
Joseph Priestly

answer
Joseph Priestley was an 18th-century English theologian, Dissenting clergyman, natural philosopher, chemist, educator, and Liberal political theorist who published over 150 works. He is usually credited with the discovery of oxygen, having isolated it in its gaseous state, although Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Antoine Lavoisier also have a claim to the discovery.
question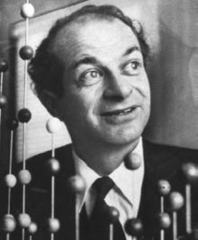
Linus Pauling
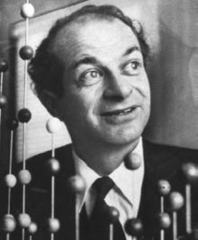
answer
Linus Carl Pauling was an American chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator. He was one of the most influential chemists in history and ranks among the most important scientists of the 20th century. Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology.
question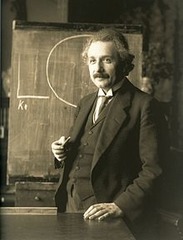
Albert Einstein
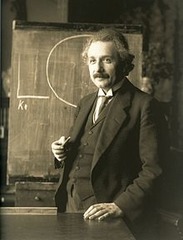
answer
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist and philosopher of science. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics (alongside quantum mechanics). He is best known in popular culture for his mass-energy equivalence formula E = mc2 (which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation"). He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect. The latter was pivotal in establishing quantum theory.
question
Johann Kepler

answer
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his laws of planetary motion, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican Astronomy. These works also provided one of the foundations for Isaac Newton's theory of universal gravitation.
question
Michael Faraday

answer
Michael Faraday, was an English scientist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include those of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis.
question
Edward Jenner

answer
Edward Jenner, was an English physician and scientist who was the pioneer of smallpox vaccine, the world's first vaccine. He is often called "the father of immunology", and his work is said to have "saved more lives than the work of any other human".
question
Madame Curie

answer
Marie Skłodowska-Curie was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the first person (and only woman) to win twice, the only person to win twice in multiple sciences, and was part of the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. She was also the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris, and in 1995 became the first woman to be entombed on her own merits in the Panthéon in Paris. Her achievements included a theory of radioactivity (a term that she coined), techniques for isolating radioactive isotopes, and the discovery of two elements, polonium and radium.
question
William Harvey

answer
William Harvey was an English physician. He was the first known to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and body by the heart, though earlier writers had provided precursors of the theory. After his death the William Harvey Hospital was constructed in the town of Ashford, several miles from his birthplace of Folkestone.
question
Andre Ampere

answer
André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". The SI unit of measurement of electric current, the ampere, is named after him.
question
Sir Isaac Newton

answer
Sir Isaac Newton was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a "natural philosopher") who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy"), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus.
question
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek

answer
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch tradesman and scientist. He is commonly known as "the Father of Microbiology", and considered to be the first microbiologist. He is best known for his work on the improvement of the microscope and for his contributions towards the establishment of microbiology.
question
Eli Whitney

answer
Eli Whitney was an American inventor best known for inventing the cotton gin. Whitney's invention made upland short cotton into a profitable crop, which strengthened the economic foundation of slavery in the United States. He continued making arms and inventing until his death in 1825.
question
Edward Teller

answer
Edward Teller was a Hungarian-born American theoretical physicist who is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb". He made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy and surface physics.
question
Robert Goddard

answer
Robert Hutchings Goddard was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket, which he successfully launched on March 16, 1926. Goddard and his team launched 34 rockets between 1926 and 1941, achieving altitudes as high as 2.6 km (1.6 mi) and speeds as high as 885 km/h (550 mph).
question
Wilhelm Rontgen

answer
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen was a German physicist, who, on 8 November 1895, produced and detected electromagnetic radiation in a wavelength range known as X-rays or Röntgen rays, an achievement that earned him the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.
question
John James Audubon

answer
John James Audubon, was an American ornithologist, naturalist, and painter. He was notable for his expansive studies to document all types of American birds and for his detailed illustrations that depicted the birds in their natural habitats. His major work, a color-plate book entitled The Birds of America, is considered one of the finest ornithological works ever completed. Audubon identified 25 new species.
question
Louis Pasteur

answer
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization. He is remembered for his remarkable breakthroughs in the causes and preventions of diseases, and his discoveries have saved countless lives ever since. He reduced mortality from puerperal fever, and created the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. His medical discoveries provided direct support for the germ theory of disease and its application in clinical medicine. He is best known to the general public for his invention of the technique of treating milk and wine to stop bacterial contamination, a process now called pasteurization. He is regarded as one of the three main founders of bacteriology, together with Ferdinand Cohn and Robert Koch, and is popularly known as the "father of microbiology".
question
James Watt

answer
James Watt was a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer whose improvements to the Newcomen steam engine were fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world.
question
Sir Humphrey Davy

answer
Sir Humphry Davy was a Cornish chemist and inventor. He is best remembered today for his discoveries of several alkali and alkaline earth metals, as well as contributions to the discoveries of the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine.
question
Gregor Mendel
answer
Gregor Johann Mendel was a German-speaking Moravian scientist and Augustinian friar who gained posthumous fame as the founder of the modern science of genetics. Though farmers had known for centuries that crossbreeding of animals and plants could favor certain desirable traits, Mendel's pea plant experiments conducted between 1856 and 1863 established many of the rules of heredity, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance.
question
Charles Darwin
answer
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist and geologist, best known for his contributions to evolutionary theory. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestors, and in a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding.
question
Jonas Salk

answer
Jonas Edward Salk was an American medical researcher and virologist. He discovered and developed the first successful inactivated polio vaccine. Born in New York City to Jewish parents, he attended New York University School of Medicine, later choosing to do medical research instead of becoming a practicing physician. Until 1957, when the Salk vaccine was introduced, polio was considered one of the most frightening public health problems in the world.
question
Neil Armstrong

answer
Neil Alden Armstrong was an American astronaut and the first person to walk on the Moon. He was also an aerospace engineer, naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
question
Antoine Lavoisier

answer
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier was a French nobleman and chemist central to the 18th-century Chemical Revolution and a large influence on both the histories of chemistry and biology. He is widely considered to be the "Father of Modern Chemistry".
question
John Dalton
answer
John Dalton was an English chemist, meteorologist and physicist. He is best known for his pioneering work in the development of modern atomic theory, and his research into color blindness.
question
Samuel F.B. Morse

answer
Samuel Finley Breese Morse was an American painter and inventor. After having established his reputation as a portrait painter, in his middle age Morse contributed to the invention of a single-wire telegraph system based on European telegraphs. He was a co-developer of the Morse code, and helped to develop the commercial use of telegraphy.
question
Rachel Carson

answer
Rachel Louise Carson was an American marine biologist and conservationist whose book Silent Spring and other writings are credited with advancing the global environmental movement.
question
Robert Koch

answer
Robert Heinrich Herman Koch was a celebrated German physician and pioneering microbiologist. The founder of modern bacteriology, he is known for his role in identifying the specific causative agents of tuberculosis, cholera, and anthrax and for giving experimental support for the concept of infectious disease. In addition to his trail-blazing studies on these diseases, Koch created and improved laboratory technologies and techniques in the field of microbiology, and made key discoveries in public health.
question
Robert Bunsen

answer
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium and rubidium with Gustav Kirchhoff. Bunsen developed several gas-analytical methods, was a pioneer in photochemistry, and did early work in the field of organoarsenic chemistry. He developed the Bunsen burner, an improvement on the laboratory burners then in use.



